Abstract
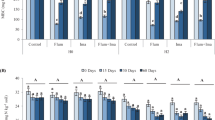
The interactive effects of vermi-compost from sewage sludge and either the sulfonylurea herbicide, rimsulfuron, or the imidazolinone herbicide, imazethapyr, on some soil biochemical and microbiological properties were investigated. The herbicides were applied at field and 10-fold field rates. Both herbicides exerted a detrimental effect on soil microbial biomass and its biochemical properties. Even though the effect of both herbicides on soil microbial biomass was not detectable at the field rate, some significant influences on acid and alkaline phosphatase were observed. The higher rate of herbicide application impaired the observed microbial parameters to a greater degree. The detrimental effects seemed to be reduced by organic amendments. Among the studied microbial characteristics, the specific respiration quotient was particularly reliable and sensitive in determining the influence of herbicides on the soil microbial biomass. In this paper a new synthetic index, specific hydrolytic activity (qFDA), for assessing microbial activity in reply to xenobiotic treatments is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 31 May 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perucci, P., Dumontet, S., Bufo, S. et al. Effects of organic amendment and herbicide treatment on soil microbial biomass. Biol Fertil Soils 32, 17–23 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000207
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000207