Abstract
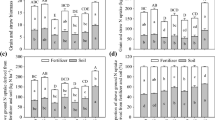
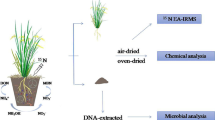
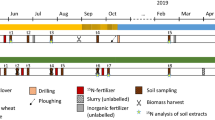
The present study was carried out on pot experiments with rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. Wuyujing 7) and winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv. Yangmai 6) rotation in a sandy and a clayey soil fertilized with 15N-labeled ammonium sulfate (AS) and 15N-labeled rabbit feces so as to study the mechanisms of reduction of fertilizer N loss by organic fertilizers. The treatments included: (1) control without any N fertilizer application; (2) fertilization with 15N-labeled AS (IF); (3) fertilization with labeled rabbit feces (OF); (4) fertilization with either 40% 15N-labeled rabbit feces and 60% unlabeled AS (IOF1) or (5) 40% unlabeled rabbit feces and 60% 15N-labeled AS (IOF2). In the rice season, the IOF treatments compared to the IF treatment decreased the percentage of lost fertilizer N from the sandy and clayey soils, whereas it increased the percentage of fertilizer N, present as mineral N and microbial biomass N (MBN). During the second season, when soils were cropped to winter wheat, the IOF treatments in comparison with the IF or OF treatment increased mineral N and MBN contents of soils sampled at tillering, jointing, and heading stages, and such increases were derived from the organic N fertilizer in the sandy soil and from the inorganic N fertilizer in the clayey soil. The increased MBN in the IOF treatments was derived from inorganic fertilizers applied both soils. Therefore, in the IOF treatment, during the rice season, the organic N increased the immobilization of inorganic N in MBN, while the inorganic N fertilizer applied to both soils stimulated the uptake of organic N and the organic N fertilizer increased the uptake of inorganic N by winter wheat; the inorganic N increased the recovery of organic N in the plant-soil system after harvesting the winter wheat.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen SC, Jose S, Nair PKR, Brecke BJ, Ramsey CL (2004) Competition for 15N-labeled fertilizer in a pecan (Carya illinoensis K. Koch)-cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) alley cropping system in the southern United States. Plant Soil 263:151–164. doi:10.1023/B:PLSO.0000047732.95283.ac
Anderson TH (2003) Microbial eco-physiological indicators to asses soil quality. Agr Ecosyst Environ 98:285–293. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(03)00088-4
Anderson TH, Domsch KH (1993) The metabolic quotient for CO2 (qCO2) as a specific activity parameter to assess the effect of environmental conditions, such as pH, on the microbial biomass of forest soils. Soil Bio Biochem 25:393–395. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(93)90140-7
Bar AR, Baggie I, Sanginga N (2000) The use of Sesbania (Sesbania rostrata) and urea in lowland rice production in Sierra Leone. Agroforest Syst 48:111–118. doi:10.1023/A:1006345920266
Barkle GF, Stenger R, Brown TN, Ledgard SF, Painter DJ (2001) Fate of the 15N-labeled faeces fraction of dairy farm effluent (DFE) irrigated onto soils under different water regimes. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 59:85–93. doi:10.1023/A:1009896707394
Bengtsson G, Bergwall C (2000) Fate of 15N labeled nitrate and ammonium in a fertilized forest soil. Soil Biol Biochem 32:545–557. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(99)00183-2
Blagodatskaya E, Anderson TH (1999) Adaptive responses of soil microbial communities under experimental acid stress in controlled laboratory studies. Appl Soil Ecol 11:207–216. doi:10.1016/S0929-1393(98)00148-6
Blagodatskaya E, Kuzyakov Y (2008) Mechanisms of real and apparent priming effects and their dependence on soil microbial biomass and community structure: critical review. Biol Fertil Soils 45:115–131. doi:10.1007/s00374-008-0334-y
Blankenau K, Olfs HW, Kuhlmann H (2002) Strategies to improve the use efficiency of mineral fertilizer nitrogen applied to winter wheat. J Agron Crop Sci 188:146–154. doi:10.1046/j.1439-037X.2002.00548.x
Breine JJ, Teugels GG, Podoor N, Ollevier F (1996) First data on rabbit dung as a water fertilizer in tropical fish culture and its effect on the growth of Oreochromis niloticus (Teleostei, Cichlidae). Hysrobiologia 321:101–107. doi:10.1007/BF00023167
