Abstract
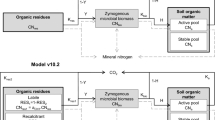
A mechanistic dynamic model (Verberne et al. 1990) was used to simulate mineralization of white-clover materials in a loam (25% clay) and a sandy loam soil (5% clay). I tested the model‘s ability to simulate the observed temporal patterns and to take account of altered physical protection as affected by soil compaction or spatial residue distribution. With default parameter values, the model greatly overestimated net N mineralization. The model was very sensitive to changes in the C/N ratio of the microbial biomass. Reducing this value from 8.0 to 6.0 improved the model performance. Nevertheless, initial N mineralization was appreciably overestimated. Two hypotheses may explain the discrepancies: (1) the C/N ratio of the microbial biomass is initially low (3–4) and gradually increases because of a succession from bacterial- to fungal-dominated biomass (H 1); (2) the C/N ratio of the substrates first attacked by microorganisms, i.e. water-soluble components such as sugars and free amino acids, is higher than the average value (6.0) assumed for the readily decomposable fraction (H 2). Conceptually, this fraction originally included N-containing polymers (proteins and nucleic acids), which in large part are water insoluble and probably attacked somewhat later than the monomers. Modification of the model, either by implementing a dynamic C/N ratio of the biomass and the effect of faunal grazing or by increasing the C/N ratio of the easily decomposable fraction, improved the model performance substantially. The two hypotheses need to be tested experimentally. The model adequately simulated measured effects of spatial residue distribution and soil compaction on N mineralization after adjustment or parameter values regulating physical protection of microbial biomass and metabolites. Moreover, there was a good agreement between simulated and measured microbial biomass N in the two soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 December 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breland, T. Modelling mineralization of plant residues on soil: effect of physical protection. Biol Fertil Soils 25, 233–239 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050308
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050308