Abstract
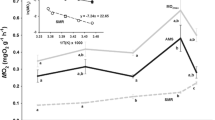
White muscle (WM) fibers in many fishes often increase in size from <50 μm in juveniles to >250 μm in adults. This leads to increases in intracellular diffusion distances that may impact the scaling with body mass of muscle metabolism. We have previously found similar negative scaling of aerobic capacity (mitochondrial volume density, V mt) and the rate of an aerobic process (post-contractile phosphocreatine recovery) in fish WM. In the present study, we examined the scaling with body mass of oxygen consumption rates of isolated mitochondria (VO2mt) from WM in three species from different families that vary in morphology and behavior: an active, pelagic species (bluefish, Pomatomus saltatrix), a relatively inactive demersal species (black sea bass, Centropristis striata), and a sedentary, benthic species (southern flounder, Paralichthys lethostigma). In contrast to our prior studies, the measurement of respiration in isolated mitochondria is not influenced by the diffusion of oxygen or metabolites. V mt was measured in WM and in high-density isolates used for VO2mt measurements. WM V mt was significantly higher in the bluefish than in the other two species and VO2mt was independent of body mass when expressed per milligram protein or per milliliter mitochondria. The size-independence of VO2mt indicates that differences in WM aerobic function result from variation in V mt and not to changes in VO2mt. This is consistent with our prior work that indicated that while diffusion constraints influence mitochondrial distribution, the negative scaling of aerobic processes like post-contractile PCr recovery can largely be attributed to the body size dependence of V mt.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- VO2max:
-
Maximal rate of oxygen consumption
- V mt :
-
Mitochondrial volume density
- VO2mt:
-
Rate of mitochondrial oxygen consumption
- RM:
-
Red muscle
- WM:
-
White muscle
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
References
Archer SD, Johnston IA (1991) Density of cristae and distribution of mitochondria in the slow muscle fibers of Antarctic fish. Physiol Zool 64:242–258
Battram JC, Johnston IA (1991) Muscle growth in the Antarctic teleost, Notothenia neglecta (nybelin). Antarct Sci 3:29–33
Bone Q (1966) On the function of two types of myotomal muscle fiber in elasmobranch fish. J Mar Biol Ass UK 46:321–349
Boyle KL, Dillaman RM, Kinsey ST (2003) Mitochondrial distribution and glycogen dynamics suggest diffusion constraints in muscle fibers of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. J Exp Zool 297A:1–16
Burke JS, Miller JM, Hoss DE (1991) Immigration and settlement pattern of Paralichthys dentatus and P. lethostigma in an estuarine nursery ground, North Carolina, USA. Neth J Sea Res 27:393–405
Curtin NA, Kushmerick MJ, Wiseman RW, Woledge RC (1997) Recovery after contraction of white muscle fibers from the dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula. J Exp Biol 200:1061–1071
Davies KJA, Packer L, Brooks GA (1981) Biochemical adaptation of mitochondria, muscle, and whole-animal respiration to endurance training. Arch Biochem Biophys 209:539–554
Dobson GP, Hochachka PW (1987) Role of glycolysis in adenylate depletion and repletion during work and recovery in teleost white muscle. J Exp Biol 129:125–140
Egginton S, Sktilbeck C, Hoofd L, Calvo J, Johnston IA (2002) Peripheral oxygen transport in skeletal muscle of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic notothenioid fish. J Exp Biol 205:769–779
Ellington WR (2001) Evolution and physiological roles of phosphagen systems. Annu Rev Physiol 63:289–325
Estabrook R (1967) Mitochondrial respiratory control and the polarographic measurement of ADP/O ratios. Methods Enzymol 10:41–47
Gill HS, Weatherley AH, Lee R, Legere D (1989) Histochemical characterization of myotomal muscle of five teleost species. J Fish Biol 34:375–386
Hardy KM, Locke BR, Da Silva MD, Kinsey ST (2006) A reaction–diffusion analysis of energetics in large muscle fibers secondarily evolved for aerobic locomotor function. J Exp Biol 209:3610–3620
Hardy KM, Dillaman RM, Lock BR, Kinsey ST (2009) A skeletal muscle model of extreme hypertrophic growth reveals the influence of diffusion on cellular design. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:R1855–R1867
Hardy KM, Lema SC, Kinsey ST (2010) The metabolic demands of swimming behavior influence the evolution of skeletal muscle fiber design in the brachyuran crab family Portunidae. Mar Biol 157(2):221–236
