Abstract
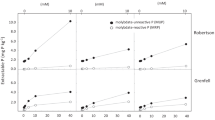
The p-nitrophenol phosphomonoesterase assay (pNPPase) is commonly used to measure cell-wall-associated and extracellular phosphatase activity of soil fungi. pNPPases are usually assayed in the context of fungal nutrition, where inorganic P supply might be enhanced by the mineralisation of organic P sources in the soil. We report here on a series of experiments with the ectomycorrhizal basidiomycete Hebeloma cylindrosporum that highlight components of accepted methodology that might impinge on the reliability of the assay. These include the loss of pNPPase after filtration, inaccuracies in measuring wall-associated enzyme and the ample pool of intracellular pNPPase can be mistakenly measured as external pNPPase if cells are accidentally damaged.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 August 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tibbett, M., Sanders, F., Grantham, K. et al. Some potential inaccuracies of the p-nitrophenyl phosphomonoesterase assay in the study of the phosphorus nutrition of soil borne fungi. Biol Fertil Soils 31, 92–96 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050629
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050629