Abstract
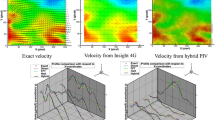
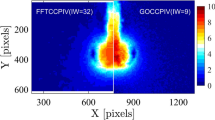
This paper presents direct comparisons between the physics-based optical flow and well-established cross-correlation methods for extraction of velocity fields from particle images. The accuracy and limitations of the optical flow method applied to particle image velocimetry are critically evaluated. After a brief review of the optical flow method, we discuss in detail the error estimates, relevant parameters to the accuracy of optical flow computation, and mathematical connection between the optical flow and the particle velocity. Quantitative evaluations of both the optical flow and correlation methods are made through simulations and physical flow measurements.



































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian RJ (1991) Particle-imaging techniques for experimental fluid mechanics. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 23:261–304
Adrian RJ, Westerweed J (2011) Particle image velocimetry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Aubert G, Kornprobst P (1999) A mathematical study of the relaxed optical flow problem in the space BV(Ω). SIAM J Math Anal 30:1282–1308
Aubert G, Deriche R, Kornprobst P (1999) Computing optical flow via variational techniques. SIAM J Appl Math 60:156–182
Baker S, Mathews I (2004) Lucas-Kanade 20 years on: a unifying framework. Int J Comput Vis 56:221–255
Barron JL, Fleet DJ, Beauchemin SS (1994) Performance of optical flow techniques. Int J of Comput Vis 12:43–77
Cassisa C, Simoens S, Prinet V, Shao L (2011) Subgrid scale formulation of optical flow for the study of turbulent flow. Exp Fluids 51(6):1739–1754
Chen X, Zille P, Shao L, Corpetti T (2015) Optical flow for incompressible turbulence motion estimation. Exp Fluids 56(8):1–14
Corpetti T, Memin E, Perez P (2002) Dense estimation of fluid flows. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24:365–380
Corpetti T, Heitz D, Arroyo G, Memin E (2006) Fluid experimental flow estimation based on an optical flow scheme. Exp Fluids 40:80–97
Dracos T, Gruen A (1998) Videogrammetric methods in velocimetry. Appl Mech Rev 51:387–413
Haussecker H, Fleet DJ (2001) Computing optical flow with physical models of brightness variation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23:661–673
Héas P, Memin E, Papadakis N, Szantai A (2007) Layered estimation of atmospheric mesoscale dynamics from satellite imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 45:4087–4104
Heitz D, Héas P, Mémin E, Carlier J (2008) Dynamic consistent correlation-variational approach for robust optical flow estimation. Exp Fluids 45:595–608
Heitz D, Memin E, Schnorr C (2010) Variational fluid flow measurements from image sequences: synopsis and perspectives. Exp Fluids 48:369–393
Hildebrand FB (1974) Introduction to numerical analysis, 2nd edn. Dover, New York
Horn BK, Schunck BG (1981) Determining optical flow. Artif Intell 17:185–204
Liu T, Shen L (2008) Fluid flow and optical flow. J Fluid Mech 614:253–291
Liu T, Sullivan J (1996) Heat transfer and flow structures in an excited circular impinging jet. Int J Heat Mass Trans 39:3695–3706
Liu T, Nink J, Merati P, Tian T, Li Y, Shieh T (2010) Deposition of micron liquid droplets on wall in impinging turbulent air jet. Exp Fluids 48:1037–1057
Liu T, Wang B, Choi D (2012) Flow structures of Jupiter’s great red spot extracted by using optical flow method. Phys Fluids 24:096601–096613
Maas HG, Gruen A, Papantoniou D (1993) Particle tracking velocimetry in three-dimensional flows. Exp Fluids 15:133–146
Quenot GM, Pakleza J, Kowalewski TA (1998) Particle image velocimetry with optical flow. Exp Fluids 25:177–189
Raffel M, Willert C, Wereley S, Kompenhans J (2007) Particle image velocimetry. Springer, Berlin
Ruhnau P, Kohlberger T, Schnorr C, Nobach H (2005) Variational optical flow estimation for particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 38:21–32
Stanislas M, Okamoto K, Kähler C (2003) Main results of the first international PIV challenge. Meas Sci Technol 14:R63–R89
Stanislas M, Okamoto K, Kähler C, Westerweel J (2005) Main results of the second international PIV challenge. Exp Fluids 39:170–191
Stanislas M, Okamoto K, Kähler C, Westerweel J, Scarano F (2008) Main results of the third international PIV challenge. Exp Fluids 45:27–71
Tikhonov AN, Arsenin VY (1977) Solutions of ill-posed problems, chapter II. Wiley, New York
Timmins BH, Wilson BW, Smith BL, Vlachos PP (2012) A method for automatic estimation of instantaneous local uncertainty in particle image velocimetry measurements. Exp Fluids 53:1133–1147
Wang B, Cai Z, Shen L, Liu T (2015) An analysis of physics-based optical flow method. J Comput Appl Math 276:62–80
Wildes RP, Amabile MJ, Lanzillotto A-M, Leu T-S (2000) Recovering estimates of fluid flow from image sequence data. Comput Vis Image Underst 80:246–266
Yuan J, Schnorr C, Memin E (2007) Discrete orthogonal decomposition and variational fluid flow estimation. J Math Imaging Vis 28:67–80
Zille P, Corpetti T, Shao L, Xu C (2014) Observation models based on scale interactions for optical flow estimation. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(8):3281–3293
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank R. Prevost (LaVision) and Z. Yang (Wright State University) for their comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Merat, A., Makhmalbaf, M.H.M. et al. Comparison between optical flow and cross-correlation methods for extraction of velocity fields from particle images. Exp Fluids 56, 166 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-015-2036-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-015-2036-1