Abstract
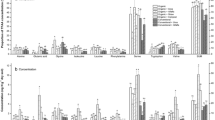
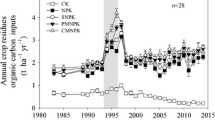
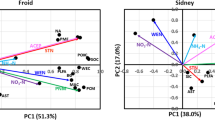
This study investigated the amino acid composition of soil organic matter extracted from ten surface soils in addition to surface soils from two long-term cropping systems [continuous corn (CCCC), corn-soybean-corn-soybean (CSCS), and corn-oats-meadow-meadow (COMM)] at two sites in Iowa: the Clarion-Webster Research Center (CWRC) and the Galva-Primghar Research Center (GPRC). Results showed that, with the exception of asparagine pluse aspartic acid and glutamine plus glutamic acid, the other 13 amino acids studied, expressed as perecentages of total amino acids extracted, were generally very uniform among the soils. The total amino acids extracted from the ten soils were significantly correlated with organic carbon (C) ( and clay content (, but not with total nitrogen (N), pH, or sand content. Expressed as percentages or organic C and N in soils, the amounts extracted ranged from 10.9% to 32.4% and from 12.0% to 27.4%, respectively. The amino acid N identified, expressed as percentages of organic N extracted, ranged from 32% to 50% and the C/N ratios of the extracted organic matter ranged from 10.1 to 14.9. The type of rotation did not significantly affect the total amino acid content of the soils from the same N treatment, but it did affect the total amino acid content of soils from the control plots. The total amino acids measured under the different crop rotations at the CWRC site were in the order: COMM>CCCC>CSCS. The order for the GPRC site was: CSCS>COMM>CCCC. The amino acid N identified, expressed as percentages of organic N extracted from soils at the CWRC site, ranged from 33.1% to 50% and for the GPRC site ranged from 26.5% to 51.4%. The C/N ratios of the organic matter extracted ranged from 10.4 to 14.1 and from 6.5 to 14.3 for the soils from CWRC and GPRC sites, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senwo, Z., Tabatabai, M. Amino acid composition of soil organic matter. Biol Fertil Soils 26, 235–242 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050373
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050373