Hochachka PW (1994) Solving the common problem: matching ATP synthesis to ATP demand during exercise. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med 38A:41–56
Hochachka PW, Mossey MK (1998) Does muscle creatine phosphokinase have access to the total pool of phosphocreatine plus creatine? Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 274:R868–R872
Hochachka PW, Somero GN (1973) Strategies of biochemical adaptation. Saunders, Philadelphia
Hood PB, Godcharles MF, Barco RS (1994) Age, growth, reproduction and feeding ecology of black sea bass, Centropristis striata (Pisces: Serranidae), in the eastern Gulf of Mexico. Bull Mar Sci 54(1):24–37
Hoppeler H, Lindstedt SL (1985) Malleability of skeletal muscle in overcoming limitations: structural elements. J Exp Biol 115:355–364
Hoppeler H, Weibel ER (2000) Structural and functional limits for oxygen supply to muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 168:445–456
Hoppeler H, Kayar SR, Claassen H, Uhlmann E, Karas RH (1987) Adaptive variation in the mammalian respiratory system in relation to energetic demand: III. Skeletal muscles—setting the demand for oxygen. Respir Physiol 69:27–46
Howard CV, Reed MG (1998) Unbiased stereology: 3-dimesional measurements in microscopy. BIOS Scientific Publishers, Oxford
Jane BC, Lauder GV (1994) How fish use slow and fast muscle fibers: Implications for models of vertebrate muscle recruitment. J Comp Physiol 175A:123–131
Jimenez AG, Locke BR, Kinsey ST (2008) The influence of oxygen and high-energy phosphate diffusion on metabolic scaling in three species of tail-flipping crustaceans. J Exp Biol 211:3214–3225
Johnson LK, Dillaman RM, Gay DM, Blum JE, Kinsey ST (2004) Metabolic influences of fiber size in aerobic and anaerobic muscles of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. J Exp Biol 207:4045–4056
Johnston IA (1981) Structure and function of fish muscles. Symp Zool Soc Lond 48:71–113
Johnston IA (1987) Respiratory characteristics of muscle fibres in a fish (Chaenocephalus aceratus) that lacks haem pigments. J Exp Biol 133:415–428
Johnston IA, Guderley H, Franklin CE, Crockford T, Kamunde C (1994) Are mitochondria subject to evolutionary temperature adaptation? J Exp Biol 195:293–306
Johnston IA, Fernández DA, Calvo J, Vieira VLA, North AW, Abercromby M, Garland T (2003) Reduction in muscle fibre number during the adaptive radiation of notothenioid fishes: a phylogenetic perspective. J Exp Biol 206:2595–2609
Kinsey ST, Moerland TS (2002) Metabolite diffusion in giant muscle fibers of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. J Exp Biol 205:3377–3386
Kinsey ST, Pathi P, Hardy KA, Jordan A, Locke BR (2005) Does intracellular metabolite diffusion limit post-contractile recovery in burst locomotor muscle? J Exp Biol 208:2641–2652
Kinsey ST, Hardy KM, Locke BR (2007) The long and winding road: influences of intracellular metabolite diffusion on cellular organization and metabolism in skeletal muscle. J Exp Biol 210:3505–3512
Leary SC, Lyons CN, Rosenberger AG, Ballantyne JS, Stillman J, Moyes CD (2003) Fiber-type differences in muscle mitochondrial profiles. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 285:R817–R826
Locke BR, Kinsey ST (2008) Diffusional contraints on energy metabolism in skeletal muscle. J Theor Biol 254:417–429
Mainwood GW, Rakusan K (1982) A model for intracellular energy transport. Can J Physiol 60:98–102
Mathieu O, Krauer R, Hoppeler H, Gehr P, Lindstedt SL, Alexander RM, Taylor CR, Weibel ER (1981) Design of the mammalian respiratory system. VII. Scaling mitochondrial volume in skeletal muscle to body mass. Respir Physiol 44:113–128
Meyer RA, Sweeny HL, Kushmerick MJ (1984) A simple analysis of the ‘phosphocreatine shuttle’. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 246:C365–C377
Milligan CL, Wood CM (1986) Tissue intracellular acid–base status and the fate of lactate after exhaustive exercise in the rainbow trout. Metabolism 37:552–556
Mommsen TP (2001) Paradigms of growth in fish. Comp Biochem Physiol 129B:207–219
Moyes CD (2003) Controlling muscle mitochondrial content. J Exp Biol 206:4385–4391
Moyes CD, Hood DA (2003) Origins and consequences of mitochondrial variation in vertebrate muscle. Annu Rev Physiol 65:177–201
Moyes CD, Buck LT, Hochachka PW, Suarez RK (1989) Oxidative properties of carp red and white muscle. J Exp Biol 143:321–331
