Abstract
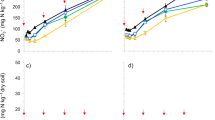
Potential effects of earthworms (Lumbricus terrestris L.) inoculated into soil on fluxes of CO2, CH4 and N2O were investigated for an untreated and a limed soil under beech in open topsoil columns under field conditions for 120 days. Gas fluxes from L. terrestris, beech litter and mineral soil from soil columns were measured separately in jars at 17 °C. The inoculation with L. terrestris and the application of lime had no effect on cumulative CO2 emissions from soil. During the first 3–4 weeks earthworms significantly (P<0.05) increased CO2 emissions by 16% to 28%. In contrast, significantly lower (P<0.05) CO2 emission rates were measured after 11 weeks. The data suggest that earthworm activity was high during the first weeks due to the creation of burrows and incorporation of beech litter into the mineral soil. Low cumulative CH4 oxidation rates were found in all soil columns as a result of CH4 production and oxidation processes. L. terrestris with fresh feces and the beech litter produced CH4 during the laboratory incubation, whereas the mineral soil oxidised atmospheric CH4. Inoculation with L. terrestris led to a significant reduction (P<0.02) in the CH4 oxidation rate of soil, i.e. 53% reduction. Liming had no effect on cumulative CH4 oxidation rates of soil columns and on CH4 fluxes during the laboratory incubation. L. terrestris significantly increased (P<0.001) cumulative N2O emissions of unlimed soil columns by 57%. The separate incubation of L. terrestris with fresh feces resulted in rather high N2O emissions, but the rate strongly decreased from 54 to 2 μg N kg–1 (dry weight) h–1 during the 100 h of incubation. Liming had a marked effect on N2O formation and significantly (P<0.001) reduced cumulative N2O emissions by 34%. Although the interaction of liming and L. terrestris was not significant, N2O emissions of limed soil columns with L. terrestris were 8% lower than those of the control.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 2 September 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borken, W., Gründel, S. & Beese, F. Potential contribution of Lumbricus terrestris L. to carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide fluxes from a forest soil. Biol Fertil Soils 32, 142–148 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000228
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000228