Abstract
In this study, several advanced analysis methods are applied to understand the relationships between the Niño-3.4 sea surface temperatures (SST) and the SSTs related to the tropical Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD). By analyzing a long data record, the authors focus on the time-frequency characteristics of these relationships, and of the structure of IOD. They also focus on the seasonal dependence of those characteristics in both time and frequency domains.
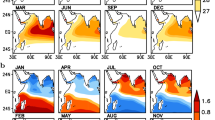
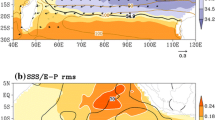
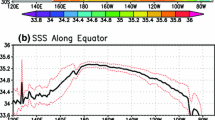
Among the Niño-3.4 SST, IOD, and SSTs over the tropical western Indian Ocean (WIO) and eastern Indian Ocean (EIO), the WIO SST has the strongest annual and semiannual oscillations. While the Niño-3.4 SST has large inter-annual variability that is only second to its annual variability, the IOD is characterized by the largest semiannual oscillation, which is even stronger than its annual oscillation. The IOD is strongly and stably related to the EIO SST in a wide range of frequency bands and in all seasons. However, it is less significantly related to the WIO SST in the boreal winter and spring. There exists a generally weak and unstable relationship between the WIO and EIO SSTs, especially in the biennial and higher frequency bands. The relationship is especially weak in summer and fall, when IOD is apparent, but appears highly positive in winter and spring, when the IOD is unimportantly weak and even disappears. This feature reflects a caution in the definition and application of IOD. The Niño-3.4 SST has a strong positive relationship with the WIO SST in all seasons, mainly in the biennial and longer frequency bands. However, it shows no significant relationship with the EIO SST in summer and fall, and with IOD in winter and spring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ailikun, B., and T. Yasunari, 2001: ENSO and Asian summer monsoon: Persistence and transitivity in the seasonal march. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 79, 145–159.
Ashok, K., Z. Guan, and T. Yamagata, 2001: Impact of the Indian Ocean dipole on the decadal relationship between the Indian monsoon rainfall and ENSO. Geophys. Res. Lett., 28, 4499–4502.
Ashok, K., Z. Guan, and T. Yamagata, 2003a: Influence of the Indian Ocean dipole on the Australian winter rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, doi: 10.1029/2003GL017926.
Ashok, K., Z. Guan, and T. Yamagata, 2003b: A look at the relationship between the ENSO and the Indian Ocean dipole. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 81, 41–56.
Ashok, K., Z. Guan, N. H. Saji, and T. Yamagata, 2004: Individual and combined influences of ENSO and the Indian Ocean dipole on the Indian summer monsoon. J. Climate, 17, 3141–3155.
Behera, S. K., and T. Yamagata, 2003: Influence of the Indian Ocean Dipole on the Southern Oscillation. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 81, 169–177.
Behera, S. K., S. Krishnan, and T. Yamagata, 1999: Unusual ocean-atmosphere conditions in the tropical Indian Ocean during 1994. Geophys. Res. Lett., 26, 3001–3004.
Black, E., 2005: The relationship between Indian Ocean sea surface temperature and east African rainfall. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London, 363, 43–47.
Black, E., J. Slingo, and K. R. Sperber, 2003: An observational study of the relationship between excessively strong short rains in coastal East Africa and Indian Ocean SST. Mon. Wea. Rev., 131, 74–94.
Chao Jiping, Chao Qingchen and Liu Lin,, 2005: The ENSO events in the tropical Pacific and dipole events in the Indian Ocean. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 63, 594–602. (in Chinese)
Ding, X., D. Zheng, and S. Yang, 2002: Variations of the surface temperature in Hong Kong during the last century. International Journal of Climatology, 22, 715–730.
Gadgil, S, and S. Sajani, 1998: Monsoon prediction in the AMIP runs. Climate Dyn., 14, 659–689.
Guan, Z., and T. Yamagata, 2003: The unusual summer of 1994 in East Asia: IOD teleconnections. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, doi:10.1029/2002GL016831.
Huang, B., and J. L. Kinter III, 2002: The interannual variability in the tropical Indian Ocean. J. Geophys. Res., 107, 3199, doi: 10:1029/2001JC001278.
Huang, R., W. Chen, B. Yang, and R. Zhang, 2004: Recent advances in studies of the interaction between the East Asian winter and summer monsoons and ENSO cycle. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 21, 407–424.
Jenkins, G., and D. Watts, 1968: Spectrum Analysis and Its Applications. Holden-Day, San Francisco, CA, 525pp.
Ju, J., and J. Slingo, 1995: The Asian summer monsoon and ENSO. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 121, 1133–1168.
Lau, K.-M., and H.-T. Wu, 2001: Principal modes of rainfall-SST variability of the Asian summer monsoon: A reassessment of the monsoon-ENSO relationship. J. Climate, 14, 2880–2895.
Lau, N.-C., and B. Wang, 2006: Interactions between the Asian monsoon and the El Niño/Southern Oscillation. The Asian Monsoon, B. Wang, Ed., Praxis Publishing Ltd, Chichester, UK, 479–512.
Li, C., and M. Mu, 2001a: Influence of the Indian Ocean dipole on Asian monsoon circulation. Exchanges, 6, 11–14.
Li, C., and M. Mu, 2001b: The influence of the Indian Ocean dipole on atmospheric circulation and climate. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 831–843.
Li Chongyin, Mu Mingquan, and Pan Jing, 2002a: Indian Ocean temperature dipole and SSTA in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47, 236–239.
Li, T., Y. Zhang, E. Lu, and D. Wang, 2002b: Relative role of dynamic and thermodynamic processes in the development of the Indian Ocean dipole: An OGCM diagnosis. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29, 2110, doi: 10.1029/2002GL015789.
