Abstract
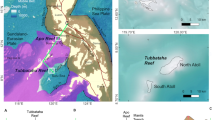
Multibeam swath bathymetric data collected in 95–120 m water depth on Australia’s North West Shelf revealed two distinct populations of sand waves: a laterally extensive, low-amplitude composite form comprising superimposed dunes and ripples, and a laterally restricted form which has unusually high bedform heights and slopes. These large subaqueous sand waves comprise bioclastic ooid/peloid sand. Significantly, evidence of seabed fluid flow was detected in association with the high-amplitude sand waves. This evidence includes seabed pockmarks approximately 2–15 m in diameter imaged with side-scan sonar, tubular and massive carbonate concretions dredged from the seabed, and potential active venting of a fluid plume from the seabed observed during an underwater camera tow. Molecular and isotopic analyses of carbonate concretions collected from within pockmarks associated with the high-amplitude sand waves indicate that the fluids from which they precipitated comprise modern seawater and are not related to thermogenic fluids or microbial gases. The fluid flow is interpreted to be driven by macrotidal currents flowing over the relatively steep slopes of the high-amplitude sand waves. Pockmarks and carbonate concretions then develop where the interstitial flows are confined and focused by subsurface ‘mounds’ in a shallow seismic reflector.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JRL (1980) Sand waves: a model of origin and internal structure. Sed Geol 26:281–328
Allen JRL (1982) Sedimentary structures; their character and physical basis. Developments in Sedimentology 30A. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Aloisi G, Bouloubassi I, Heijs SK, Pancost RD, Pierre C, Sinninghe Damsté JS, Gottschal JC, Forney LJ, Rouchy J-M (2002) CH4-consuming microorganisms and the formation of carbonate crusts at cold seeps. Earth Planet Sci Lett 203:195–203
Ashley GM, Boothroyd JC, Bridge JS, Clifton HE, Dalrymple RW, Elliot T, Flemming BW, Harms JC, Harris PT, Hunter RE, Kreisa RD, Lancaster N, Middleton GV, Payla C, Rubin DM, Smith JD, Southard JB, Terwindt JHT, Twichell DC Jr (1990) Classification of large-scale subaqueous bedforms: a new look at an old problem. J Sediment Petrol 60:160–172
Batchelor GK (1967) An introduction to fluid dynamics. Cambridge University Press, New York
Brunskill GJ, Burns KA, Opdyke B (2005) Biogeochemical processes, effects and signatures of hydrocarbon and ground-water seepage within a tropical, carbonate-rich system: Australia’s Timor Sea. http://www.marine.csiro.au/nationalfacility/voyagedocs/2005/index.htm
Bucher WH (1919) On ripples and related sedimentary surface forms and their palaeogeographical interpretations. Am J Sci 47(149–210):241–269
Burnett WC, Bokuniewicz H, Huettel M, Moore WS, Taniguchi M (2003) Groundwater and pore water inputs to the coastal zone. Biogeochemistry 66:3–33
Butterfield DA (2000) Deep ocean hydrothermal vents. In: Sigurdsson H (ed) Encyclopaedia of volcanoes. Academic, New York, pp 857–875
Campbell K (2006) Hydrocarbon seep and hydrothermal vent paleoenvironments and paleontology: past developments and future research directions. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 232:362–407
Chappell J, Shackleton NJ (1986) Oxygen isotopes and sea level. Nature 324:137–140
Díaz-del-Río V, Somoza L, Martínez-Frias J, Mata MP, Delgado A, Hernandez-Molina FJ, Lunar R, Martín-Rubí JA, Maestro A, Fernández-Puga MC, León R, Llave E, Medialdea T, Vázquez JT (2003) Vast fields of hydrocarbon-derived carbonate chimneys related to the accretionary wedge/olistostrome of the Gulf of Cádiz. Mar Geol 195:177–200
