Abstract
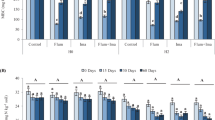
Soil organic matter level, soil microbial biomass C, ninhydrin-N, C mineralization, and dehydrogenase and alkaline phosphatase activity were studied in soils under different crop rotations for 6 years. Inclusion of a green manure crop of Sesbania aculeata in the rotation improved soil organic matter status and led to an increase in soil microbial biomass, soil enzyme activity and soil respiratory activity. Microbial biomass C increased from 192 mg kg–1 soil in a pearl millet-wheat-fallow rotation to 256 mg kg–1 soil in a pearl millet-wheat-green manure rotation. Inclusion of an oilseed crop such as sunflower or mustard led to a decrease in soil microbial biomass, C mineralization and soil enzyme activity. There was a good correlation between microbial biomass C, ninhydrin-N and dehydrogenase activity. The alkaline phosphatase activity of the soil under different crop rotations was little affected. The results indicate the green manuring improved the organic matter status of the soil and soil microbial activity vital for the nutrient turnover and long-term productivity of the soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 January 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chander, K., Goyal, S., Mundra, M. et al. Organic matter, microbial biomass and enzyme activity of soils under different crop rotations in the tropics. Biol Fertil Soils 24, 306–310 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050248
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050248