Abstract
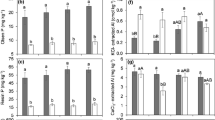
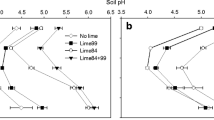
This study assessed the effect of eight lime application rates, with four field replications, on the activities of 14 enzymes involved in C, N, P, and S cycling in soils. The enzymes were assayed at their optimal pH values. The soil used was a Kenyon loam located at the Northeast Research Center in Nashua, Iowa. Lime was applied in 1984 at rates ranging from 0 to 17,920 kg effective calcium carbonate equivalent (ha–1), and surface samples (0–15 cm) were taken after 7 years. Results showed that organic C and N were not significantly affected by lime application, whereas the soil pH was increased from 4.9 to 6.9. The activities of the following enzymes were assayed: α- and β-glucosidases, α- and β-galactosidases, amidase, arylamidase, urease, l-glutaminase, l-asparaginase, l-aspartase, acid and alkaline phosphatases, phosphodiesterase, and arylsulfatase. With the exception of acid phosphatase, which was significantly (P<0.001) but negatively correlated with soil pH (r=–0.69), the activities of all the other enzymes were significantly (P<0.001)and positively correlated with soil pH, with r values ranging from 0.53 for the activity of α-galactosidase to 0.89 for alkaline phosphatase and phosphodiesterase. The Δ activity/Δ pH values ranged from 4.4 to 38.5 for the activities of the glycosidases, from 1.0 to 107 for amidohydrolases and arylamidase, 97 for alkaline phosphatase, 39.4 for phosphodiesterase, and 11.2 for arylsulfatase. This value for acid phosphatase was –35.0. The results support the view that soil pH is an important indicator of soil health and quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 May 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acosta-Martínez, V., Tabatabai, M. Enzyme activities in a limed agricultural soil. Biol Fertil Soils 31, 85–91 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050628
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050628