Abstract
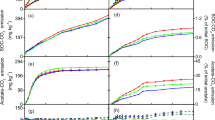
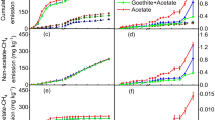
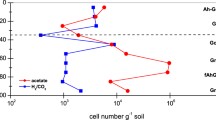
Wetland rice soils from Italy (Pavia) and the Philippines (Bugallon, Luisiana, Maligaya) were incubated under anoxic conditions at 31 different temperatures ranging from 4.7 °C to 49.5 °C. Production of CO2 was most intensive at the beginning of the incubation (0–4 days) and was predominantly coupled to the reduction of free Fe(III). The optimum temperature for these processes was between 32 °C and 41 °C. After 9–16 days, CO2 production rates had decreased and the available Fe(III) had been completely reduced at the optimum temperatures. However, Fe(III) was still available at temperatures below and above the optimum. Maximum CH4 production rates were observed after 4–16 days (except in soil from Maligaya) with temperature optima between 32 °C and 41 °C, similar to those for CO2 production and Fe reduction. Since ongoing Fe reduction is known to suppress CH4 production, the temperature range of optimum CH4 production was restricted to those temperatures at which Fe(III) had already been depleted. Nevertheless, the temperature characteristics of both CO2 and CH4 production often exhibited two temperature optima at some time during the incubation, suggesting a complex pattern of adaptation of the methanogenic microbial community to temperature. When available Fe(III) was completely depleted by anoxic pre-incubation at 30 °C, CH4 was produced at a constant rate (steady state conditions) which increased with increasing temperature. Steady state CH4 production reached a first maximum at about 40 °C, but increased further up to at least 50 °C, suggesting the presence of thermophilic microorganisms whose activity was apparently masked when Fe had not been completely reduced. The apparent activation energy of CH4 production at steady state ranged between 48 kJ mol–1 and 65 kJ mol–1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 August 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, H., Conrad, R. Effect of temperature on reduction of iron and production of carbon dioxide and methane in anoxic wetland rice soils. Biol Fertil Soils 32, 135–141 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000227
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000227