Abstract
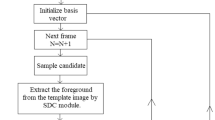
Visual object tracking is a core research area in the field of pattern recognition and computer vision. It becomes one of the most significant tasks in computer vision application. But tracking of a visual object is not an easy task as it is always restricted by appearance change, illumination, occlusion and so on. Object tracking based on principal component analysis (PCA) is one of the most effective tracking methods as it can handle the different challenging problems of the tracking algorithm. But in this PCA-based tracking method, the background pixels are also included in the subspace representation of the target object, and so this method cannot overcome all the problems of tracking. In this work, a robust visual object tracking method is proposed by introducing sparse discriminative classifier (SDC) feature selection in PCA subspace representation. The SDC method is utilized to extract the target object from the template image target by removing the background pixels which is unnecessary for tracking task without much computational complexity. The PCA algorithm adequately represents a presentation model of the target object and account of occlusion with trivial template. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of different diverse videos shows that the newly proposed method outperforms the other existing state-of-the-art tracking algorithm.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Comaniciu, Dorin: Ramesh, Visvanathan, Meer, Peter: kernel-based object tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 5, 564–575 (2003)
Ross, D.A., Lim, J., Lin, R.S., Yang, M.H.: Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis 77(1–3), 125–141 (2008)
Amit, A., Rivlin, E., Shimshoni, I.: Robust fragments-based tracking using the integral histogram In: 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06) 1, 798–805 (2006)
Wang, D., Lu, H., Chen Y.W.: Incremental MPCA for color object tracking. In: 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. pp. 1751-1754 (2010)
Weiming, Hu, Xi, Li, Xiaoqin, Zhang, Xinchu, Shi, Stephen, Maybank, Zhongfei, Zhang: Incremental tensor subspace learning and its applications to foreground segmentation and tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 91(3), 303–327 (2011)
Grabner, H., Bischof, H.: On-line boosting and vision. In: 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06) 1, pp. 260–267 (2006)
Avidan, Shai: Ensemble tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(2), 261–271 (2007)
Babenko, B., Ming-Hsuan Y., Serge, B.: Visual tracking with online multiple instance learning. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 983–990 (2009)
Grabner, H., Leistner, C., Bischof, H.: Semi-supervised on-line boosting for robust tracking. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 234–247 (2008)
Avidan, S.: Support vector tracking, In: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. CVPR (2001)
Tang, F., Brennan, S., Zhao, Q., Tao, H.: Co-tracking using semi-supervised support vector machines. In: 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 1–8 (2007)
Mei, X., Ling, H.: Robust visual tracking using l1 minimization. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 1436–1443 (2009)
Bao, C., Wu, Y., Ling, H., Ji, H.: Real time robust l1 tracker using accelerated proximal gradient approach. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 1830–1837 (2012)
Zhong, W., Lu, H., Yang, M.H.: Robust object tracking via sparse collaborative appearance model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(5), 2356–2368 (2014)
Jia, X., Lu, H., Yang M.H.: Visual tracking via adaptive structural local sparse appearance model. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1822–1829 (2012)
Chen, F., Wang, Q., Wang, S., Zhang, W., Xu, W.: Object tracking via appearance modeling and sparse representation. Image Vis. Comput. 29(11), 787–796 (2011)
Dong, Wang: Huchuan, Lu, Yang, Ming-Hsuan: Obect tracking with sparse prototypes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(1), 314–325 (2012)
Lu, W., Bai, C., Kpalma, K., Ronsin, J.: Multi-object tracking using sparse representation. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 2312–316 (2013)
Liu, B., Huang, J., Yang, L., Kulikowsk, C.: Robust tracking using local sparse appearance model and k-selection, In: CVPR 2011, pp. 1313–1320 (2011)
Stephan, Liwicki, Zafeiriou, Stefanos, Tzimiropoulos, Georgios, Pantic, Maja: Efficient online subspace learning with an indefinite kernel for visual tracking and recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 23(10), 1624–1636 (2012)
Yu, G., Hu, Z., Lu, H.: Robust incremental subspace learning for object tracking. pp. 819–828 (2009)
Haicang, Liu, Li, Shutao, Fang, Leyuan: Robust object tracking based on principal component analysis and local sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 64(11), 2863–2875 (2015)
Kalal, Z., Matas, J., Mikolajczyk, k.: Pn learning: bootstrapping binary classifiers by structural constraints. In: 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 49–56 (2010)
Kwon, J., Lee, K. M.: Visual tracking decomposition. In: 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1269–1276 (2010)
Liu, B., Yang, L., Huang, J., Meer, P., Gong, L., Kulikowski, C.: Robust and fast collaborative tracking with two stage sparse optimization. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 624–637 (2010)
Guoliang, Yang, Zhengwei, Hu, Tang, Jun: Robust visual tracking via incremental subspace learning and local sparse representation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43(2), 627–636 (2018)
Dian-bing, Chen, Zhu, Ming, Wang, Hui-li: Visual tracking based on the sparse representation of the PCA subspace. Optoelectron. Lett. 13(5), 392–396 (2018)
Fan, H., Lin, L., Yang, F., Chu, P., Deng, G., Yu, S., Bai, H., Xu, Y., Liao, C. and Ling, H.: Lasot: a high-quality benchmark for large-scale single object tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5374–5383 (2019)
Danelljan, M., Shahbaz Khan, F., Felsberg, M. and Van de Weijer, J., Adaptive color attributes for real-time visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1090–1097 (2014)
Henriques, J.F., Caseiro, R., Martins, P. and Batista, J.: October. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 702–715, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2012)
Danelljan, M., Häger, G., Khan, F. and Felsberg, M.: Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking. In: British Machine Vision Conference, Nottingham, September 1–5, 2014. BMVA Press (2014)
Fan, H. and Ling, H.: Parallel tracking and verifying: a framework for real-time and high accuracy visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5486–5494 (2017)
Henriques, J.F., Caseiro, R., Martins, P., Batista, J.: High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(3), 583–596 (2014)
Choi, J., Jin Chang, H., Jeong, J., Demiris, Y. and Young Choi, J.: Visual tracking using attention-modulated disintegration and integration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4321–4330(2016)
Mueller, M., Smith, N. and Ghanem, B.: Context-aware correlation filter tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1396–1404 (2017)
Bertinetto, L., Valmadre, J., Golodetz, S., Miksik, O. and Torr, P.H.: Staple: complementary learners for real-time tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1401–1409 (2016)
Zhang, Dejun, Zhang, Zhao: Lu, Zou, Zhuyang Xie, He, Fazhi, Yiqi, Wu, Zhigang, Tu: part-based visual tracking with spatially regularized correlation filters. Vis. Comput. 36(3), 509–527 (2020)
Zhang, W., Du, Y., Chen, Z., et al.: Robust adaptive learning with Siamese network architecture for visual tracking. Vis. Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01839-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devi, R.B., Chanu, Y.J. & Singh, K.M. Discriminative object tracking with subspace representation. Vis Comput 37, 1207–1219 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01862-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01862-0