Abstract
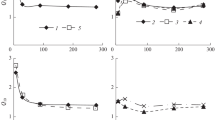
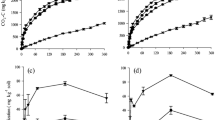
The influence of biochemical characteristics of 15 crop residues on C and N mineralisation in soil was investigated by following the decomposition of roots, stems and leaves of four subtropical species and one temperate species buried into the soil. The C, N and polyphenols contents were measured in different biochemical pools obtained from residues of the different organs. The mineralisation of root C was significantly lower than that of leaves and stems. Chemical analysis showed a higher polyphenol content in the leaves and a higher ligninlike content in the roots. Carbon and N mineralisation were simulated with the STICS decomposition submodel and tested against the data set. The model predicted leaf and stem C mineralisation for all five species fairly accurately, but failed to predict root C mineralisation, indirectly revealing the more complex composition of the root tissue. The results showed the interest of separately considering the different plant parts when studying plant residue decomposition and the need to develop other methods of residue quality characterisation to improve the prediction of residue decomposition.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annoussamy M, Chabbert B, Recous S (2000) Changes in mechanical strength and biochemical composition of wheat straw during decomposition. In: Spatz HC, Speck T (eds) Proceedings of the 3rd plant biomechanics conference, Freiburg, Badenweiler, August 27–September 2, 2000. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, pp 169–176
Balesdent J, Balabane M (1996) Major contribution of roots to soil carbon storage inferred from maize cultivated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 28(9):1261–1263
Bolinder MA, Angers DA, Giroux M, Laverdière MR (1999) Estimating C inputs retained as soil organic matter from corn (Zea Mays L.). Plant Soil 215:85–91
De Freitas PL, Blancaneaux P, Gavinelli E, Larré-Larrouy MC, Feller C (2000) Nivel e natureza do estoque organico de la latossolos sob diferentes sistemas de uso e manejo. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 35:157–170
Estone DE, Peterson CA, Ma F (2003) Root endodermis and exodermis: structure, function and responses to the environment. J Plant Growth Regul 21:335–351
Gaillard V, Chenu C, Recous S, Richard G (1999) Carbon, nitrogen and microbial gradients induced by plant residues decomposing in soil. Eur J Soil Sci 50:567–578
Hatfield RD, Ralph J, Grabber JH (1999) Cell wall structural foundations: molecular basis for improving forage digestibilities. Crop Sci 39:27–37
Heal OW, Anderson JM, Swift MJ (1997) Plant litter quality and decomposition: an historical overview. In: Cadish G, Giller GE (eds) Driven by nature. Plant litter quality and decomposition. CABI Publishing, New York, pp 3–30
King HG, Health GW (1967) The chemical analyses of small samples of leaf material and the relationship between the disappearance and composition of leaves. Pedobiologia 7:192–197
Linères M, Djarkovitch JL (1993) Caractérisation de la stabilité biologique des apports organiques par l'analyse biochimique. In: Decroux J, Ignazi JC (eds) Matières organiques et agricultures, Quatrièmes journées de l'analyse de terre et cinquième forum de la fertilisation raisonnée. GEMAS-COMIFER Publishing, Blois, pp 159–168
Lu Y, Watanabe A, Kimura M (2003) Carbon dynamics of rhizodeposits, root- and shoot-residues in a rice soil. Soil Biol Biochem 35:1223–1230
Ma F, Petersen CA (2003) Current insights into the development, structure, and chemistry of the endodermis and exodermis of roots. Can J Bot 81:405–421
Mauseth JD (1995) Roots. In: Botany, an introduction to plant ecology, vol 7. Saunders College Publishing, Philadelphia, pp 173–194
Molina JAE, Smith P (1998) Modeling carbon and nitrogen processes in soils. Adv Agron 62:253–298
Nicolardot B, Recous S, Mary B (2001) Simulation of C and N mineralization during crop residue decomposition: a simple dynamic model based on the C:N ratio of the residues. Plant Soil 228:83–103
Oglesby KA, Fownes JH (1992) Effects of chemical composition on N mineralization from green manures of seven tropical species. Plant Soil 143:127–132
Palm CA, Rowland AP (1997) A minimum dataset for characterization of plant quality for decomposition. In: Cadish G, Giller GE (eds) Driven by nature. Plant litter quality and decomposition. CABI Publishing, New York, pp 379–392
Palm CA, Sanchez PA (1991) Nitrogen release from the leaves of some tropical legumes as affected by their lignin and polyphenolic contents. Soil Biol Biochem 23:83–88
Palm CA, Giller KE, Mafongoya PL, Swift MJ (2001) Management of organic matter in tropics: translating theory into practice. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 61:63–75
Puget P, Drinkwater LE (2001) Short-term dynamics of root- and shoot-derived carbon from a leguminous green manure. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:771–779
Rasse D, Rumpel C, Dignac MF (2005) Is soil carbon mostly root carbon? Mechanisms for a specific stabilisation. Plant Soil 269:341–356
Recous S, Robin D, Darwis D, Mary B (1995) Soil inorganic N availability: effect on maize residue decomposition. Soil Biol Biochem 7:1529–1538
Sariyildiz T, Anderson JM (2003) Interactions between litter quality, decomposition and soil fertility: a laboratory study. Soil Biol Biochem 35:391–399
Scholes MC, Powlson D, Tian G (1997) Input control of organic matter dynamics, Management of carbon in tropical soils under global change: science, practice and policy. In: Proceedings of a workshop, Nairobi, Kenya. Geoderma 79:25–47
Schreiber L, Hartmann K, Skrabs M, Zeier J (1999) Apoplastic barriers in roots: chemical composition of endodermal and hypodermal cell walls. J Exp Bot 50:1267–1280
Silver WL, Miya RK (2001) Global patterns in root decomposition: comparisons of climate and litter quality effects. Oecologia 129:407–419
Tian G, Brussaard L, Kang BT (1995) An index for assessing the quality of plant residues and evaluating their effects on soil and crop in the subhumid tropics. Appl Soil Ecol 2:25–32
Trinsoutrot I, Recous S, Bentz B, Linières M, Cheneby D, Nicolardot B (2000) Biochemical quality of crop residues and carbon and nitrogen mineralization kinetics under nonlimiting nitrogen conditions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:918–926
Van Soest PJ (1963) Use of detergents in the analysis of fibrous feeds I: preparation of fiber residues of low nitrogen content. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 46:825–835
Zeier J, Ruel K, Ryser U, Schreiber L (1999) Chemical analysis and immunolocalisation of lignin and suberin in endodermal and hypodermal/rhizodermal cell walls of developing maize (Zea mays L.) primary roots. Planta 209:1–12
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Muguette Boucher, Laurence Foulon, Olivier Delfosse, Gonzague Alavoine and Gaétan Bentivegna for their technical assistance. This work was carried out as part of INRA–CIRAD collaborative research from 2000 to 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abiven, S., Recous, S., Reyes, V. et al. Mineralisation of C and N from root, stem and leaf residues in soil and role of their biochemical quality. Biol Fertil Soils 42, 119–128 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-005-0006-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-005-0006-0