Abstract
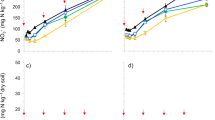
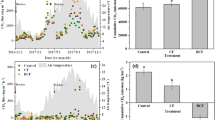
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of biochar application on soil methane (CH4) emission. Experiments were conducted over an 84-day incubation period with the following treatments: each of two soils (a paddy soil and a forest soil) was treated with or without biochar at three soil moisture levels (35, 60, and 100 % water-filled pore space (WFPS) for the paddy soil; 35, 60, and 85 % WFPS for the forest soil). Biochar application (P < 0.05) significantly increased soil pH and stimulated C mineralization at the early incubation stage. The effects of biochar application on CH4 emission were related to the soil moistures, with reduction of CH4 emission at 35 and 60 % WFPS and stimulation at the highest soil moisture. While both soils changed from CH4 sinks to sources by increasing soil moisture regardless of biochar addition, the effect was enhanced with biochar application. At lower soil moistures, the CH4 oxidation activity in soils was higher with biochar than without biochar, while the trend became opposite at higher soil moistures. Therefore, the CH4 production and consumption processes were influenced by different soil moisture levels and microbial communities of different soils.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842
Cabrera ML, Beare MH (1993) Alkaline persulfate oxidation for determining total nitrogen in microbial biomass extracts. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57:1007–1012
Campbell CA, Biederbeck VO, Zentner RP, Lafond GP (1991) Effect of crop rotations and cultural practices on soil organic matter, microbial biomass and respiration in a thin black Chernozem. Can J Soil Sci 71:363–376
Chan ASK, Parkin TB (2001) Methane oxidation and production activity in soils from natural and agricultural ecosystems. J Environ Qual 30:1896–1903
Chan KY, Xu Z (2009) Biochar: nutrient properties and their enhancement. In: Lehmann J, Joseph S (eds) Biochar for environmental management: science and technology. Earthscan, London, pp 67–84
Chidthaisong A, Conrad R (2000) Turnover of glucose and acetate coupled to reduction of nitrate, ferric iron and sulfate and to methanogenesis in anoxic rice field soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 31:73–86
Czepiel PM, Crill PM, Harriss RC (1995) Environmental factors influencing the variability of methane oxidation in temperate zone soils. J Geophys Res 100:9359–9364
Fierer N, Schimel JP (2003) A proposed mechanism for the pulse in carbon dioxide production commonly observed following the rapid rewetting of a dry soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67:798–805
Fontaine S, Mariotti A, Abbadie L (2003) The priming effect of organic matter: a question of microbial competition? Soil Biol Biochem 35:837–843
Forster P, Ramaswamy V, Artaxo P, Berntsen T, Betts R, Fahey DW, Haywood J, Lean J, Lowe DC, Myhre G, Nganga J, Prinn R, Raga G, Schulz M, Van Dorland R (2007) Changes in atmospheric constituents and in radiative forcing. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 140–143
Glaser B, Lehmann J, Zech W (2002) Ameliorating physical and chemical properties of highly weathered soils in the tropics with charcoal—a review. Biol Fertil Soils 35:219–230
Gulledge J, Schimel JP (1998) Moisture control over atmospheric CH4 consumption and CO2 production in diverse Alaskan soils. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1127–1132
Hamer U, Marschner B, Brodowski S, Amelung W (2004) Interactive priming of black carbon and glucose mineralization. Org Geochem 35:823–830
Hilscher A, Heister K, Siewert C, Knicker H (2009) Mineralization and structural changes during the initial phase of microbial degradation of pyrogenic plant residues in soil. Org Geochem 40:332–342
Hütsch BW (1996) Methane oxidation in soils of two long-term fertilization experiments in Germany. Soil Biol Biochem 28:773–782
Inubushi K, Otakel S, Furukawa Y, Shibasaki N, Ali M, Itang AM, Tsuruta H (2005) Factors influencing methane emission from peat soils: comparison of tropical and temperate wetlands. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 71:93–99
Karagöz S, Bhaskar T, Muto A, Sakata Y (2005) Comparative studies of oil compositions produced from sawdust, rice husk, lignin and cellulose by hydrothermal treatment. Fuel 84:875–884
Karhu K, Mattila T, Bergstrom I, Regina K (2011) Biochar addition to agricultural soil increased CH4 uptake and water holding capacity: results from a short-term pilot field study. Agr Ecosyst Environ 140:309–313
King GM, Schnell S (1994) Effect of increasing atmospheric methane concentration on ammonium inhibition of soil methane consumption. Nature 370:282–284
Klüber HD, Conrad R (1998) Inhibitory effects of nitrate, nitrite, NO and N2O on methanogenesis by Methanosarcina barkeri and Methanobacterium bryantii. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 25:331–339
