Abstract
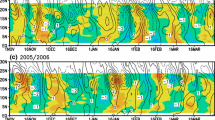
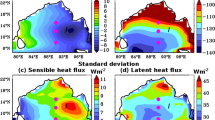
The apparent heat sources (〈Q1 〉) and moisture sinks (〈Q2 〉) are calculated based on the reanalyzed data of the South China Sea Monsoon Experiment (SCSMEX) from May 1 to August 31, 1998. It is found that the formation and distribution of the atmospheric heat sources are important for the monsoon onset. The earlier onset of the SCS monsoon is the result of enduring atmospheric heating in the Indo–China Peninsula and South China areas. The atmospheric heating firstly appears in the Indo–China Peninsula area and the sensible heat is the major one. The 30–50 day periodic oscillation of atmospheric heat sources between the SCS area and the western Pacific warm pool has a reverse phase distribution before the middle of July and the low frequency oscillation of heat sources in SCS area has an obvious longitudinal propagation. The 30–50 day low frequency oscillation has vital modificatory effects on the summer monsoon evolution during 1998.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang Ningbao, and Luo Huibang, 1993: Intraseasonal variations of the atmospheric heat sources and moisture sinks over Asian monsoon region. Part I: Heat sources. J. of Tropical Meteor, 9(4), 299–307 (in Chinese).
Jiang Ningbao, and Luo Huibang, 1993b: Intraseasonal variations of the atmospheric heat sources and moisture sinks over Asian monsoon region Part II: Moisture sinks. J. of Tropical Meteor., 10(1), 1–8 (in Chinese).
Jiang Ningbo, and Luo Huibang, 1995: The first transition of the circulation in Asia around mid-May from 7-year mean ECMWF data. J. of Tropical Meteor, 11(4), 289–296 (in Chinese).
Luo Huibang and Michio Yanai, 1983: The large-scale circulation and heat sources over the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas during the summer of 1979. Part I: Precipitation and kinematic analyses. Mon. Wea. Rev., 111, 922–943.
Luo Huibang and Michio Yanai, 1984: The large-scale circulation and heat sources over the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas during the summer of 1979. Part II: Heat and moisture budgets. Mon. Wea. Rev., 112, 966–989.
Michio Yanai, and Tomohiko Tomita, 1998: Seasonal and interannual variability of atmospheric heat sources and moisture sinks as determined from NCEP-NCAR reanalysis. Journal of Climate, 11, 463–482.
Murakami T., and J. Matsumoto, 1994: Summer monsoon over the Asian continent and western North Pacific. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan., 72, 719–745.
Yang Hui, Song Zhenshan, and Zhu Baozhen, 1998: Formation of Southeast Asia summer monsoon and the effect of the Tibetan Plateau in May, 1979. Scientia Atmospherica Sinica, 22(6), 858–866 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Sponsored by the National Key Project of Fundamental Research “ SCSMEX” and the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education: “ Study of the Air-sea Interaction in the SCS Monsoon Region”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiyu, W., Yongfu, Q. Diagnostic study of apparent heat sources and moisture sinks in the south china sea and its adjacent areas during the onset of 1998 SCS monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 17, 285–298 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-000-0010-0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-000-0010-0