Moyes CD, Mathieu-Costello OA, Brill RW, Hochachka PW (1991) Mitochondrial metabolism of cardiac and skeletal muscle from a fast (Katsuwonis pelamis) and a slow (Cyprinus carpio) fish. Can J Zool 272:C1345–C1351
Moyes CD, Schulte PM, Hochachka PW (1992) Recovery metabolism in white fish muscle: the role of the mitochondria. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 262:295–304
Moyes CD, Battersby BJ, Leary SC (1998) Regulation of muscle mitochondrial design. J Exp Biol 201:299–307
Nyack AC, Locke BR, Valencia A, Dillaman RM, Kinsey ST (2007) Scaling of postcontractile phosphocreatine recovery in fish white muscle: effect of intracellular diffusion. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292:R2077–R2088
Olla BL, Katz HM, Studholme AL (1970) Prey capture and feeding motivation in the bluefish, Pomatomus Saltatrix. Copeia 1970:360–362
Rayner MD, Keenan MJ (1967) Role of red and white muscle in the swimming of the skipjack tuna. Nature 214:392–393
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate with high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212
Schmidt-Nielsen K (1984) Scaling: why is animal size so important?. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Schulte PM, Moyes CD, Hochachka PW (1992) Integrating metabolic pathways in post-exercise recovery of white muscle. J Exp Biol 166:181–195
Schwerzmann K, Cruz-Olive LM, Eggman R, Sanger A, Weibel ER (1986) Molecular architecture of the inner membrane of mitochondria from rat liver: a combined biochemical and stereological study. J Cell Biol 102:97–103
Schwerzmann K, Hoppeler H, Kayar SR, Weibel ER (1989) Oxidative capacity of muscle mitochondria: correlation of physiological, biochemical, and morphometric characteristics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:1583–1587
Spurr RA (1969) A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium of electron microscopy. J Ultra Res 26:31–34
Stienen GJM, Kiers JL, Bottinelli R, Reggiani C (1996) Myofibrillar ATPase activity in skinned human skeletal muscle fibres: fibre type and temperature dependence. J Physiol 493:299–307
Suarez RK (1996) Upper limits to mass-specific metabolic rates. Annu Rev Physiol 58:583–605
Suarez RK, Darveau CA, Childress JJ (2004) Metabolic scaling: a many-speldoured thing. Comp Biochem Physiol 139B:531–541
Taylor CR (1987) Structural and functional limits to oxidative metabolism: insights from scaling. Annu Rev Physiol 155:163–170
Taylor CR, Weibel ER (1981) Design of the mammalian respiratory system. I. Problem and strategy. Respir Physiol 44:1–10
Taylor CR, Weibel ER, Karas RH, Hoppeler H (1989) Matching structures and functions in the respiratory system: Allometric and adaptive variations in energy demand. In: Wood SC (ed) Comparative pulmonary physiology: current concepts. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 27–65
Weatherly AH, Gill HS (1985) Dynamics of increase in muscle fibers in teleosts in relation to size and growth. Experientia 41:353–354
Weibel ER (1987) Scaling of structural and functional variables in the respiratory system. Annu Rev Physiol 49:147–159
Weibel ER (2002) The pitfalls of power laws. Nature 417:131–132
Weibel ER, Bacigalupe LD, Schmitt B, Hoppeler H (2004) Allometric scaling of maximal aerobic rate in mammals: muscle aerobic capacity as determinant factor. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 140:115–132
Weis-Fough T (1964) Diffusion in insect wing muscle: the most active tissue known. J Exp Biol 41:229–256
West GB, Brown JH, Enquist BJ (1997) A general model for the origin of allometric scaling laws in biology. Science 276:122–126
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a National Science Foundation Grant to S.T.K. and R.M.D. (IOS-0719123) and a National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Grant to S.T.K. (R15-AR052708). We also thank Mark Gay for assistance with microscopy, Dr. Heather Koopman for constructive comments on the manuscript, and Dr. Christopher D. Moyes for helpful suggestions on experimental procedures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Heldmaier.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burpee, J.L., Bardsley, E.L., Dillaman, R.M. et al. Scaling with body mass of mitochondrial respiration from the white muscle of three phylogenetically, morphologically and behaviorally disparate teleost fishes. J Comp Physiol B 180, 967–977 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-010-0474-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-010-0474-x