Abstract
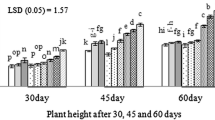
The effects of cow manure vermicompost on plant growth, metabolite contents, and antioxidant activities of Chinese cabbage were investigated in pot cultures. Five treatments were designed by mixing vermicompost and soil at ratio of 0:7, 1:7, 2:7, 4:7, 7:0 (w/w). Marketable weight of Chinese cabbage was significantly (p < 0.05) higher in the 2:1 treatment than in the other treatments, while plants grown in the full soil treatment (0:7) showed the lowest marketable weight (Fig. 1a). Vermicompost application significantly increased the nutrient content of Chinese cabbage leaves (p < 0.05), especially in the 4:7 treatment, with increases in the contents of soluble sugar (Fig. 2a), soluble protein (Fig. 2b), vitamin C (Fig. 3a), total phenols (Fig. 3b), and total flavonoids (Fig. 3c) by 62%, 18%, 200%, 25%, and 17% compared to the full soil treatment, respectively. The antioxidant activities expressed by 2, 2-Dipenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl-scavenging activity (Fig. 4a), hydroxyl (OH)-scavenging activity (Fig. 4b), and iron (Fe2+)-chelating activity (Fig. 4c) were higher by 92%, 40%, and 36% in the 4:7 than 0:7 the treatment, respectively. Vermicompost application significantly increased (p < 0.05) the plant contents of 16 essential amino acids (Table 1); the total amino acid content showed the greatest increase in the 4:7 treatment, 90% compared to the full soil treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albanell E, Plaixats J, Cabrero T (1988) Chemical changes during vermicomposting (Eisenia fetida) of sheep manure mixed with cotton industrial wastes. Biol Fertil Soils 6:266–269
Alves MR, Landgraf MD, Resende MOO (2001) Absorption and desorption of herbicide alaclor on humic acid fractions obtained from two vermicompost. J Environ Sci Health 36:797–808
Arancon NQ, Edwards CA, Bierman P, Metzger JD, Lucht C (2005) Effects of vermicromposts produced from cattle manure, food waste and paper waste on the growth and yield of peppers in the field. Pedobiologia 49:297–306
Arancon NQ, Edwards CA, Bierman P (2006) Influences of vermicomposts on field strawberries: part 2. effects on soil microbiological and chemical properties. Bioresour Technol 97:831–840
Asami DK, Hong YJ, Barrett DM, Mitchel AE (2003) Comparison of the total phenolic and ascorbic acid content of freeze-dried and air dried marionberry, strawberry, and corn using conventional, organic, and sustainable agricultural practices. J Agric Food Chem 51:1237–1241
Atiyeh RM, Edwards CA, Subler S, Metzger JD (2001) Pig manure vermicompost as a component of a horticultural bedding plant medium: effects on physicochemical properties and plant growth. Bioresour Technol 78:11–20
Basu M, Bhadoria PBS, Mahapatra SC (2008) Growth, nitrogen fixation, yield and kernel quality of peanut in response to lime, organic and inorganic fertilizer levels. Bioresour Technol 99:4675–4683
Bellomo G (1991) Cell damage by oxygen free radicals. Cytotechnology 5:71–73
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of “protein-dye binding”. Anal Biochem 38:248–254
Burrin DG, Stoll B (2009) Metabolic fate and function of dietary glutamate in the gut. Am Soc Nutria 90(suppl):850S–856S
Canellas LP, Olivares FL, Okorokova-Façanha AL, Façanha AR (2002) Humic acids isolated from earthworm compost enhance root elongation, lateral root emergence, and plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity in maize roots. Plant Physiol 130:1951–1957
Chang CC, Yang MH, Wen HM, Chern JC (2002) Estimation of total flavonoid content in propolis by two complementary colorimetric methods. J Food Drug Anal 10:178–182
Gundgaard J, Nielsen JN, Olsen J, Sorensen J (2003) Increased intake of fruit and vegetables: estimation of impact in terms of life expectancy and healthcare costs. Public Health Nutr 6:25–30
Gutiérrez-Miceli FA, Santiago-Borraz JS, Molina JAM, Nafate CC, Abud-Archila M, Llaven MAO, Rincón-Rosales R, Dendooven L (2007) Vermicompost as a soil supplement to improve growth, yield and fruit quality of tomato (Lycopersicum esculentu). Bioresour Technol 98:2781–2786
Hodges DM, Andrews CJ, Johnson DA, Hamilton RI (1996) Antioxidant compound responses to chilling stress in differentially sensitive inbred maize 23 lines. Physiol Plant 98:685–692
Hollman PCH, Hertog MGL, Katan MB (1996) Analysis and health effects on flavonoids. Food Chem 57:43–46