Dix GR, James NP, Kyser TK, Bone Y, Collins LB (2005) Genesis and dispersal of carbonate mud relative to late quaternary sea-level change along a distally-steepened carbonate ramp (Northwestern Shelf, Western Australia). J Sediment Res 75:665–678
Dugan B, Flemings PB (2000) The New Jersey margin: compaction and fluid flow. J Geochem Explor 69(70):477–481
Dugan B, Flemings PB (2002) Fluid flow and stability of the US Continental Slope offshore New Jersey from the Pleistocene to the present. Geofluids 2:137–146
Elvert M, Suess E, Greinert J, Whiticar MJ (2000) Archaea mediating anaerobic methane oxidation in deep-sea sediments at cold seeps of the eastern Aleutian subduction zone. Org Geochem 31:1175–1187
Fenster MS, Fitzgerald DM, Moore MS (2006) Assessing decadal-scale changes to a giant sand wave field in eastern Long Island Sound. Geology 34:89–92
Flemming BW (1988) Zur Klassifikation subaquatischer, strömungstransversaler Transportkörper. Bochumer Geol Geotechnol Arb 29:44–47
Fyfe WS (1994) The water inventory of the Earth: fluids and tectonics. In: Parnell J (ed) Geofluids: origin, migration and evolution of fluids in sedimentary basins. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 78:1–7
Harrington PK (1985) Formation of pockmarks by pore-water escape. Geo-Mar Lett 5:193–197. doi:10.1007/BF02281638
Harris PT, Ashley GM, Collins MB, James AE (1986) Topographic features of the Bristol Channel sea-bed: a comparison of SEASAT (synthetic aperture radar) and side-scan sonar images. Int J Remote Sens 7:119–136
Harvey JG (1966) Large sand waves in the Irish Sea. Mar Geol 4:49–55
Hovland M (1993) Submarine gas seepage in the North Sea and adjacent areas. In: Parker JR (ed) Petroleum geology of Northwest Europe. Proc 4th Conf, Geological Society, London, pp 1333–1338
Hovland M, Judd AG (1988) Seabed pockmarks and seepages. Graham and Trotman, London
Huettel M, Gust G (1992) Impact of bioroughness on interfacial solute exchange in permeable sediments. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 89:253–267
Huettel M, Ziebis W, Forster S (1996) Flow-induced uptake of particulate matter in permeable sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 41:309–322
Hulscher SJMH (1996) Tidal induced large-scale regular bed form patterns in a three-dimensional shallow water model. J Geophys Res 101(C9):20727–20744
Hulscher SJMH, Van den Brink GM (2001) Comparison between predicted and observed sand waves and sandbanks in the North Sea. J Geophys Res 106(C5):9327–9338
James NP, Bone Y, Kyser TK, Dix GR, Collins LB (2004) The importance of changing oceanography in controlling late Quaternary carbonate sedimentation on a high-energy, tropical, oceanic ramp: north-western Australia. Sedimentology 51:1179–1205
Jones HA (1973) Marine geology of the northwestern Australian continental shelf. BMR Bull 136
Jones AT, Logan GA, Kennard JM, Rollet N (2005a) Reassessing potential origins of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) slicks from the Timor Sea region of the North West Shelf on the basis of field and ancillary data. APPEA J 45:311–331
Jones AT, Logan GA, Kennard JM, O’Brien PE, Rollet N, Sexton M, Glenn KC (2005b) Testing natural hydrocarbon seepage detection tools on the Yampi Shelf, northwestern Australia, Geoscience Australia survey S267—post-survey report. Geoscience Australia Record 2005/15
Jones AT, Kennard JM, Ryan GJ, Bernadel G, Earl KL, Rollet N, Grosjean E, Logan GA (2007) Geoscience Australia marine survey SS06/2006 post-survey report: natural hydrocarbon seepage survey on the central North West Shelf. Geoscience Australia Record 2007/21
Judd AG, Hovland M (2007) Seabed fluid flow: The impact on geology, biology and the marine environment. Cambridge University Press, New York
Keene JB, Harris PT (1995) Submarine cementation in tide-generated bioclastic sand dunes: epicontinental seaway, Torres Strait, north-east Australia. Spec Publ Int Assoc Sediment 24:225–236
