Abstract.
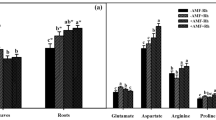
Our objective was to evaluate how increasing levels of N in the medium (0, 4, 8 and 16 mmol N added kg–1 soil) affect the interaction between Sinorhizobium and arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) fungi in the tripartite symbiosis with Medicago sativa. Growth response, nutrient acquisition, protein content, and nitrate reductase (NR) activity were measured both in plant shoots and roots. Results showed that N levels in soil did not affect mycorrhizal colonization but they strongly influenced nodulation, particularly of mycorrhizal plants. Mycorrhizal colonization was required for a proper nodulation when no N was applied to soil. In contrast, the addition of 4 mmol N kg–1 soil reduced nodulation only in mycorrhizal plants and 8 mmol N added kg–1 soil allowed nodule formation only in non-mycorrhizal plants. Nodulation was totally inhibited in all treatments with the addition of 16 mmol N added kg–1 soil. N addition enhanced NR activity in all the treatments, while AM colonization increased the proportion of NR allocated to roots. This effect was more pronounced under the lowest N levels in the medium. The two AM fungal species showed different distribution pattern of enzymatic activities in plant tissues indicating specific physiological traits. Protein content as well as the relative proportion of protein in roots were greatly increased after mycorrhizal colonization. Glomus intraradices-colonized plants had the highest protein content in shoot and root. Mycorrhizal effects on growth, N acquisition and biochemical variables cannot be interpreted as an indirect P-mediated effect since P content was lower in mycorrhizal plants than in those which were P fertilized. Mycorrhizal colonization increased the N content in plants irrespective of the N level, but the effectiveness of AM fungi on plant N acquisition depended on the AM fungus involved, G. intraradices being the most effective, particularly at the highest N rate. N2 fixation, enhanced by AM colonization, contributed to N acquisition when a moderate N quantity was available in the soil. Nevertheless, under a high N amount the nodulating process and/or fixing capacity by Sinorhizobium was reduced in AM plants. In contrast, the AM fungal mycelium from a particular mycorrhizal fungus may continue to contribute efficiently to the N uptake from the soil even at high N levels. These results demonstrate the particular sensitivity of AM fungal species in terms of their growth and/or function to increasing N amounts in the medium. A selection of AM fungi used to address specific environmental conditions, such as N fertilization regimes comparable to those used in agronomic practices, is required for a better use of N applied to soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vázquez, M., Barea, J. & Azcón, R. Impact of soil nitrogen concentration on Glomus spp.-Sinorhizobium interactions as affecting growth, nitrate reductase activity and protein content of Medicago sativa. Biol Fertil Soils 34, 57–63 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740100373
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740100373