Abstract
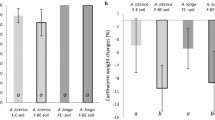
Low phosphorus (P) availability in Ferralsols of the Malagasy Highlands is a major limitation to crop growth. Direct seeding mulch-based cropping practices which were adopted in the region to improve and sustain soil fertility are known to favour earthworms’ presence. The mesocosm study aims to analyse the effect of an endogeic geophageous earthworm species on the soil P status. Total P content (P t), NaOH-extractable P content, P ions (Pi) concentration (C p) in solution and rapid and slow reactions of Pi in solution with solid phase were determined in two Malagasy Ferralsols. Both C p and reactions rates were assessed in laboratory batch experiments using 32Pi labelling and isotopic exchange kinetics (IEK). The P t values were 836 and 349 mg P g−1 in a clayey soil and a sandy–clayey soil, respectively. For both soils, NaOH-extractable organic P was significantly higher in earthworm casts than in parent soils, whereas Pt was unchanged. Also, the effect of earthworm ingestion significantly changed parameters of the IEK. In casts compared with the soil from which they were derived, the immediate isotopically exchangeable Pi (E 1 min) increased by 116%, whereas relative rates of Pi release at the solid-to-solution with time were slightly lowered. The effect of earthworm ingestion on IEK corresponded to a transfer of slowly exchangeable Pi towards quicker Pi pools of exchange. However, according to the literature, the increase in E 1 min remained below the critical level for optimal growth, stating that the soils remained P-deficient even in the presence of active and numerous earthworms.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barois I, Lavelle P (1986) Changes in respiration rate and some physicochemical properties of a tropical soil during transit through Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossoscolecidae, Oligochaeta). Soil Biol Biochem 18:539–541. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(86)90012-X
Barois I, Villemin G, Lavelle P (1993) Transformation of the soil structure through Pontoscolex corethrurus (Oligochaeta) intestinal tract. Geoderma 56:57–66. doi:10.1016/0016-7061(93)90100-Y
Blanchart E, Marilleau N, Cambier C, Drogoul A, Perrier E, Chotte JL (2008) SWORM: an agent-based model to simulate the effect of earthworms on soil structure. Eur J Soil Sci.. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2008.01091.x
Bowman RA, Cole CV (1978) An exploratory method for fractionation of organic phosphorus from grassland soils. Soil Sci 125:95–101
Brossard M, Lavelle P, Laurent JY (1996) Digestion of a vertisol by the endogeic earthworm Polypheretima elongata, Megascolecidae, increases soil phosphate extractability. Eur J Soil Biol 32:107–111
Bünemann EK, Steinebrunner F, Smithson PC, Frossard E, Oberson A (2004) Phosphorus dynamics in a highly weathered soil as revealed by isotopic labeling techniques. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:1645–1655
Chapuis-Lardy L, Brossard M, Lavelle P, Schouller E (1998) Phosphorus transformations in a Ferralsol through ingestion by Pontoscolex corethrurus, a geophagous earthworm. Eur J Soil Biol 34:61–67. doi:10.1016/S1164-5563(99)90002-X
Coq S, Barthès BG, Oliver R, Rabary B, Blanchart E (2007) Earthworm activity affects soil aggregation and organic matter dynamics according to the quality and localization of crop residues—an experimental study (Madagascar). Soil Biol Biochem 39:2119–2128. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.03.019
FAO (1998) World reference base for soil resources. FAO, ISRIC, ISSS, Rome
Fardeau JC (1993) Le phosphore assimilable des sols: sa représentation par un modèle fonctionnel à plusieurs compartiments. Agronomie 13:317–331. doi:10.1051/agro:19930409
Fardeau JC (1996) Dynamics of phosphate in soils—an isotopic outlook. Fertil Res 45:91–100. doi:10.1007/BF00790658
Fardeau JC, Morel C, Boniface R (1991) Cinétiques de transfert des ions phosphates du sol vers la solution du sol. Agronomie 11:577–584. doi:10.1051/agro:19910909
Fardeau JC, Guiraud G, Marol C (1996) The role of isotopic techniques on the evaluation of the effectiveness of P fertilizers. Fertil Res 45:101–109. doi:10.1007/BF00790659
Friesen DK, Rao IM, Thomas RJ, Oberson A, Sanz JI (1997) Phosphorous acquisition and cycling in crop and pasture systems in low fertility tropical soils. Plant Soil 196:289–294. doi:10.1023/A:1004226708485
Frossard E, Sinaj S (1997) The isotope exchange kinetic technique: a method to describe the availability of inorganic nutrients—applications to K, P, S and Zn. Isotopes Environ Health Stud 33:61–77. doi:10.1080/10256019708036332
Frossard E, Brossard M, Hedley MJ, Metherell A (1995) Reactions controlling the cycling of P in soils. In: Tiessen H (ed) Phosphorus in the global environment. Transfers, cycles and management. SCOPE 54. Wiley, NY, pp 107–137
Guggenberger G, Haumaier L, Thomas RJ, Zech W (1996) Assessing the organic phosphorous status of an Oxisol under tropical pastures following native savanna using 31P NMR spectroscopy. Biol Fertil Soils 23:332–339. doi:10.1007/BF00335963
