Abstract
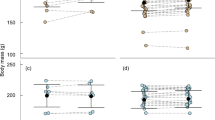
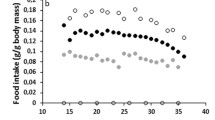
The arctic fox (Alopex lagopus) is a medium-sized predator of the high Arctic experiencing extreme seasonal fluctuations in food availability, photoperiod and temperature. In this study, the plasma leptin, ghrelin and growth hormone (GH) concentrations of male arctic foxes were determined during a food deprivation period of 13 days and the subsequent recovery in November and May. Leptin, ghrelin and GH were present in arctic fox plasma in amounts comparable to other carnivores. The plasma leptin concentrations did not react to food deprivation unlike in humans and rodents. However, the leptin levels increased during re-feeding as an indicator of increasing energy reserves. The relatively high ghrelin–leptin ratio, decrease in the plasma ghrelin concentration, an increase in the circulating GH concentrations and the observed negative correlation between plasma ghrelin and free fatty acid levels during fasting suggest that these hormones take part in the weight-regulation and energy metabolism of this species by increasing fat utilisation during food deprivation. The results strengthen the hypothesis that the actions of these weight-regulatory hormones are species–specific and depend on seasonality and the life history of the animals.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FFA :
-
free fatty acid
- GH :
-
growth hormone
- RMR :
-
resting metabolic rate
References
Ahima RS, Prabakaran D, Mantzoros C, Qu D, Lowell B, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS (1996) Role of leptin in the neuroendocrine response to fasting. Nature 382:250–252
Ahlstrøm Ø, Fuglei E, Mydland T (2003) Comparative nutrient digestibility of arctic foxes (Alopex lagopus) on Svalbard and farm-raised blue foxes (Alopex lagopus). Comp Biochem Physiol A 134:63–68
Arnould JPY, Morris MJ, Rawlins DR, Boyd IL (2002) Variation in plasma leptin level in response to fasting in Antarctic fur seal (Arctocephalus gazella). J Comp Physiol B 172:27–34
Boyer BB, Ormseth OA, Buck L, Nicolson M, Pelleymounter MA, Barnes BM (1997) Leptin prevents posthibernation weight gain but does not reduce energy expenditure in arctic ground squirrels. Comp Biochem Physiol C 118:405–412
Brück K (1983) Functions of the endocrine system. In: Schmidt RF, Thews G (ed) Human physiology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 658–687
Caro J, Sinha MK, Kolaczynski JW, Zhang PL, Considine RV (1996) Leptin: the tale of an obesity gene. Diabetes 45:1455–1462
Dubuc GR, Phinney SD, Stern JS, Havel PJ (1998) Changes of serum leptin and endocrine and metabolic parameters after 7 days of energy restriction in men and women. Metabolism 47:429–434
Eckert ED, Pomeroy C, Raymond N, Kohler PF, Thuras P, Bowers CY (1998) Leptin in anorexia nervosa. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:791–795
Frafjord K (1993) Food habits of arctic foxes (Alopex lagopus) on the western coast of Svalbard. Arctic 46:49–54
Fuglei E (2000) Physiological adaptations of the arctic fox to high Arctic conditions. Doctorate Scientific Dissertation, University of Oslo, Norway
Fuglei E, Øritsland NA (1999) Seasonal trends in body mass, food intake and resting metabolic rate, and induction of metabolic depression in arctic foxes (Alopex lagopus) at Svalbard. J Comp Physiol B 169:361–369
Fuglei E, Aanestad M, Berg JP (2000) Hormones and metabolites of arctic foxes (Alopex lagopus) in response to season, starvation and re-feeding. Comp Biochem Physiol A 126:287–294
Haga ØE (1993) A seasonal study of the energetics of arctic foxes (Alopex lagopus) from Svalbard (In Norwegian). Cand Scientific Thesis, University of Tromsø, Tromsø, Norway
Henttonen H, Fuglei E, Gower C, Haukisalmi V, Ims RA, Niemimaa J, Yoccoz NG (2001) Echinococcus multilocularis on Svalbard: introduction of an intermediate host has enabled the local life-cycle. Parasitology 123:547–552
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K (1999) Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402:656–660
