Abstract
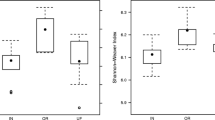
We analyzed soil prokaryotic and fungal community composition in soils with varying histories of cattle manure application. The manure treatments were (i) annual application for 43 years (MF), (ii) annual application for 14 years followed by 29 years without application (MF14), and (iii) annual application for 30 years followed by 13 years without application (MF30). An annual application of chemical nitrogen (N) fertilizer (CNF) and a non-amended control (Con) were also included. Soil prokaryotic evenness and diversity significantly decreased in MF relative to other treatments in fall, but were similar to the other fertilizer treatments in spring and summer. Distinct prokaryotic and fungal community composition was observed in MF compared to other treatments across fall, spring, and summer seasons. The MF treatment significantly increased the relative abundance of Firmicutes, Gammaproteobacteria, and Gemmatimonadetes, but significantly decreased the relative abundance of Acidobacteria. In fall, the soil prokaryotic and fungal community composition with MF30 was significantly different than the other fertilization treatments. Overall, the study showed that annual manure application (MF) led to a different microbial community composition than the other fertilizer treatments. Soil without manure application for 13 years (MF30) had a significantly different microbial community composition from other fertilizer treatments in fall, while the soil without manure application for 29 years (MF14) resembled a microbial community that had never received manure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison SD, Martiny JB (2008) Resistance, resilience, and redundancy in microbial communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(Supplement 1):11512–11519. 10.1073/pnas.0801925105
Anderson MJ (2001) A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol 26:32–46
Bastida F, Hernández T, Albaladejo J, García C (2013) Phylogenetic and functional changes in the microbial community of long-term restored soils under semiarid climate. Soil Biol Biochem 65:12–21. 10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.04.022
Bastida F, Kandeler E, Hernández T, García C (2008) Long-term effect of municipal solid waste amendment on microbial abundance and humus-associated enzyme activities under semiarid conditions. Microb Ecol 55(4):651–661. 10.1007/s00248-007-9308-0
Bastida F, Torres IF, Romero-Trigueros C, Baldrian P, Větrovský T, Bayona JM, Alarcón JJ, Hernández T, García C, Nicolás E (2017) Combined effects of reduced irrigation and water quality on the soil microbial community of a citrus orchard under semi-arid conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 104:226–237. 10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.10.024
Bastida F, Moreno J, Garcia C, Hernández T (2007) Addition of urban waste to semiarid degraded soil: long-term effect. Pedosphere 17(5):557–567. 10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60066-6
Bellemain E, Carlsen T, Brochmann C, Coissac E, Taberlet P, Kauserud H (2010) ITS as an environmental DNA barcode for fungi: an in silico approach reveals potential PCR biases. BMC Microbiol 10(1):189. 10.1186/1471-2180-10-189
Benke MB, Indraratne SP, Hao X (2013) Long-term manure applications impact on irrigated barley forage mineral concentrations. Agron J 105(5):1441–1450. 10.2134/agronj2012.0204
Bonanomi G, De Filippis FD, Cesarano G, Storia AL, Ercolini D, Scala F (2016) Organic farming induces changes in soil microbiota that affect agro-ecosystem functions. Soil Biol Biochem 103:327–336. 10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.09.005
Calleja-Cervantes ME, Fernández-González AJ, Irigoyen I, Fernández-López M, Aparicio-Tejo PM, Menéndez S (2015) Thirteen years of continued application of composted organic wastes in a vineyard modify soil quality characteristics. Soil Biol Biochem 90:241–254. 10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.07.002
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336. 10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Lozupone CA, Turnbaugh PJ, Fierer N, Knight R (2011) Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(Supplement_1):4516–4522. 10.1073/pnas.1000080107
