Abstract.
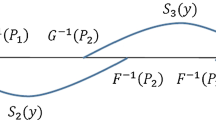
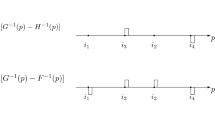
As is well known, the use of the Gini coefficient in comparisons is inconsistent with an utilitarian approach. This paper analyzes the Gini coefficient's normative significance in welfare comparisons evaluating income distributions according to Yaari dual social welfare function. When generalized Lorenz curves cross once, the Gini coefficient is decisive in determining welfare rankings if we strengthen the Principle of Transfers applying a Positional version of the Principle of Transfer Sensitivity. This result can also be extended to the case of multiple crossings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 August 1996 / Accepted: 22 October 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zoli, C. Intersecting generalized Lorenz curves and the Gini index. Soc Choice Welfare 16, 183–196 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003550050139
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003550050139