Hooda PS, Truesdale VW, Edwards AC, Withers PJA, Aitken MN, Miller A, Rendell AR (2001) Manuring and fertilization effects on phosphorus accumulation in soils and potential environmental implications. Adv Environ Res 5:13–21. doi:10.1016/S1093-0191(00)00037-X
John MK (1970) Colorimetric determination of phosphorus in soil and plant materials with ascorbic acid. Soil Sci 109:214–220. doi:10.1097/00010694-197004000-00002
Lavelle P, Barros E, Blanchart E, Brown G, Desjardins T, Mariani L, Rossi JP (2001) Soil organic matter management in the tropics: why feeding the soil macrofauna? Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 61:53–61. doi:10.1023/A:1013368715742
López-Hernández D, Lavelle P, Fardeau JC, Niño M (1993) Phosphorous transformations in two P-sorption contrasting tropical soils during transit through Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossoscolecidae, Oligochaeta). Soil Biol Biochem 25:789–792. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(93)90124-T
Mehra OP, Jackson ML (1960) Iron oxide removal from soils and clays by a dithionite–citrate system buffered with sodium bicarbonate. Clay Miner 7:317–327
Morel C, Tiessen H, Moir J, Stewart JWB (1994) Phosphorus transformations and availability due to crop rotations and mineral fertilization assessed by an isotopic exchange method. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:1439–1445
Morel C, Tunney H, Plénet D, Pellerin S (2000) Transfer of phosphate ion between soil and solution. Perspectives in soil testing. J Environ Qual 29:50–59
Nziguheba G, Bünneman EK (2005) Organic phosphorus dynamics in tropical agroecosystems. In: Turner BL, Frossard E, Baldwin DS (eds) Organic phosphorus in the environment. CABI, Wallingford, UK, pp 243–268
Oberson A, Bünemann EK, Friesen DK, Rao IM, Smithson PC, Turner BL, Frossard E (2006) Improving phosphorus fertility in tropical soils through biological interventions. In: Uphoff NT, Uphoff N, Ball AS (eds) Biological approaches to sustainable soil systems. CRC, Boca Raton, FL, pp 531–546
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2, Chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 421–422
Rabary B, Sall BPL, Husson O, Ralambofetra E, Moussa N, Chotte JL (2008) Effects of living mulches or residue amendments on soil microbial properties in direct seeded cropping systems of Madagascar. Appl Soil Ecol 39:236–243. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2007.12.012
Rabeharisoa L (2004) Gestion de la fertilité et de la fertilisation phosphatée des sols ferrallitiques des Hautes Terres de Madagascar. Thèse d’Etat thesis, University of Antananarivo, Antananarivo, 213 pp. http://www.bordeaux.inra.fr/tcem/document/These%20Lilia%202004.pdf
Razafimbelo TM, Albrecht A, Oliver R, Chevallier T, Chapuis-Lardy L, Feller C (2008) Aggregate associated-C and physical protection in a tropical clayey soil under Malagasy conventional and no-tillage systems. Soil Tillage Res 98:140–149. doi:10.1016/j.still.2007.10.012
SAS Institute (1995) SAS/STAT Version 5.7. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC
Sinaj S, Buerkert A, El-Hajj G, Bationo A, Traore H, Frossard E (2001) Effects of fertility management strategies on phosphorus bioavailability in four West African soils. Plant Soil 233:71–83. doi:10.1023/A:1010314108931
Six J, Feller C, Denef K, Ogle SM, de Moraes Sa JC, Albrecht A (2002) Soil organic matter, biota and aggregation in temperate and tropical soils: effects of no-tillage. Agronomie 22:755–775. doi:10.1051/agro:2002043
Standing D, Baggs EM, Wattenbach M, Smith P, Killham K (2007) Meeting the challenge of scaling up processes in the plant–soil–microbe system. Biol Fertil Soils 44:245–257. doi:10.1007/s00374-007-0249-z
Statsoft (2004) Statistica. http://www.statsoft.com
Stroia C, Morel C, Jouany C (2007) Dynamics of diffusive soil phosphorus in two grassland experiments determined both in field and laboratory conditions. Agric Ecosyst Environ 119:60–74. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2006.06.007
Tabatabai MA (1982) Soil enzymes. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2, Chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 903–948
Tiessen H, Moir JO (1993) Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. In: Carter MR (ed) Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL, pp 75–86
Turner BL, Frossard E, Oberson A (2006) Enhancing phosphorus availability in low-fertility soils. In: Uphoff NT, Uphoff N, Ball AS (eds) Biological approaches to sustainable soil systems. CRC, Boca Raton, FL, pp 191–206
van Veldhoven PP, Mannaerts GP (1987) Inorganic and organic phosphate measurements in the nanomolar range. Anal Biochem 161:45–48. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(87)90649-X
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank L. Weber from ETH Zurich for her participation to experimental setup. Also, the authors warmly thank International Atomic Energy Agency (AIEA, Vienna, Austria) for his support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chapuis-Lardy, L., Ramiandrisoa, R.S., Randriamanantsoa, L. et al. Modification of P availability by endogeic earthworms (Glossoscolecidae) in Ferralsols of the Malagasy Highlands. Biol Fertil Soils 45, 415–422 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-008-0350-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-008-0350-y