Abstract.
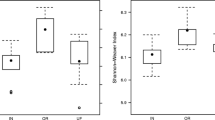
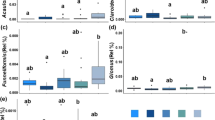
Microbial community responses to alternative management may be indicative of soil quality change. In this study, soils were collected from research plots over 2 years and from commercial grower fields over 1 year. Treatments at the sites included 1–9 years of either winter cover cropping or winter fallow practices. Soils were assayed for microbial fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs), direct count microscopy and Biolog substrate utilization potentials to assess management and environmental influences on soil communities. The strongest influence was season. Soils in early spring (prior to termination of the cover crop) utilized fewer carboxylic acids and generally were enriched in eukaryotic FAMEs, whereas proportionally more bacterial FAMEs were detected in soils at canopy closure and harvest of the summer vegetable crop. Within a season, community FAME and Biolog patterns were related to field properties. FAME profiles from grower fields in early spring and harvest were correlated significantly with soil texture, cation exchange capacity, and carbon content. Changes in community structure and Biolog potential occurred in some soils in response to winter cover crops, although effects were not observed until cover crop incorporation. Greater amounts of fungal and protozoan FAME markers were detected in some cover-cropped soils compared to winter fallow soils. Cover crop residues increased FAME diversity at one research station and Biolog diversity at two research stations and the grower fields. Although seasonal and field-dependent factors are major determinants of microbial community structure, shifts can occur as soil physical and chemical properties change in response to alternative practices, as demonstrated by this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schutter, .M., Sandeno, .J. & Dick, .R. Seasonal, soil type, and alternative management influences on microbial communities of vegetable cropping systems. Biol Fertil Soils 34, 397–410 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-001-0423-7
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-001-0423-7