Korhonen H, Alasuutari S (1995) Dominance relations in captive groups of adult and juvenile arctic blue foxes (Alopex lagopus). Polar Biol 15:353–358
Mustonen A-M, Nieminen P, Hyvärinen H (2001a) Preliminary evidence that pharmacologic melatonin treatment decreases rat ghrelin levels. Endocrine 16:43–46
Mustonen A-M, Nieminen P, Hyvärinen H (2001b) Effects of seasonality and fasting on the body mass and plasma growth hormone concentrations of the raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) and the blue fox (Alopex lagopus). Z Naturforsch C 56:437–443
Nieminen P, Asikainen J, Hyvärinen H (2001) Effects of seasonality and fasting on the plasma leptin and thyroxin levels of the raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) and the blue fox (Alopex lagopus). J Exp Zool 289:109–118
Nieminen P, Mustonen A-M, Asikainen J, Hyvärinen H (2002) Seasonal weight regulation of the raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides): interactions between melatonin, leptin, ghrelin, and growth hormone. J Biol Rhythms 17:155–163
Øritsland NA (1990) Starvation survival and body composition in mammals with particular reference to Homo sapiens. Bull Math Biol 51:643–655
Prestrud P (1982) Seasonal variations in basal metabolic rate and fat deposition of the arctic fox (Alopex lagopus) in Svalbard (In Norwegian). Cand real thesis, University of Oslo, Norway, pp 95
Prestrud P (1992) Food habits and observations of the hunting behaviour of arctic foxes, (Alopex lagopus), in Svalbard. Can Field-Nat 106:225–236
Prestrud P, Nilssen K (1992) Fat deposition and seasonal variation in body composition of arctic foxes in Svalbard. J Wildl Manage 56:221–233
Shintani M, Ogawa Y, Ebihara K, Aizawa-Abe M, Miyanaga F, Takaya K, Hosoda K, Hayashi T, Inoue G, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Nakao K (2001) Ghrelin is a novel orexigenic peptide that antagonizes leptin action through the activation of hypothalamic neuropeptideY/Y1 pathway. Diabetes 50:227–232
Steffensen EL (1982) The climate at Norwegian arctic stations. Klima 5:3-14
Tschöp M, Smiley DL, Heiman ML (2000) Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 407:908–913
Tschöp M, Weyer C, Tataranni PA, Devanarayan V, Ravussin E, Heiman ML (2001) Circulating ghrelin levels are decreased in human obesity. Diabetes 50:707–709
Underwood LS (1971) The bioenergetics of the arctic fox (Alopex lagopus L.). PhD Thesis, Pennsylvania State University
Widmaier EP, Long J, Cadigan B, Gurgel S, Kunz TH (1997) Leptin, corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), and neuropeptide Y (NPY) in free-ranging pregnant bats. Endocrine 7:145–150
Acknowledgements
We thank: the staff at the Research Station of the Norwegian Polar Institute in Ny-Ålesund for assistance with feeding the foxes; E. Johansen, K. Fossan, E. Molstad, N. M. Molstad (deceased), S. Onarheim and A. Grimnaes for assistance and help with the trapping of some of the foxes; E. Molstad and N. M. Molstad (deceased) for assistance with collecting the blood samples; the Governor of Svalbard and Kings Bay A/S for permitting capture of the foxes. The arctic foxes used in the present work were cared for in accordance with the principles and guidelines of the Norwegian Animal Welfare Act, with permission from the National Animal Research Authority. This project got financial support from an Arctic scholarship, Norwegian National Committee on Polar Research, in 1995, from the Faculty of Science of the University of Joensuu, from the Helve Foundation and from the National Technology Agency of Finland in 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Heldmaier
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuglei, E., Mustonen, AM. & Nieminen, P. Effects of season, food deprivation and re-feeding on leptin, ghrelin and growth hormone in arctic foxes (Alopex lagopus) on Svalbard, Norway. J Comp Physiol B 174, 157–162 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-003-0400-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-003-0400-6