Abstract
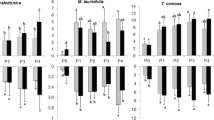
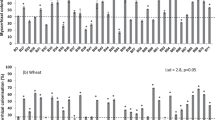
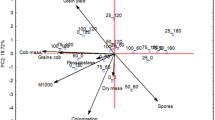
A pot experiment was conducted with soil from a long-term (74-year) fertilization field experiment to compare the effects of organic and mineral fertilizers on mycorrhiza formation in clover, and mycorrhiza-mediated plant P uptake. Five treatments were selected from the field experiment representing different forms and levels of P. Mycorrhizal effects on plant growth and P uptake were estimated by comparing plants grown in untreated soil containing indigenous arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi, with plants grown in pasteurized soil. Short-term versus residual effects of fertilizer/manure were also measured by comparing treatments with or without fertilizers added at the start of the pot experiment. Mycorrhiza formation was greatest in soil that had received no P for 74 years, followed by soil having received 30 or 60 Mg ha–1 farmyard manure (FYM), and soil having received 25 or 44 kg P ha–1 in NPK fertilizers. Plant growth and P uptake were severely reduced in the absence of AM fungi for all mineral fertilizer treatments. In contrast, plants growing in soil that had received FYM grew equally well or better when non-mycorrhizal. Recent additions of NK fertilizer and FYM had no effect on mycorrhiza formation, while additions of NPK led to reduced colonization. It thus seems that moderate quantities of FYM have less adverse effects on AM than equivalent amounts of nutrients in NPK fertilizers, a phenomenon that is most likely due to a temporal difference in P availability and its gradual release that balance plant demand.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 November 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joner, E. The effect of long-term fertilization with organic or inorganic fertilizers on mycorrhiza-mediated phosphorus uptake in subterranean clover. Biol Fertil Soils 32, 435–440 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000279
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000279