Abstract
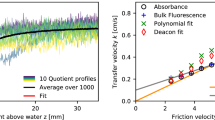
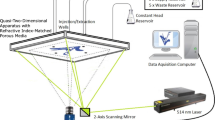
A laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) technique is described to measure vertical concentration profiles of gases in the aqueous mass boundary layer at a free water surface. The technique uses an acid-base reaction of the fluorescence indicator fluorescein at the water surface to visualize the concentration profiles. The technique is capable of measuring two-dimensional vertical concentration profiles at a rate of 200 frames/s and a spatial resolution of 16 μm. The mass boundary layer at a free surface is characterized by significant fluctuations. Direct surface renewal is observed. The mean profiles also support rather surface renewal models than turbulent diffusion models.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 21 May 1997/Accepted: 18 December 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Münsterer, T., Jähne, B. LIF measurements of concentration profiles in the aqueous mass boundary layer. Experiments in Fluids 25, 190–196 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480050223
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480050223