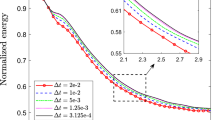
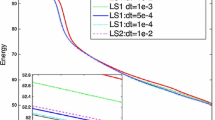
Abstract
In this study, we establish a phase-field two-phase surfactant system using two conservative Allen–Cahn type equations. Two nonlocal Lagrange multipliers are used to achieve the mass conservations. Comparing with the Cahn–Hilliard-type binary surfactant models which consist of two fourth-order nonlinear partial differential equations, the present model is easier because we solve two second-order nonlinear equations. In phase-field surfactant models, the existences of nonlinear terms lead to high challenges in energy estimation and numerical computation. To deal with these problems, we present first- and second-order time-accurate methods using a new time-dependent auxiliary variable approach. Due to the introduction of a new auxiliary variable, all nonlinear terms are explicitly solved. The energy dissipation law can be proved. To achieve linear and totally decoupled computation, we describe an efficient splitting algorithm. Various two- and three-dimensional computational tests are presented to show that our proposed schemes have desired accuracy, energy dissipation property, and work well for surfactant-laden coarsening.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
James AJ, Lowengrub J (2014) A surfactant-conserving volume-of-fluid method for interfacial flows with insoluble surfactant. J Comput Phys 201(2):685–772
Cleret de Langavant C, Guittet A, Theillard M, Temprano-Coleto F, Gibou F (2017) Level-set simulations of soluble surfactant deriven flows. J Comput Phys 348:271–297
Xu JJ, Shi W, Lai MC (2018) A level-set method for two-phase flows with soluble surfactant. J Comput Phys 353:336–355
Hu WF, Lai MC, Misbah C (2018) A coupled immersed boundary and immersed interface method for interfacial flows with soluble surfactant. Comput Fluids 168:201–215
Seol Y, Hsu SH, Lai MC (2018) An immersed boundary method for simulating interfacial flows with insoluble surfactant in three dimensions. Commun Comput Phys 23:640–664
Laradji M, Guo H, Grant M, Zuckermann MJ (1992) The effect of surfactants on the dynamics of phase separation. J Phys Condens Matter 32(4):6715
Guo Z, Yu F, Lin P, Wise S, Lowengrub J (2021) A diffuse domain method for two-phase flows with large density ratio in complex geometries. J Fluid Mech 907:A38
Rebholz L, Wise SM, Xiao M (2018) Penalty-projection schemes for the Cahn-Hilliard-Navier-Stokes diffuse interface model of two phase flow and their connection to divergence-free schemes. Int J Numer Anal Model 15:649–676
Yang J, Kim J (2020) An unconditionally stable second-order accurate method for systems of Cahn-Hilliard equations. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 87:105276
Liang H, Shi BC, Chai ZH (2016) Lattice Boltzmann modeling of three-phase incompressible flows. Phys Rev E 93:013308
Liang H, Xu J, Chen J, Chai Z, Shi B (2019) Lattice Boltzmann modeling of wall-bounded ternary fluid flows. Appl Math Model 73:487–513
Kim J (2006) Numerical simulations of phase separation dynamics in a water-oil-surfactant system. J Colloid Interf Sci 303:272–279
Gu S, Zhang H, Zhang Z (2014) An energy-stable finite-difference scheme for the binary fluid-surfactant system. J Comput Phys 270:416–431
Chen W, Wang C, Wang S, Wang X, Wise SM (2020) Energy stable numerical schemes for ternary Cahn-Hilliard system. J Sci Comput 84:27
Cheng K, Wang C, Wise SM (2020) A weakly nonlinear, energy stable scheme for the strongly anisotropic Cahn-Hilliard equation and its convergence analysis. J Comput Phys 405:109109
Shin J, Lee HG (2021) A linear, high-order, and unconditionally energy stable scheme for the epitaxial thin film growth model without slope selection. Appl Numer Math 163:30–42
Liu Z, Li X (2020) Efficient modified stabilized invariant energy quadratization approaches for phase-field crystal equation. Numer Algor 85:107–132
Liu Z, Li X (2019) Efficient modified techniques of invariant energy quadratization approach for gradient flows. Appl Math Lett 98:206–214
Liu Z, Li X (2020) The exonential scalr auxiliary variable (E-SAV) approach for phase field models and its explicit computing. SIAM J Sci Comput 42(3):B630–B655
