Abstract
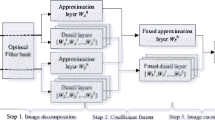
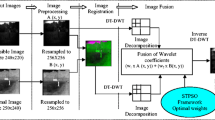
Image fusion is a useful context in image processing. It goals to produce more informative image using multi-image data with different sensors. In this study, an effective approach in discrete wavelet transform domain for infrared and visible image fusion is proposed. In fact, important parts of thermal images along with details of visual image must be considered in fused images. Therefore, dual tree discrete wavelet transform is used to extract both subjects based on an optimization process. The optimization considers parts of input images with maximum entropy and minimum mean square error in fused image in comparison with both input images. Experimental results on a standard database demonstrate that proposed method can achieve a superior performance compared with other fusion methods in both subjective and objective assessments.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Convolutional Neural Network.
Generative Adversarial Network.
References
Zhou, Z., Dong, M., Xie, X., Gao, Z.: Fusion of infrared and visible images for night-vision context enhancement. Appl. Opt. 55, 6480–6490 (2016)
Ma, J., Jiang, J., Liu, C., Li, Y.: Feature guided Gaussian mixture model with semi-supervised EM and local geometric constraint for retinal image registration. Inf. Sci. 417, 128–142 (2017)
Liu, C., Ma, J., Ma, Y., Huang, J.: Retinal image registration via feature-guided Gaussian mixture model. JOSA A 33, 1267–1276 (2016)
Bhatnagar, G., Wu, Q.J., Liu, Z.: A new contrast based multimodal medical image fusion framework. Neurocomputing 157, 143–152 (2015)
Li, H., Manjunath, B., Mitra, S.K.: Multisensor image fusion using the wavelet transform. Graph. Models Image Process. 57, 235–245 (1995)
Wei, Z., Han, Y., Li, M., Yang, K., Yang, Y., Luo, Y., et al.: A small UAV based multi-temporal image registration for dynamic agricultural terrace monitoring. Remote Sens. 9, 904 (2017)
Yang, K., Pan, A., Yang, Y., Zhang, S., Ong, S.H., Tang, H.: Remote sensing image registration using multiple image features. Remote Sens. 9, 581 (2017)
Dong, L., Yang, Q., Wu, H., Xiao, H., Xu, M.: High quality multi-spectral and panchromatic image fusion technologies based on Curvelet transform. Neurocomputing 159, 268–274 (2015)
Chen, C., Li, Y., Liu, W., Huang, J.: Image fusion with local spectral consistency and dynamic gradient sparsity. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2760–2765. (2014)
Zhou, C., Zhao, J., Pan, Z., Hong, Q., Huang, L.: Fusion of visible and infrared images based on IHS transformation and regional variance matching degree. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, p. 012021. (2019)
Gao, Y., Ma, J., Yuille, A.L.: Semi-supervised sparse representation based classification for face recognition with insufficient labeled samples. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26, 2545–2560 (2017)
Kong, S.G., Heo, J., Boughorbel, F., Zheng, Y., Abidi, B.R., Koschan, A., et al.: Multiscale fusion of visible and thermal IR images for illumination-invariant face recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 71, 215–233 (2007)
Toet, A., Ijspeert, J.K., Waxman, A.M.: Aguilar, fusion of visible and thermal imagery improves situational awareness. Displays 18, 85–95 (1997)
Ghaneizad, M., Kavehvash, Z., Aghajan, H.: Human detection in occluded scenes through optically inspired multi-camera image fusion. JOSA A 34, 856–869 (2017)
Yang, C., Ma, J., Qi, S., Tian, J., Zheng, S., Tian, X.: Directional support value of Gaussian transformation for infrared small target detection. Appl. Opt. 54, 2255–2265 (2015)
Ma, J., Zhao, J., Ma, Y., Tian, J.: Non-rigid visible and infrared face registration via regularized Gaussian fields criterion. Pattern Recogn. 48, 772–784 (2015)
Wang, N., Ma, Y., Zhan, K.: Spiking cortical model for multifocus image fusion. Neurocomputing 130, 44–51 (2014)
Meng, F., Guo, B., Song, M., Zhang, X.: Image fusion with saliency map and interest points. Neurocomputing 177, 1–8 (2016)
Li, Y., Tao, C., Tan, Y., Shang, K., Tian, J.: Unsupervised multilayer feature learning for satellite image scene classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 13, 157–161 (2016)
Ma, J., Zhao, J., Jiang, J., Zhou, H., Guo, X.: Locality preserving matching. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1–20 (2017)
Yang, Y., Ong, S.H., Foong, K.W.C.: A robust global and local mixture distance based non-rigid point set registration. Pattern Recogn. 48, 156–173 (2015)
Ma, J., Zhao, J., Tian, J., Bai, X., Tu, Z.: Regularized vector field learning with sparse approximation for mismatch removal. Pattern Recogn. 46, 3519–3532 (2013)
