Abstract
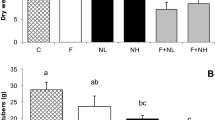
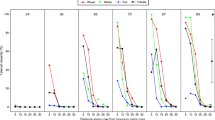
Take-all and brown foot rot, caused respectively by Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici and Fusarium culmorum, are two important components of the foot and root fungal disease complex of winter cereals world-wide. These fungi persist in soil and in crop debris in the same layer of agricultural soil as Collembola, a well represented taxon of soil animals. Previous in vitro tests showed that these fungi grown on agarised medium were readily consumed by springtails. In a simplified experimental system with wheat plants and the pathogenic fungi grown on millet and wheat kernels, the severity of disease was significantly reduced by collembolan feeding activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 April 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabatini, M., Innocenti, G. Effects of Collembola on plant-pathogenic fungus interactions in simple experimental systems. Biol Fertil Soils 33, 62–66 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000290
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000290