Inbar Y, Hadar Y, Chen Y (1993) Recycling of cattle manure: the composting process and characterization of maturity. J Environ Qual 22:857–863
Jordao CP, Pereira MG, Einloft R, Santana MB, Bellato CR, Vargas de Mello JW (2002) Removal of Cu, Cr, Ni, Zn and Cd from electroplating wastes and synthetic solutions by vermicompost of cattle manure. J Environ Sci Health 37:875–892
Lisiewska Z, Kmiecik W (1996) Effects of level of nitrogen fertilizer, processing conditions and period of storage of frozen boccoli and cauliflower on vitamin C retention. Food Chem 57:267–270
Liu ZH, Jiang LH, Li XL, Hardter R, Zhang WJ, Zhang YL, Zheng DF (2008) Effect of N and K fertilizers on yield and quality of greenhouse vegetable crops, effect of N and K fertilizers on yield and quality of greenhouse vegetable crops. Pedosphere 18:496–502
Liu M, Hu F, Chen X, Huang Q, Jiao J, Zhang B, Li H (2009) Organic amendments with reduced chemical fertilizer promote soil microbial development and nutrient availability in a subtropical paddy field: the influence of quantity, type and application time of organic amendments. Appl Soil Ecol 42:166–175
Manda KD, Adams C, Ercal N (2010) Biologically important thiols in aqueous extracts of spices and evaluation of their in vitro antioxidant properties. Food Chem 118:589–593
Meda A, Lamien CE, Romito M, Millogo J, Nacoulma OG (2005) Determination of the total phenolic, flavonoid and praline contents in Burkina Fasan honey, as well as their radical scavenging activity. Food Chem 91:571–577
Nagao M, Minami A, Arakawa K, Fujikawa S, Takezawa D (2005) Rapid degradation of starch in chloroplasts and concomitant accumulation of soluble sugars associated with ABA-induced freezing tolerance in the moss Phscomitrella patens. J Plant Physiol 162:169–180
Oliveira C, Ferreira ACS, Pinto MM, Hogg T, Alves F, de Pinho PG (2003) Carotenoid compounds in grapes and their relationship to plant water status. J Agric Food Chem 51:5967–5971
Padel S, Röcklinsberg H, Schmid O (2009) The implementation of organic principles and values in the European regulation for organic food. Food Policy 34:245–251
Paradelo R, Cendón Y, Moldes AB, Barral MT (2007) A pot experiment with mixtures of slate processing fines and compost. Geoderma 141:363–369
Podsędek A (2007) Natural antioxidants and antioxidant capacity of Brassica vegetables: a review. LWT Food Sci Technol 40:1–11
Rhoads JM, Wu G (2009) Glutamine, argine, and leucine signalling in the intestine. Amino Acids 37:111–122
Rimmer DL (2006) Free radicals, antioxidants, and soil organic matter recalcitrance. Eur J Soil Sci 57:91–94
Scherer HW (2001) Sulphur in crop production-invited paper. Eur J Agron 14:81–111
Singh KP, Snman A, Singh PN, Srivastava TK (2007) Improving quality of sugarcane-growing soils by organic amendments under subtropical climatic conditions of India. Biol Fertil Soils 44:367–376
Sivakumar R, Babu PVA, Shyamaladevi CS (2008) Protective effects of aspartate and glutamate on cardiac mitochondrial function during myocardial infarction in experimental rats. Chem Biol Interact 176:227–233
Sousa C, Valentão P, Rangel J, Lopes G, Pereira JA, Ferreres F, Seabra RM, Andrade PB (2005) Influence of two fertilization regimens on the amounts of organic acids and phenolic compounds of tronchuda cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. Var. costata DC). J Agric Food Chem 53:9128–9132
Tejada M, Gonzalez JL, García-Martínez AM, Parrado J (2008) Effects of different green manures on soil biological properties and maize yield. Bioresour Technol 99:1758–1767
Toor RK, Savage GP, Heeb A (2006) Influence of different types of fertilisers on the major antioxidant components of tomatoes. J Food Compos Anal 19:20–27
Wilson ID, Neill SJ, Hancock JT (2008) Nitric oxide synthesis and signaling in plants. Plant Cell Environ 31:622–631
Wirtz M, Droux M (2005) Synthesis of the sulfur amino acids: cysteine and methionine. Photosynth Res 86:345–362
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Technology R&D Program during the National 11th Five-Year Plan of China Period (2008BADA4B05) and by the Applied Agricultural Technology Foundation of Shandong Province
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Shi, Q., Wang, X. et al. Influence of cow manure vermicompost on the growth, metabolite contents, and antioxidant activities of Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis). Biol Fertil Soils 46, 689–696 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-010-0473-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-010-0473-9