Kotiaho M, Fritze H, Merilä P, Juottonen H, Leppälä M, Laine J, Laiho R, Yrjälä K, Tuittila ES (2010) Methanogen activity in relation to water table level in two boreal fens. Biol Fertil Soils 46:567–575
Knoblauch C, Maarifat AA, Preiffer EM, Haefele SM (2011) Degradability of black carbon and its impact on trace gas fluxes and carbon turnover in paddy soils. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1768–1778
Kuzyakov Y, Friedel JK, Stahr K (2000) Review of mechanisms and quantification of priming effects. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1485–1498
Le Mer J, Roger P (2001) Production, oxidation, emission and consumption of methane by soils: a review. Eur J Soil Biol 37:25–50
Lehmann J, Pereira da Silva J, Steiner C, Nehls T, Zech W, Glaser B (2003) Nutrient availability and leaching in an archaeological anthrosol and a ferralsol of the Central Amazon basin: fertilizer, manure and charcoal amendments. Plant Soil 249:343–357
Lehmann J (2007a) A handful of carbon. Nature 447:143–144
Lehmann J (2007b) Bio-energy in the black. Front Ecol Environ 5:381–387
Lehmann J, Rillig MC, Thies J, Masiello CA, Hockaday WC, Crowley D (2011) Biochar effects on soil biota: a review. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1812–1836
Liu Y, Yang M, Wu Y, Wang H, Chen Y, Wu W (2011) Reducing CH4 and CO2 emissions from waterlogged paddy soil with biochar. J Soils Sediments 11:930–939
Major J, Lehmann J, Rondon M, Goodale C (2010) Fate of soil-applied black carbon: downward migration, leaching and soil respiration. Global Change Biol 16:1366–1397
Moore JM, Klose S, Tabatabai MA (2000) Soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen as affected by cropping systems. Biol Fertil Soils 31:200–210
Nguyen BH, Lehmann J (2009) Black carbon decomposition under varying water regimes. Org Geochem 40:846–853
Novak JM, Busscher WJ, Laird DL, Ahmedna M, Watts DW, Niandou MAS (2009) Impact of biochar amendment on fertility of a southeastern coastal plain soil. Soil Sci 174:105–112
Novak JM, Busscher WJ, Watts DW, Laird DA, Ahmedna MA, Niandou MAS (2010) Short-term CO2 mineralization after additions of biochar and switchgrass to a Typic Kandiudult. Geoderma 154:281–288
Ryan J, Estefan G, Rashid A (2001) Soil and plant analysis laboratory manual. Jointly published by International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) and the National Agricultural Research Center (NARC), USA
Scheid D, Stubner S, Conrad R (2003) Effects of nitrate- and sulfate-amendment on the methanogenic populations in rice root incubations. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 43:309–315
Spokas KA, Koskinen WC, Baker JM, Reicosky DC (2009) Impacts of woodchip biochar additions on greenhouse gas production and sorption/degradation of two herbicides in a Minnesota soil. Chemosphere 77:574–581
Spokas KA, Reicosky DC (2009) Impacts of sixteen different biochars on soil greenhouse gas production. Ann Environ Sci 3:179–193
Thies JE, Rillig MC (2009) Characteristics of biochar: biological properties. In: Lehmann J, Joseph S (eds) Biochar for environmental management: science and technology. Earthscan, London, pp 33–43
Van Zwieten L, Singh B, Joseph S, Kimber S, Cowie A, Chan KY (2009) Biochar and emission of non-CO2 greenhouse gases from soil. In: Lehmann J, Joseph S (eds) Biochar for environmental management: science and technology. Earthscan, London, pp 227–249
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–704
Verheijen F, Jeffery S, Bastos AC, van der Velde M, Diafas I (2009) Biochar application to soils. A critical scientific review of effects on soil properties, processes and functions. EUR 24099 EN. Office for the Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxemburg, pp 101–107
Xiang SR, Doyle A, Holden PA, Schimel JP (2008) Drying and rewetting effects on C and N mineralization and microbial in surface and subsurface California grassland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2281–2289
Yanai Y, Toyota K, Okazaki M (2007) Effects of charcoal addition on N2O emissions from soil resulting from rewetting air-dried soil in short-term laboratory experiments. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 53:181–188
Zhang A, Cui L, Pan G, Li L, Hussain Q, Zhang X, Zheng J, Crowley D (2010) Effect of biochar amendment on yield and methane and nitrous oxide emissions from a rice paddy from Tai Lake plain, China. Agr Ecosyst Environ 139:469–475
Zimmerman AR, Gao B, Ahn MY (2011) Positive and negative carbon mineralization priming effects among a variety of biochar-amended soils. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1169–117
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by grants from the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (nos. 51039007 and 51179212) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Tang, J., Zhang, R. et al. Effects of biochar application on soil methane emission at different soil moisture levels. Biol Fertil Soils 49, 119–128 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-012-0703-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-012-0703-4