Li, T., B. Wang, C.-P. Chang, and Y. Zhang, 2003: A theory for the Indian Ocean dipole-zonal mode. J. Atmos. Sci., 60, 2119–2135.
Loschnigg, J., G. A. Meehl, P. J. Webster, J. M. Arblaster, and G. P. Compo, 2003: The Asian monsoon, the tropospheric biennial oscillation, and the Indian Ocean zonal mode in the NCAR GCM. J. Climate, 16, 1617–1642.
Meehl, G. A., J. M. Arblaster, and J. Loschnigg, 2003: Coupled ocean-atmosphere dynamical processes in the tropical Indian and Pacific Oceans and the TBO. J. Climate, 16, 2138–2158.
Morlet, J., G. Arehs, I. Fourgeau, and D. Giard, 1982: Wave propagation and sampling theory. Geophysics, 47, 203–221.
Powell, M., and J. Reid, 1969: On applying Householder’s method to linear least squares problem. Proce. IFIP Congress 1968, A. Morell, Ed., North-Holland, Amsterdam, 122–126.
Rao, S. A., and S. K. Behera, 2005: Subsurface influence on SST in the tropical Indian Ocean: Structure and interannual variability. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans, 39, 103–135.
Rasmusson, E. M., and T. H. Carpenter, 1982: Variations in tropical sea surface temperature and surface wind fields associated with the Southern Oscillation/El Niño. Mon. Wea. Rev., 110, 354–384.
Rasmusson, E. M., and T. H. Carpenter, 1983: The relationship between eastern equatorial Pacific sea surface temperatures and rainfall over India and Sri Lanka. Mon. Wea. Rev., 111, 517–528.
Ropelewski, C. F., and M. S. Halpert, 1987: Global and regional scale precipitation patterns associated with the El Niño/Southern Oscillation. Mon. Wea. Rev., 115, 1606–1626.
Saji, N. H., and T. Yamagata, 2003a: Possible impacts of Indian Ocean dipole mode events on global climate. Climate Research, 25, 151–169.
Saji, N. H., and T. Yamagata, 2003b: Structure of SST and surface wind variability during Indian Ocean dipole mode events: COADS observations. J. Climate, 16, 2735–2751.
Saji, N. H., B. N. Goswami, P. N., Vinayachandran, and T. Yamagata, 1999: A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature, 401, 360–363.
Saji, N. H., T. Ambrizzi, and S. E. T. Ferraz, 2005: Indian Ocean Dipole mode events and austral surface temperature anomalies. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans, 39, 87–101.
Smith, T. M., and R. W. Reynolds, 2003: Extended reconstruction of global sea surface temperatures based on COADS data (1854–1997). J. Climate, 16, 1495–1510.
Thomason, D., 1982: Spectrum estimation and harmonic analysis. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Proc., 70, 1055–1096.
Wang, B., R. Wu, and X. Fu, 2000: Pacific-East Asian teleconnection: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J. Climate, 13, 1517–1536.
Webster, P. J., and S. Yang, 1992: Monsoon and ENSO: Selectively interactive systems. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 118, 877–926.
Webster, P. J., A. M. Moore, J. P. Loschnigg, and R. R. Leben, 1999: Coupled ocean-atmosphere dynamics in the Indian Ocean during 1997–98. Nature, 401, 356–360.
Wu, R., and B. P. Kirtman, 2004: Impacts of the Indian Ocean on the Indian summer monsoon-ENSO relationship. J. Climate, 17, 3037–3054.
Yan, X., T. M. Smith, and R. W. Reynolds, 2003: Interdecadal changes of 30-yr SST normals during 1871–2000. J. Climate, 16, 1601–1612.
Yang, H., and C. Li, 2005: The influence of tropical Pacific-Indian Ocean associated mode on South-Asia high. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 29, 99–110.
Yang, S., and K.-M. Lau, 2006: Interannual variability of the Asian monsoon. The Asian Monsoon, B. Wang, Ed., Praxis Publishing Ltd, Chichester, UK, 259–293.
Yang, S., X. Ding, D. Zheng, and Q. Li, 2007: Depiction of the variability of Great Plains precipitation and its relationship with the tropical central-eastern Pacific SST. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 46, 136–153.
Yoo, S.-H., S. Yang, and C.-H. Ho, 2006: Variability of the Indian Ocean sea surface temperature and its impacts on Asian-Australian monsoon climate. J. Geophys. Res., 111, D03108, doi: 10.1029/2005JD006001.
Yu, J.-Y., S.-P. Weng, and J. D. Farrara, 2003: Ocean roles in the TBO transitions of the Indian-Australian monsoon system. J. Climate, 16, 3072–3080.
Yulaeva, E., and J. M. Wallace, 1994: Signature of ENSO in global temperature and precipitation fields derived from the microwave sounding unit. J. Climate, 7, 1719–1736.
Zhang, Q., and S. Yang, 2007: Seasonal phase-locking of the peak events in eastern Indian Ocean. Adv. Atmos. Sci. (in press)
Zhang, R., A. Sumi, and M. Kimoto, 1999: A diagnostic study of the impact of El Niño on the precipitation in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 16, 229–241.
Zheng, D. W., B. F. Chao, Y. H. Zhou, and N. H. Yu, 2000: Improvement of edge effect of the wavelet time-frequency spectrum: Application to the length of day series. J. Geodesy, 74, 249–254.
Zhou Yonghong, and Zheng Dawei, 1999: Monte Carlo simulation test of correlation significance levels. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 22, 313–318. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Ding, X., Zheng, D. et al. Time-frequency characteristics of the relationships between tropical Indo-Pacific SSTs. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 24, 343–359 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-007-0343-z
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-007-0343-z