Land LA, Paull CK (2000) Submarine karst belt rimming the continental slope in the Straits of Florida. Geo-Mar Lett 20:123–132. doi:10.1007/s003670000041
Land LA, Paull CK, Hobson B (1995) Genesis of a submarine sinkhole without subaerial exposure: Straits of Florida. Geology 23:949–951
Martínez JI, De Deckker P, Barrows TT (1999) Palaeoceanography of the last glacial maximum in the eastern Indian Ocean: planktonic foraminiferal evidence. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 147:73–99
McCave IN (1971) Sand waves in the North Sea off the coast of Holland. Mar Geol 10:199–225
Moore CH (1989) Carbonate diagenesis and porosity. Developments in sedimentology 46. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Németh AA, Hulscher SJMH, de Vriend HJ (2002) Modelling sand wave migration in shallow shelf seas. Cont Shelf Res 22:2795–2806
Németh AA, Hulscher SJMH, van Damme RMJ (2004) Modelling sand wave migration and height, comparing model results with data. In: Hulscher S, Garlan T, Idier D (eds) Int Worksh marine sandwave and river dune dynamics II, 1–2 April 2004. University of Twente, The Netherlands, pp 232–239
Németh AA, Hulscher SJMH, van Damme RMJ (2007) Modelling offshore sand wave evolution. Cont Shelf Res 27:713–728
Pape T, Blumenberg M, Seifert R, Egorov VN, Gulin SB, Michaelis W (2005) Lipid geochemistry of methane-seep-related Black Sea carbonates. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 227:31–47
Paull C, Ussler W, Maher N, Greene HG, Rehder G, Lorenson T, Lee H (2002) Pockmarks of Big Sur, California. Mar Geol 181:323–335
Reitner J, Peckmann J, Blumenberg M, Michaelis W, Reimer A, Thiel V (2005) Concretionary methane-seep carbonates and associated microbial communities in Black Sea sediments: geobiology of ancient and modern methane-seeps. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 227:18–30
Rollet N, Logan GA, Kennard JM, O’Brien P, Jones AT, Sexton M (2006) Characterisation and correlation of active hydrocarbon seepage using geophysical data sets: an example from the tropical, carbonate Yampi Shelf, Northwest Australia. Mar Petrol Geol 23:145–164
Rollet N, Logan GA, Ryan G, Judd AG, Totterdell JM, Glenn K, Jones AT, Kroh F, Struckmeyer HIM, Kennard JM, Earl KL (2009) Shallow gas and fluid migration in the northern Arafura Sea (offshore Northern Australia). Mar Petrol Geol 26:129–147
Schlichting H (1987) Boundary layer theory, 7th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Scholle PA, Halley RB (1985) Burial diagenesis: out of sight, out of mind. In: Schneidermann N, Harris PM (eds) Carbonate cements. SEPM Spec Publ 36:309–334
Shinn EA (1969) Submarine lithification of Holocene carbonate sediments in the Persian Gulf. Sedimentology 12:109–144
Shum KT, Sundby B (1996) Organic matter processing in continental shelf sediments—the subtidal pump revisited. Mar Chem 53:81–87
Taniguchi M, Burnett WC, Cable JE, Turner JV (2002) Investigation of submarine groundwater discharge. Hydrol Process 16:2115–2129
Terwindt JHJ (1971) Sand waves in the Southern Bight of the North Sea. Mar Geol 10:51–67
Thiel V, Peckmann J, Richnow HH, Luth U, Reitner J, Michaelis W (2001) Molecular signals for anaerobic methane oxidation in Black Sea seep carbonates and a microbial mat. Mar Chem 73:97–112
Van Veen J (1935) Sand waves in the North Sea. Hydrogr Rev 12:21–29
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, A.T., Kennard, J.M., Logan, G.A. et al. Fluid expulsion features associated with sand waves on Australia’s central North West Shelf. Geo-Mar Lett 29, 233–248 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-009-0137-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-009-0137-7