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen-total. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis part 2. Chemical and Microbiological properties. ASA-SSSA, Madison, WI, pp 595–624
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method for measuring microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(85)90144-0
Cassman KG, Peng S, Olk DC, Ladha JK, Reichardt W, Dobermann A, Singh U (1998) Opportunities for increased nitrogen-use efficiency from improved resource management in irrigated rice systems. Field Crops Res 56:7–39. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(97)00140-8
Edmeades DC (2003) The long-term effects of manures and fertilisers on soil productivity and quality: a review. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 66:165–180. doi:10.1023/A:1023999816690
Elmacı OL, Seçer M, Erdemir O, Iqbal N (2002) Ammonium fixation properties of some arable soils from the Aegean region of Turkey. Eur J Agron 17:199–208. doi:10.1016/S1161-0301(02)00010-2
Gentile R, Vanlauwe B, Chivenge P, Six J (2008) Interactive effects from combining fertilizer and organic residue inputs on nitrogen transformations. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2375–2384. doi:10. 1016/j.soilbio.2008.05.018
Gil MV, Carballo MT, Calvo LF (2008) Fertilization of maize with compost from cattle manure supplemented with additional mineral nutrients. Waste Manag 28:1432–1440. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2007.05.009
Gill HS, Meelu OP (1982) Studies on the substitution of inorganic fertilizers with organic manure and their effect on soil fertility in rice–wheat rotation. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 3:303–314. doi:10. 1007/BF01048935
Hassink J (1994) Effect of soil texture on the size of the microbial biomass and on the amount of C and N mineralized per unit of microbial biomass in Dutch grassland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 26:1573–1581. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(94)90100-7
Hauck RD (1982) Nitrogen–isotope ratio analysis. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis part 2: chemical and microbiological properties. Agronomy Monograph 9. SSSA and ASA, Madison, WI, pp 735–779
Jansson SL, Persson J (1982) Mineralization and immobilization of soil nitrogen. In: Stevenson FJ (ed) Nitrogen in agricultural soils. Agronomy no. 22. ASA, CSSA, SSSA, Madison, WI, pp 229–252
Jenkinson DS, Fox RH, Rayner JH (1985) Interactions between fertilizer nitrogen and soil nitrogen—the so-called ‘priming’effect. J Soil Sci 36:425–444. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.1985.tb00348.x
Jensen LS, Pedersen IS, Hansen TB, Nielsen NE (2000) Turnover and fate of 15N-labeled cattle slurry ammonium-N applied in the autumn to winter wheat. Eur J Agron 12:23–35. doi:10.1016/S1161-0301(99)00040-4
Jörgensen RG, Müeller T (1996) The fumigation-extraction method to estimate soil microbial biomass: calibration of the kEN value. Soil Biol Biochem 28:33–37. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(95)00101-8
Ju XT, Liu XJ, Pan JR, Zhang FS (2007) Fate of 15N-Labeled urea under a winter wheat summer maize rotation on the north China plain. Pedosphere 17:52–61. doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60007-1
Keeney DR, Nelson DW (1982) Nitrogen—inorganic forms. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Agronomy 9, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, pp 643–698
Kramer AW, Doane TA, Horwath WR, van Kessel C (2001) Combining fertilizer and organic inputs to synchronize N supply in alternative cropping systems in California. Agr Ecosyst Environ 91:233–243. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(01)00226-2
Kramer AW, Doane TA, Horwath WR, van Kessel C (2002) Short-term nitrogen-15 recovery vs long-term total soil N gains in conventional and alternative cropping systems. Soil Biol Biochem 34:43–50. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00149-3
Ladha JK, Hill JE, Duxbury JM, Gupta RK, Buresh RJ (2003) Improving the productivity and sustainability of rice–wheat system: issues and impacts. ASA Special Publication, American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, p 231
López-Bellido L, López-Bellido RJ, Redondo R (2005) Nitrogen efficiency in wheat under rainfed Mediterranean conditions as affected by split nitrogen application. Field Crops Res 94:86–97. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2004.11.004