Chang C, Sommerfeldt TG, Entz T (1991) Soil chemistry after eleven annual applications of cattle feedlot manure. J Environ Qual 20(2):475–480. 10.2134/jeq1991.00472425002000020022x
Chinnadurai C, Gopalaswamy G, Balachandar D (2014) Long term effects of nutrient management regimes on abundance of bacterial genes and soil biochemical processes for fertility sustainability in a semi-arid tropical Alfisol. Geoderma 232-234:563–572. 10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.06.015
Deluca TH, Drinkwater LE, Wiefling BA, Denicola DM (1996) Free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria in temperature cropping systems: influence of nitrogen source. Biol Fertil Soils 23(2):140–144. 10.1007/BF00336054
Diacono M, Montemurro F (2010) Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. Agron. Sustainable Dev 30:401–422
Dinesh R, Srinivasan V, Hamza S, Manjusha A (2010) Short-term incorporation of organic manures and biofertilizers influences biochemical and microbial characteristics of soils under an annual crop [turmeric (Curcuma longa L.)]. Bioresour Technol 101(12):4697–4702. 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.108
Dos Santos PC, Zhong F, Mason SW, Setubal JC, Dixon R (2012) Distribution of nitrogen fixation and nitrogenase-like sequences amongst microbial genomes. BMC Genomics 13:162. 10.1186/1471-2164-13-162
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10(10):996–998. 10.1038/nmeth.2604
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27(16):2194–2200. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381
Fierer N, Bradford MA, Jackson RB (2007) Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 88(6):1354–1364. 10.1890/05-1839
Fierer N, Lauber CL, Ramirez KS, Zaneveld J, Bradford MA, Knight R (2012) Comparative metagenomic, phylogenetic and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients. ISME J 6(5):1007–1017. 10.1038/ismej.2011.159
Francioli D, Schulz E, Lentendu G, Wubet T, Buscot F, Reitz T (2016) Mineral vs. organic amendments: microbial community structure, activity and abundance of agriculturally relevant microbes are driven by long-term fertilization strategies. Front Microbiol 7:1446. 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01446
Geisseler D, Scow KM (2014) Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms—a review. Soil Biol Biochem 75:54–63. 10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.03.023
Ghosh S, Lockwood P, Daniel H, King K, Hulugalle N, Kristiansen P (2010) Short-term effects of organic amendments on properties of a Vertisol. Waste Manage Res 28(12):1087–1095. 10.1177/0734242X09359105
Ginting D, Kessavalou A, Eghball B, Doran JW (2003) Greenhouse gas emissions and soil indicators four years after manure and compost applications. J Environ Qual 32(1):23–32. 10.2134/jeq2003.2300
Hao X, Chang C, Li X (2004) Long-term and residual effects of cattle manure application on distribution of P in soil aggregates. Soil Sci 169(10):715–728. 10.1097/01.ss.0000146018.23441.23
Hao X, Godlinski F, Chang C (2008) Distribution of phosphorus forms in soil following long-term continuous and discontinuous cattle manure applications. Soil Sci Soc Am J 72(1):90–97. 10.2136/sssaj2006.0344
Hartmann M, Frey B, Mayer J, Mader P, Widmer F (2015) Distinct soil microbial diversity under long-term organic and conventional farming. ISME J 9(5):1177–1194. 10.1038/ismej.2014.210
Hartmann M, Brunner I, Hagedorn F, Bardgett RD, Stierli B, Herzog C, Chen X, Zingg A, Graf-Pannatier E, Rigling A, Frey B (2016) A decade of irrigation transforms the soil microbiome of a semi-arid pine forest. Mol Ecol 26:1190–1206
IUSS Working Group (2015) World reference base for soil resources 2014. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps. Update 2015. Word Soil Resources Reports No. 106. FAO, Rome, 172–173
Kunin V, Engelbrektson A, Ochman H, Hugenholtz P (2010) Wrinkles in the rare biosphere: pyrosequencing errors can lead to artificial inflation of diversity estimates. Environ Microbiol 12(1):118–123. 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.02051.x
Lazcano C, Gómez-Brandón M, Revilla P, Domínguez J (2013) Short-term effects of organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil microbial community structure and function. Biol Fertil Soils 49(6):723–733. 10.1007/s00374-012-0761-7
