Abstract
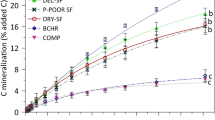
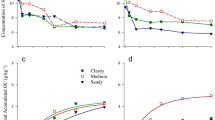
The relative contributions of water-soluble, water-non-soluble, Van Soest-soluble, and neutral detergent fiber (NDF) fractions of pig slurry (PS), cattle slurry (CS), cattle farmyard manure (FYM), and composted cattle farmyard manure (CFYM) to the overall C and N mineralization of the raw wastes were studied by incubating treated soil for 107 days at 15°C under non-limiting N conditions. The C or N mineralization of soluble fractions was calculated from the difference between C or N mineralization of the raw and non-soluble fractions. The organic N content of raw wastes ranged from 15 to 32 mg N g−1 dry matter and organic C to organic N ratio from 13 to 29. The water-soluble fraction (SOLW) was close to 100 mg C g−1 raw waste C for CS, FYM, and CFYM but reached 200 mg C g−1 for PS. The Van Soest-soluble fraction (SOLVS) was the main fraction for PS, CS, and CFYM (>500 mg C g−1 raw waste C) but only 303 mg C g−1 raw waste C for FYM. Both soluble and non-soluble fractions contributed to C decomposition of slurries, with half to more than half of the decomposed C derived from the degradation of soluble compounds. Most of the C decomposed from FYM was derived from the large NDF fraction, but the contribution from the water-soluble C to the decomposition was also significant. Carbon mineralization of CFYM was due to the degradation of the NDF fraction, whereas soluble C did not contribute. Amounts of N mineralized or immobilized by raw wastes and non-soluble fractions at the end of incubation were significantly correlated (P < 0.01) with their organic C to organic N ratio. The contribution of the Van Soest-soluble fraction to N mineralization varied greatly between the four wastes. Finally, large differences in the C degradability and N availability of the water and Van Soest-soluble fractions were demonstrated.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AFNOR (1999) Norme NF ISO 10694, Dosage du carbone organique et du carbone total après combustion sèche. In: Qualité des sols, 1. AFNOR, Paris, pp 361–371
Angers DA, Rochette P, Chantigny MH, Lapierre H (2007) Use of 13C abundance to study short-term pig slurry decomposition in the field. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1234–1237. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.12.028
Atallah T, Andreux F, Choné T, Gras F (1995) Effect of storage and composting on the properties and degradability of cattle manure. Agric Ecosyst Environ 54:203–213. doi:10.1016/0167-8809(95)00595-J
Bernal MP, Sanchez-Monedero MA, Paredes C, Roig A (1998) Carbon mineralization from organic wastes at different composting stages during their incubation with soil. Agric Ecosyst Environ 69:175–189. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(98)00106-6
Beraud J, Fine P, Yermiyahu U, Keinan M, Rosenberg R, Hadas A, Bar-Tal A (2005) Modeling carbon and nitrogen transformations for adjustment of compost application with nitrogen uptake by wheat. J Environ Qual 34:664–675
Bertora C, Alluvione F, Zavattaro L, van Groeningen JW, Velthof G, Grignani C (2008) Pig slurry treatment modifies slurry composition, N2O, and CO2 emissions after soil incorporation. Soil Biol Biochem 40:1999–2006. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.03.021
Bremner JM (1996) Nitrogen—total. In: Sparks D-L, Page A-L, Helmke P-A, Loeppert R-H, Soltanpour P-N, Tabatabai M-A, Johnston C-T, Sommers M-E (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 3, chemical methods. ASA–SSSA, Madison, WI, pp 1085–1121
Bruun S, Stenberg B, Breland TA, Gudmundsson J, Henriksen TM, Jensen S, Korsaeth A, Luxhoi J, Palmason F, Pedersen A, Salo T (2005) Empirical predictions of plant material C and N mineralization patterns from near infrared spectroscopy, stepwise chemical digestion and C/N ratio. Soil Biol Biochem 37:2283–2296. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.04.006
Calderon FJ, McCarty GW, Reeves JB III (2006) Pyrolisis—MS and FT-IR analysis of fresh and decomposed dairy manure. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 76:14–23. doi:10.1016/j.jaap.2005.06.009
Chadwick DR, John F, Pain BF, Chambers BJ, Williams J (2000) Plant uptake of nitrogen from the organic nitrogen fraction in animal manures: a laboratory experiment. J Agric Sci 134:159–168. doi:10.1017/S0021859699007510
Corbeels M, Hofman G, Van Cleemput O (1999) Simulation of net immobilisation and mineralisation in substrate-amended soils by the NCSOIL computer model. Biol Fertil Soils 28:422–430. doi:10.1007/s003740050515
Cordovil CMDS, Coutinho J, Goss M, Cabral F (2005) Potentially mineralizable nitrogen from organic materials applied to a sandy soil: fitting the one-pool exponential model. Soil Use Manage 21:65–72. doi:10.1079/SUM2005294