Zhang C, Ouyang J, Wang C, Wise SM (2020) Numerical comparison of modified-energy stable SAV-type schemes and classical BDF methods on benchmark problems for the functionalized Cahn-Hilliard equation. J Comput Phys 423:109772
Li Q, Mei L (2021) Efficient, decoupled, and second-order unconditionally energy stable numerical schemes for the coupled Cahn-Hilliard system in copolymer/homopolymer mixtures. Comput Phys Commun 260:107290
Yang J, Kim J (2021) An improved scalar auxiliary variable (SAV) approach for the phase-field surfactant model. Appl Math Model 90:11–29
Qin Y, Xu Z, Zhang H, Zhang Z (2020) Fully decoupled, linear and unconditionally energy stable schemes for the binary fluid-surfactant model. Commun Comput Phys 28:1389–1414
Zhu G, Kou J, Yao J, Li A, Sun S (2020) A phase-field moving contact line model with soluble surfactants. J Comput Phys 405:109170
Aihara B, Takaki T, Takada D (2019) Multi-phase-field modeling using a conservative Allen-Cahn equation for multiphase flow. Comput Fluid 178:141–151
Begmohammadi A, Haghani-Hassan-Abadi R, Fakhari A, Bolster D (2020) Study of phase-field lattice Boltzmann models based on the conservative Allen-Cahn equation. Phys Rev E 102:023305
Weng Z, Zhuang Q (2017) Numerical approximation of the conservative Allen-Cahn equation by operator splitting method. Math Methods Appl Sci 40(12):4462–4480
Huang Z, Lin G, Ardekani AM (2020) Consistent and conservative scheme for incompressible two-phase flows using the conservative Allen-Cahn model. J Comput Phys 420:109718
Yang J, Jeong D, Kim J (2021) A fast and practical adaptive finite difference method for the conservative Allen-Cahn model in two-phase flow system. Int J Multiphase Flow 137:103561
Zheng L, Zheng S, Zhai Q (2020) Multiphase flows of \(N\) immiscible incompressible fluids: conservative Allen-Cahn equation and lattice Boltzmann equation method. Phys Rev E 101:013305
Yang J, Kim J (2021) A variant of stabilized-scalar auxiliary variable (S-SAV) approach for a modified phase-field surfactant model. Comput Phys Commun 261:107825
Liao HL, Tang T, Zhou T (2020) On energy stable, miximum-pribciple preserving, second-order BDF scheme with variable steps for the Allen-Cahn equation. SIAM J Numer Anal 58(4):2294–2314
Shen J, Xu J, Yang J (2018) The scalar auxiliary variable (SAV) approach for gradient flows. J Comput Phys 353:407–416
Cheng Q, Liu C, Shen J (2020) A new Lagrange multiplier approach for gradient flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 367:113070
Han S, Ye Q, Yang X (2021) Highly efficient and stable numerical algorithms for a two-component phase-field crystal model for binary alloys. J Comput Appl Math 390:113371
Yang X (2021) A novel fully-decoupled, second-order time-accurate, unconditionally energy stable scheme for a flow-coupled volume-conserved phase-field elastic bending energy model. J Comput Phys 432:110015
Yang X (2021) On a novel fully-decoupled, linear and second-order accurate numerical scheme for the Cahn-Hilliard-Darcy system of two-phase Hele-Shaw flow. Comput Phys Commun 263:107868
Shin J, Kim S, Lee D, Kim J (2013) A parallel multigrid method of the Cahn-Hilliard equation. Comput Mater Sci 71:89–96
Sun M, Feng X, Wang K (2020) Numerical simulation of binary fluid-surfactant phase field model coupled with geometric curvature on the curved surface. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 367:113123
Zhang M, Xiao X, Feng X (2020) Numerical simulations for the predator-prey model on surfaces with lumped mass method. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00929-4
Qiao Y, Qian L, Feng X (2021) Fast numerical approximation for the space-fractional semilinear parabolic equations on surfaces. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01357-z
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author (J.S. Kim) is supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education(NRF-2019R1A2C1003053). The authors wish to thank the reviewers for the constructive and helpful comments on the revision of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Kim, J. Efficient and structure-preserving time-dependent auxiliary variable method for a conservative Allen–Cahn type surfactant system. Engineering with Computers 38, 5231–5250 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01583-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01583-5