Leff JW, Jones SE, Prober SM, Barberán A, Borer ET, Firn JL, Harpole WS, Hobbie SE, Hofmockel KS, Knops JM (2015) Consistent responses of soil microbial communities to elevated nutrient inputs in grasslands across the globe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(35):10967–10972. 10.1073/pnas.1508382112
Li F, Chen L, Zhang J, Yin J, Huang S (2017) Bacterial community structure after long-term organic and inorganic fertilization reveals important associations between soil nutrients and specific taxa involved in nutrient transformations. Front Microbiol 8:187. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00187
Lin X, Feng Y, Zhang H, Chen R, Wang J, Zhang J, Chu H (2012) Long-term balanced fertilization decreases arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal diversity in an arable soil in North China revealed by 454 pyrosequencing. Environ Sci Technol 46(11):5764–5771. 10.1021/es3001695
Lopes AR, Bello D, Prieto-Fernández Á, Trasar-Cepeda C, Manaia CM, Nunes OC (2015) Relationships among bulk soil physicochemical, biochemical, and microbiological parameters in an organic alfalfa-rice rotation system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(15):11690–11699. 10.1007/s11356-015-4410-1
Lueders T, Kindler R, Miltner A, Friedrich MW, Kaestner M (2006) Identification of bacterial micropredators distinctively active in a soil microbial food web. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(8):5342–5348. 10.1128/AEM.00400-06
Manzoni S, Schimel JP, Porporato A (2012) Responses of soil microbial communities to water stress: results from a meta-analysis. Ecology 93(4):930–938. 10.1890/11-0026.1
Neufeld KR, Grayston SJ, Bittman S, Krzic M, Hunt DE, Smukler SM (2017) Long-term alternative dairy manure management approaches enhance microbial biomass and activity in perennial forage grass. Biol Fert Soils 53:613–626
Nilsson RH, Tedersoo L, Ryberg M, Kristiansson E, Hartmann M, Unterseher M, Porter TM, Bengtsson-Palme J, Walker DM, De Sousa F (2015) A comprehensive, automatically updated fungal ITS sequence dataset for reference-based chimera control in environmental sequencing efforts. Microbes Environ 30(2):145–150. 10.1264/jsme2.ME14121
Pietri JA, Brookes P (2008) Relationships between soil pH and microbial properties in a UK arable soil. Soil Biol Biochem 40(7):1856–1861. 10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.03.020
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glockner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41(Database issue):D590–D596. 10.1093/nar/gks1219
Core Team R (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Rousk J, Baath E, Brookes PC, Lauber CL, Lozupone C, Caporaso JG, Knight R, Fierer N (2010) Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J 4(10):1340–1351. 10.1038/ismej.2010.58
Rousk J, Brookes PC, Bååth E (2009) Contrasting soil pH effects on fungal and bacterial growth suggest functional redundancy in carbon mineralization. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(6):1589–1596. 10.1128/AEM.02775-08
Ryckeboer JR, Mergaert J, Vaes K, Klammer S, Clercq DD, Coosemans J, Insam H, Swings J (2003) A survey of bacteria and fungi occurring during composting and self-heating processes. Ann of Microbiol 53:349–410
Schöler A, Jacquiod S, Vestergaard G, Schulz S, Schloter M (2017) Analysis of soil microbial communities based on amplicon sequencing of marker genes. Biol Fert Soils 53:485–489
Sommerfeldt TG, Chang C (1985) Changes in soil properties under annual applications of feedlot manure and different tillage practices. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49(4):983–987. 10.2136/sssaj1985.03615995004900040038x
St-Pierre B, Wright A-D (2014) Comparative metagenomic analysis of bacterial populations in three full-scale mesophilic anaerobic manure digesters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(6):2709–2717. 10.1007/s00253-013-5220-3
Stieglmeier M, Alves RJ, Schleper C (2014) The phylum Thaumarchaeota, the Prokaryotes. Springer, pp.347–362
Sun R, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang D, Chu H (2015) Bacterial diversity in soils subjected to long-term chemical fertilization can be more stably maintained with the addition of livestock manure than wheat straw. Soil Biol Biochem 88:9–18. 10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.05.007
