Abstract
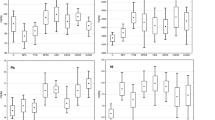
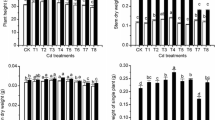
An incubation experiment lasting 120 days was carried out to ascertain the effect on the soil microbial activity and organic matter mineralization of adding a sewage sludge compost contaminated with two different levels of Cd to an arid soil. Two composts, with a low (2 mg kg–1) and high (815 mg kg–1) Cd content, respectively, were used in this experiment. Both composts increased the total organic C, humic substance and water-soluble C contents, the beneficial effects still being noticeable after 120 days of incubation. The most labile C fraction (water-soluble C) was the most sensitive to the high Cd content. The high Cd concentration decreased soil microbial biomass C and stimulated the metabolic activity of the microbial biomass, the metabolic quotient (qCO2) revealing itself to be a very sensitive index of the stress that the incorporation of a Cd-contaminated sewage sludge compost causes in a soil. The effect of Cd contamination on enzyme activities (urease, protease that hydrolyse N-α-benzoil-l-arginamide, phosphatase, and β-glucosidase) depended on the enzyme studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 September 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreno, J., Hernández, T. & Garcia, C. Effects of a cadmium-contaminated sewage sludge compost on dynamics of organic matter and microbial activity in an arid soil. Biol Fertil Soils 28, 230–237 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050487
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050487