De Neve S, Hofman G (1996) Modelling N mineralization of vegetable crop residues during laboratory incubations. Soil Biol Biochem 28:1451–1457. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(96)00154-X
FAO–UNESCO (1987) Soils of the World, Food and Agriculture Organization and United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. Elsevier Science, New York
Garnier P, Néel C, Aita C, Recous S, Mary B, Lafolie F (2003) Modelling carbon and nitrogen dynamics in a bare soil with and without straw incorporation. Eur J Soil Sci 54:555–568. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2389.2003.00499.x
Gigliotti G, Kaiser K, Guggenberger G, Haumaier L (2002) Differences in the chemical composition of dissolved organic matter from waste material of different sources. Biol Fertil Soils 36:321–329. doi:10.1007/s00374-002-0551-8
Godwin JC, Jones CA (1991) Nitrogen dynamics in soil–plant systems. In: Ritchie JT, Hanks RJ (eds) Agron. Monogr. 31. ASA, CSSA and SSSA, Madison, WI, pp 378–421
Gutser R, Ebertseder T, Weber A, Schraml M, Schmidhalter U (2005) Short-term and residual availability of nitrogen after long-term application of organic fertilizers on arable land. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 168:439–446. doi:10.1002/jpln.200520510
Hadas A, Kautsky L, Goek M, Kara EE (2004) Rates of decomposition of plant residues and available nitrogen in soil, related to residue composition through simulation of carbon and nitrogen turnover. Soil Biol Biochem 36:255–266. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2003.09.012
Henriksen A, Selmer-Olsen AR (1970) Automatic methods for determining nitrate and nitrite in water and soil extracts. Analyst (Lond) 95:514–518. doi:10.1039/an9709500514
Henriksen TM, Breland TA (1999) Evaluation of criteria for describing crop residue degradability in a model of carbon and nitrogen turnover in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 31:1135–1149. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(99)00031-0
Henriksen TM, Korsaeth A, Breland TA, Stenberg B, Jensen S, Bruun S, Gudmundsson J, Palmason F, Pedersen A, Salo TJ (2007) Stepwise chemical digestion, near-infrared spectroscopy or total N measurement to take account of decomposability of plant C and N in a mechanistic model. Soil Biol Biochem 30:3115–3126. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.06.023
IFEN (2002) L’environnement en France. La Découverte, Paris
Inbar Y, Chen Y, Hadar Y (1989) Solid-state carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance and infrared spectroscopy of composted organic matter. Soil Sci Am J 53:1695–1701
Inbar Y, Chen Y, Hadar Y (1991) Carbon-13 CPMAS and FTIR spectroscopic analysis of organic matter transformations during composting of solid wastes from wineries. Soil Sci 152:272–282. doi:10.1097/00010694-199110000-00005
Inbar Y, Chen Y, Hadar Y (1993) Recycling of cattle manure: the composting process and characterization of maturity. J Environ Qual 22:857–863
Keeney DR, Nelson DW (1982) Nitrogen—inorganic forms. In: Page A-L, Miller R-H, Keeney D-R (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. ASA–SSSA, Madison, WI, pp 643–698
Kirchmann H, Lundvall A (1993) Relationship between N immobilization and volatile fatty acids in soil after application of pig and cattle slurry. Biol Fertil Soils 15:161–164. doi:10.1007/BF00361605
Krom MD (1980) Spectrophotometric determination of ammonia: a study of a modified Berthelot reaction using salicylate and dichloroisocyanurate. Analyst (Lond) 105:305–316. doi:10.1039/an9800500305
Kyvsgaad P, SØrensen P, Møller E, Magid J (2000) Nitrogen mineralization from sheep faeces can be predicted from the apparent digestibility of the feed. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 57:207–214. doi:10.1023/A:1009874500769
Levasseur P (2005) Composition des effluents porcins. Institut Technique du Porc, Paris
Linères M, Djakovitch JL (1993) Caractérisation de la stabilité biologique des apports organiques par l’analyse biochimique. In: Decroux J, Ignazi JC (eds) Matières Organiques et Agricultures. Quatrième Journées de l’Analyse de Terre et Cinquième Forum de la Fertilisation Raisonnée. GEMAS–COMIFER, Paris, pp 159–168
Mashaee SS, Aliasgharzade N, Ostan S (2008) Kinetics of nitrogen mineralization in soils amended with compost, vermicompost and cattle manure. J Sci Technol Agr Nat Resour 11:405–415
Morvan T (1999) Quantification et modélisation des flux d’azote résultant de l’épandage de lisier. PhD thesis, Université Paris VI
Morvan T, Nicolardot B, Péan L (2006) Biochemical composition and kinetics of C and N mineralization of animal wastes in soil: a typological approach. Biol Fertil Soils 42:513–522. doi:10.1007/s00374-005-0045-6
Nicolardot B, Fauvet G, Chèneby D (1994) Carbon and nitrogen cycling through soil microbial biomass at various temperatures. Soil Biol Biochem 26:253–261. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(94)90165-1