Tedersoo L, Bahram M, Polme S, Koljalg U, Yorou NS, Wijesundera R, Villarreal RL, Vasco-Palacios AM, Thu PQ, Suija A, Smith ME, Sharp C, Saluveer E, Saitta A, Rosas M, Riit T, Ratkowsky D, Pritsch K, Poldmaa K, Piepenbring M, Phosri C, Peterson M, Parts K, Partel K, Otsing E, Nouhra E, Njouonkou AL, Nilsson RH, Morgado LN, Mayor J, May TW, Majuakim L, Lodge DJ, Lee SS, Larsson KH, Kohout P, Hosaka K, Hiiesalu I, Henkel TW, Harend H, Guo LD, Greslebin A, Grelet G, Geml J, Gates G, Dunstan W, Dunk C, Drenkhan R, Dearnaley J, De Kesel A, Dang T, Chen X, Buegger F, Brearley FQ, Bonito G, Anslan S, Abell S, Abarenkov K (2014) Fungal biogeography. Global diversity and geography of soil fungi. Science 346(6213):1256688. 10.1126/science.1256688
Tian W, Wang L, Li Y, Zhuang K, Li G, Zhang J, Xiao X, Xi Y (2015) Responses of microbial activity, abundance, and community in wheat soil after three years of heavy fertilization with manure-based compost and inorganic nitrogen. Agric Ecosyst Environ 213:219–227. 10.1016/j.agee.2015.08.009
Torres IF, Bastida F, Hernández T, García C (2015) The effects of fresh and stabilized pruning wastes on the biomass, structure and activity of the soil microbial community in a semiarid climate. Appl Soil Ecol 89:1–9. 10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.12.009
Vestergaard G, Schulz S, Schöler A, Schloter M (2017) Making big data smart—how to use metagenomics to understand soil quality. Biol Fert Soils 53:479–484
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(16):5261–5267. 10.1128/AEM.00062-07
Weiss SJ, Xu Z, Amir A, Peddada S, Bittinger K, González A, Lozupone C, Zaneveld J, Vázquez-Baeza Y, Birmingham A, Knight R (2015) Effects of library size variance, sparsity, and compositionality on the analysis of microbiome data. Peer J Preprint 3:e1408
Whitman T, Peperanney C, Enders A, Koechli C, Campbell A, Buckley DH, Lehmann J (2016) Dynamics of microbial community composition and soil organic carbon mineralization in soil following addition of pyrogenic and fresh organic matter. ISME J 10(12):2918–2930. 10.1038/ismej.2016.68
Wyngaard N, Franklin DH, Habteselassie MY, Mundepi A, Cabrera ML (2016) Legacy effect of fertilization and tillage systems on nitrogen mineralization and microbial communities. Soil Sci Soc Am J 80(5):1262–1271. 10.2136/sssaj2016.03.0070
Yashiro E, Pintofigueroa E, Buri A, Spangenberg JE, Adatte T, Niculita-Hirzel H, Guisan A, van der Meer JR (2016) Local environmental factors drive divergent grassland soil bacterial communities in the western Swiss Alps. Appl Environ Microbiol 82(21):6303–6316. 10.1128/AEM.01170-16
Zeng J, Liu X, Song L, Lin X, Zhang H, Shen C, Chu H (2016) Nitrogen fertilization directly affects soil bacterial diversity and indirectly affects bacterial community composition. Soil Biol Biochem 92:41–49. 10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.09.018
Zhang N, Castlebury LA, Miller AN, Huhndorf SM, Schoch CL, Seifert KA, Rossman AY, Rogers JD, Kohlmeyer J, Volkmann-Kohlmeyer B, Sung GH (2006) An overview of the systematics of the Sordariomycetes based on a four-gene phylogeny. Mycologia 98(6):1076–1087. 10.1080/15572536.2006.11832635
Zhang Q, Sun J, Liu S, Wei Q (2013) Manure refinement affects apple rhizosphere bacterial community structure: a study in sandy soil. PLoS One 8(10):e76937. 10.1371/journal.pone.0076937
Zhang Y, Shen H, He X, Thomas BW, Lupwayi NZ, Hao X, Thomas MC, Shi X (2017) Fertilization shapes bacterial community structure by alteration of soil pH. Front Microbiol 8:1325. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01325
Zhong W, Gu T, Wang W, Zhang B, Lin X, Huang Q, Shen W (2010) The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity. Plant Soil 326(1-2):511–522. 10.1007/s11104-009-9988-y
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Drs T. Sommerfeldt and C. Chang for initiating this long-term manure trial, and to the technical staff and field crew for field operations. We thank Agriculture & Agri-Food Canada for funding this study under the Growing Forward 2 program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1090 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Hao, X., Alexander, T.W. et al. Long-term and legacy effects of manure application on soil microbial community composition. Biol Fertil Soils 54, 269–283 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-017-1257-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-017-1257-2