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic Press
Meng L, Zhang XL, Jiang XF, Wang QJ, Huang QW, Xu YC, Yang XM, Shen QR (2009) Effects of partial mineral nitrogen substitution by organic fertilizer nitrogen on the yields of rice grains and their proper substitution rate. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 42:532–542. doi:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2009.02.019
Murashkina MA, Southard RJ, Pettygrove GS (2007) Silt and fine sand fractions dominate K fixation in soils derived from granitic alluvium of the San Joaquin Valley, California. Geoderma 141:283–293. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.06.011
Pan GX, Zhou P, Li ZP, Pete S, Li LQ, Qiu DS, Zhang XH, Xu XB, Shen SY, Chen XM (2009) Combined inorganic/organic fertilization enhances N efficiency and increases rice productivity through organic carbon accumulation in a rice paddy from the Tai Lake region, China. Agr Ecosys Environ 131:274–280. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2009.01.020
Perelo LW, Jimenez M, Munch JC (2006) Microbial immobilisation and turnover of 15N labeled substrates in two arable soils under field and laboratory conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 38:912–922. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.07.013
Rowe EC, Mv N, Suprayogo D, Hairiah K, Giller KE, Cadisch G (2001) Root distributions partially explain 15N uptake patterns in Gliricidia and Peltophorum hedgerow intercropping systems. Plant Soil 235:167–179. doi:10.1023/A:1011961409353
Sikora LJ, Enkiri NK (2001) Uptake of 15N fertilizer in compost-amended soils. Plant Soil 235:65–73. doi:10.1023/A:1011855431544
Sørensen P, Jensen ES (1995) Mineralization-immobilization and plant uptake of nitrogen as influenced by the spatial distribution of cattle slurry in soils of different texture. Plant Soil 173:283–291. doi:10.1007/BF00011466
Sørensen P, Jensen ES (1998) The use of 15N labelling to study the turnover and utilization of ruminant manure N. Biol Fertil Soils 28:56–63. doi:10.1007/s003740050463
Thomsen IK (2000) C and N transformations in 15N cross-labeled solid ruminant manure during anaerobic and aerobic storage. Bioresource Technol 72:267–274. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(99)00114-5
Tian Y, Haibara K, Toda H, Ding F, Liu Y, Choi D (2008) Microbial biomass and activity along a natural pH gradient in forest soils in a karst region of the upper Yangtze River, China. J For Res 13:205–214. doi:10.1007/s10310-008-0073-9
Timsina J, Connor DJ (2001) Productivity and management of rice–wheat cropping systems: issues and challenges. Field Crops Res 69:93–132. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(00)00143-X
Van Cleemput O, Hofman G, Baert L (1981) Fertilizer nitrogen balance study on sandy loam with winter wheat. Fertilizer Res 2:119–126. doi:10.1007/BF01080098
Van Veen JA, Ladd JN, Amato M (1985) Turnover of carbon and nitrogen through the microbial biomass in a sandy loam and a clay soil incubated with [14C(U)]glucose and[15N](NH4)2SO4 under different moisture regimes. Soil Biol Biochem 17:747–756. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(85)90128-2
Weigel C (1993) Fertilisations organiques. Pour raccourcir la chaine alimentaire. Aqua Rev 51:16–23
Yadav RL, Dwivedi BS, Prasad K, Tomar OK, Shurpali NJ, Pandey PS (2000) Yield trends, and changes in soil organic-C and available NPK in a long-term rice–wheat system under integrated use of manures and fertilisers. Field Crops Res 68:219–246. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(00)00126-X
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by China Science and Technology Ministry (2007CB109304). We also thank Professor Warren A. Dick from Ohio State University, USA, and Professor Paolo Nannipieri from University of Florence, Italy, for their careful revisions of the manuscript. Mao would like to thank the National Science Foundation (EAR-0843996) for supporting his research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, CL., Shen, QR., Mao, JD. et al. Fate of 15N after combined application of rabbit manure and inorganic N fertilizers in a rice–wheat rotation system. Biol Fertil Soils 46, 127–137 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-009-0420-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-009-0420-9