Burt, P., Adelson, E.: The Laplacian pyramid as a compact image code. IEEE Trans. Commun. 31, 532–540 (1983)
Toet, A.: Image fusion by a ratio of low-pass pyramid. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 9, 245–253 (1989)
Toet, A.: A morphological pyramidal image decomposition. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 9, 255–261 (1989)
Nencini, F., Garzelli, A., Baronti, S., Alparone, L.: Remote sensing image fusion using the curvelet transform. Inf. Fusion 8, 143–156 (2007)
Zhenfeng, S., Jun, L., Qimin, C.: Fusion of infrared and visible images based on focus measure operators in the curvelet domain. Appl. Opt. 51, 1910–1921 (2012)
Adu, J., Gan, J., Wang, Y., Huang, J.: Image fusion based on nonsubsampled contourlet transform for infrared and visible light image. Infrared Phys. Technol. 61, 94–100 (2013)
Zhang, Q., Maldague, X.: An adaptive fusion approach for infrared and visible images based on NSCT and compressed sensing. Infrared Phys. Technol. 74, 11–20 (2016)
Huang, Y., Bi, D., Wu, D.: Infrared and visible image fusion based on different constraints in the non-subsampled shearlet transform domain. Sensors 18, 1169 (2018)
El-Khamy, S.E., Hadhoud, M.M., Dessouky, M.I., Salam, B.M., El-Samie, F.E.A.: Blind multichannel reconstruction of high-resolution images using wavelet fusion. Appl. Opt. 44, 7349–7356 (2005)
Zhou, Y., Gao, K., Dou, Z., Hua, Z., Wang, H.: Target-aware fusion of infrared and visible images. IEEE Access 6, 79039–79049 (2018)
Ma, J., Zhou, Z., Wang, B., Zong, H.: Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 82, 8–17 (2017)
Hou, R., Nie, R., Zhou, D., Cao, J., Liu, D.: Infrared and visible images fusion using visual saliency and optimized spiking cortical model in non-subsampled shearlet transform domain. Multimed. Tools Appl. 78, 28609–28632 (2019)
Jin, X., Jiang, Q., Yao, S., Zhou, D., Nie, R., Lee, S.-J., et al.: Infrared and visual image fusion method based on discrete cosine transform and local spatial frequency in discrete stationary wavelet transform domain. Infrared Phys. Technol. 88, 1–12 (2018)
Heijmans, H.J., Goutsias, J.: Nonlinear multiresolution signal decomposition schemes. II. Morphological wavelets. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 9, 1897–1913 (2000)
Toet, A., Van Ruyven, L.J., Valeton, J.M.: "Merging thermal and visual images by a contrast pyramid. Opt. Eng. 28, 287789 (1989)
Kingsbury, N.: Image processing with complex wavelets. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 357, 2543–2560 (1999)
Sun, C., Zhang, C., Xiong, N.: Infrared and visible image fusion techniques based on deep learning: a review. Electronics 9, 2162 (2020)
Hou, R., Zhou, D., Nie, R., Liu, D., Xiong, L., Guo, Y., et al.: VIF-Net: an unsupervised framework for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 6, 640–651 (2020)
Li, H., Wu, X.-J., Durrani, T.S.: Infrared and visible image fusion with ResNet and zero-phase component analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 102, 103039 (2019)
Lagarias, J.C., Reeds, J.A., Wright, M.H., Wright, P.E.: Convergence properties of the Nelder-Mead simplex method in low dimensions. SIAM J. Optim. 9, 112–147 (1998)
http://figshare.com/articles/TNO_Image_Fusion_Dataset/1008029
AbouRayan, M.: Real-time image fusion processing for astronomical images. (2016)
Sadjadi, F.: Comparative image fusion analysais. In: 2005 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR'05)-workshops, pp. 8–8. (2005)
Leung, L.W., King, B., Vohora, V.: Comparison of image data fusion techniques using entropy and INI. In: 22nd Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, p. 9. (200)
Chandana, M., Amutha, S., Kumar, N.: A hybrid multi-focus medical image fusion based on wavelet transform. Int. J. Res. Rev. Comput. Sci. 2, 948 (2011)
Thung, K.H., Raveendran, P.: A survey of image quality measures. In: 2009 international conference for technical postgraduates (TECHPOS), pp. 1–4. (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
All images used in this paper are provided by database [43] and they are in turn as follows:
-
1.
Duine,
-
2.
Soldier in trench
-
3.
Bunker
-
4.
Bench
-
5.
Nato camp
-
6.
Lake
-
7.
Two men in front of the house
-
8.
Soldier behind smoke
-
9.
Man in doorway
-
10.
Soldier behind smoke 2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aghamaleki, J.A., Ghorbani, A. Image fusion using dual tree discrete wavelet transform and weights optimization. Vis Comput 39, 1181–1191 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02396-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02396-9