Pansu M, Thuriès L (2003) Kinetics of C and N mineralization, N immobilization and N volatilization of organic inputs in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 35:37–48. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00234-1
Quemada M, Cabrera ML (1995) CERES-N model predictions of nitrogen mineralized from cover crop residues. Soil Sci Soc Am J 59:1059–1065
Recous S, Robin D, Darwis D, Mary B (1995) Soil inorganic N availability: effect on maize residue decomposition. Soil Biol Biochem 27:1529–1538. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(95)00096-W
Rochette P, Angers DA, Chantigny MH, Gagnon B, Bertrand N (2006) In situ mineralization of dairy cattle manures as determined using soil-surface carbon dioxide fluxes. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:744–752. doi:10.2136/sssaj2005.0242
Saviozzi A, Levi-Minzi R, Riffaldi R, Vanni G (1997) Role of chemical constituents of wheat straw and pig slurry on their decomposition in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 25:401–406. doi:10.1007/s003740050332
Sleutel S, De Neve MR, Prat Roibas MR, Hofman G (2005) The influence of model type and incubation time on the estimation of stable organic carbon in organic materials. Eur J Soil Sci 56:505–514. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2004.00685.x
Sorensen P (1998) Effects of storage time and straw content of cattle slurry on the mineralization of nitrogen and carbon in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 27:85–91. doi:10.1007/s003740050404
Sorensen P (2004) Immobilisation, remineralisation and residual effects in subsequent crops of dairy cattle slurry nitrogen compared to mineral fertiliser nitrogen. Plant Soil 267:285–296. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-0121-6
Sorensen P, Weisbjerg MR, Lund P (2003) Dietary effects on the composition and plant utilization of nitrogen in dairy cattle manure. J Agric Sci 141:79–91. doi:10.1017/S0021859603003368
Standing D, Baggs EM, Wattenbach M, Smith P, Killham K (2007) Meeting the challenge of scaling up processes in the plant–soil–microbe system. Biol Fertil Soils 44:245–258. doi:10.1007/s00374-007-0249-z
Thuriès L, Pansu M, Feller C, Herrmann P, Rémy JC (2001) Kinetics of added organic matter decomposition in a Mediterranean. Soil Biol Biochem 33:997–1010. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00003-7
Tiquia SM (2003) Evaluation of organic matter and nutrient composition of partially decomposed and composted spent pig litter. Environ Technol 24:97–107. doi:10.1080/09593330309385540
Trinsoutrot I, Recous S, Mary B, Nicolardot B (2000) C and N fluxes of decomposing 13C and 15N Brassica napus L.: effects of residue composition and N content. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1717–1730. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00090-0
Van Kessel JS, Reeves JB III, Meisinger JJ (1999) Storage and handling can alter the mineralization characteristics of manure. J Environ Qual 28:1994–1990
Van Kessel JS, Reeves JB III, Meisinger JJ (2000) Nitrogen and carbon mineralization of potential manure components. J Environ Qual 29:1669–1677
Van Soest PJ (1963) Use of detergents in the analysis of fibrous feeds. II. A rapid method for the determination of fiber and lignin. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 46:825–835
Van Soest PJ, Wine RH (1967) Use of detergents in the analysis of fibrous feeds. IV. Determination of plant cell-wall constituents. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 50:50–55
Vanlauwe B, Dendooven L, Merckx R (1994) Residue fractionation and decomposition: The significance of the active fraction. Plant Soil 158:263–274. doi:10.1007/BF00009500
Whitmore AP (1996) Describing the mineralization of carbon added to soil in crop residues using second-order kinetics. Soil Biol Biochem 28:1435–1442. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(96)00153-8
Zibilske LM (1994) Carbon mineralization. In: Weaver R-W, Angle S, Bottomley P, Bezdicek D, Smith S, Tabatabai A, Wollum A (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2, microbiological and biochemical properties. ASA–SSSA, Madison, WI, pp 835–863
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the coordinated scientific program “AGREDE” funded by INRA and ADEME. We would like to thank Béatrice Trinkler, Maryvonne Leroy, Sylvie Millon, Marie-Jeanne Herre, and Gonzague Alavoine for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morvan, T., Nicolardot, B. Role of organic fractions on C decomposition and N mineralization of animal wastes in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 45, 477–486 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-009-0355-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-009-0355-1