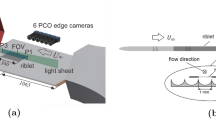
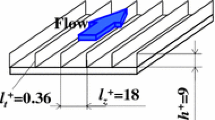
Abstract
A surface grooved with microscopic riblets aligned parallel to the flow is an effective means to reduce the turbulent skin friction up to 10% compared to a smooth surface. The maximum drag reduction is found for a dimensionless rib spacing s + in the range of 15–17. For s + < 10, a linear behaviour of the drag reduction curve is predicted by viscous theory. This linear slope of the drag reduction curve is in contradiction to Schlichting’s postulation of a hydraulically smooth behaviour of small-scale roughness in a turbulent flow. This regime of evanescent dimensionless rib spacings is investigated experimentally by direct wall shear stress measurements in a fully developed channel flow. Additionally, a numerical calculation of the viscous flow over riblets was carried out to predict the drag reducing behaviour. The experimental results show a linear drag reducing behaviour down to s + = 0.3, which is in good agreement with the numerical results of the viscous simulation. The postulation of Schlichting’s hydraulically smooth regime of a rough surface was not confirmed, neither for a riblet surface nor for a surface geometry with grooves oriented perpendicular to the flow. In the latter case, the drag increases as a quadratic function of the roughness height.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron A, Quadrio M, Vigevano L (1993) On the boundary layer/riblets interaction mechanisms and the prediction of turbulent drag reduction. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 14(4)
Bechert DW, Bartenwerfer M (1989) The viscous flow on surfaces with longitudinal ribs. J Fluid Mech 209:105–129
Bechert DW, Hoppe G, van der Hoeven JGTh, Makris R (1992) The Berlin oil channel for drag reduction research. Exp Fluids 12:251–260
Bechert DW, Bruse M, Hage W, van der Hoeven JGTh, Hoppe G (1997) Experiments on drag-reducing surfaces and their optimization with an adjustable geometry. J Fluid Mech 338:59–87
Bechert DW, Bruse M, Hage W (2000) Experiments with three-dimensional riblets as an idealized model of shark skin. Exp Fluids 28:403–412
Blasius H (1913) Das Ähnlichkeitsgesetz bei Reibungsvorgängen in Flüssigkeiten, Forsch.-Arb. Ing.-Wes. Heft 131
Bradshaw P (2000) A note on “critical roughness height” and “transitional roughness”. Phys Fluids 12(6):1611–1614
Choi H, Moin P, Kim J (1993) Direct numerical simulation of turbulent flow over riblets. J Fluid Mech 255:503–539
COMSOL Multiphysics 3.2 (2010) COMSOL Multiphysics GmbH, Berliner Str. 4, D-37073 Göttingen, Germany
Frohnapfel B, Lammers P, Jovanović J, Durst F (2007) Interpretation of the mechanism associated with turbulent drag reduction in terms of anisotropy invariants. J Fluid Mech 577:457–499
García-Mayoral R, Jiménez J (2009) Breakdown of the viscous regime and maximum drag reduction in riblet surfaces. In: Proceedings of the CEAS/KATnet II conference, 12–14 May 2009, Bremen
Goldstein D, Handler R, Sirovich L (1995) Direct numerical simulation of turbulent flow over a modelled riblet covered surface. J Fluid Mech 302:333–376
Jiménez J (2004) Turbulent flows over rough walls. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 36:173–196
Koury E, Virk PS (1995) Drag reduction by polymer solutions in a riblet-lined pipe. Appl Sci Res 54:323–347
Luchini P, Manzo F, Pozzi A (1991) Resistance of a grooved surface to parallel flow and crossflow. J Fluid Mech 228:87–109
Nikuradse J (1932) Gesetzmäßigkeiten der turbulenten Strömung in glatten Rohren, Forschungsheft 356, Beilage zu Forschung auf dem Gebiete des Ingenieurwesens, Ausgabe B Band 3, VDI-Verlag, Berlin
Nikuradse J (1933) Strömungsgesetze in rauhen Rohren, Forschungsheft 361, Beilage zu Forschung auf dem Gebiete des Ingenieurwesens, Ausgabe B Band 4, VDI-Verlag, Berlin
Rapp H, Zorić I, Kasemo B (2006) Microstructured surfaces for drag reduction purposes: experiments and simulation on rectangular 2D riblets. Mater Res Soc Symp Proc, vol. 899E
Rohr J, Anderson GW, Reidy LW (1989) An experimental investigation of the drag reducing effects of riblet in pipes. In: Sellin, Moses (eds) Drag reduction in fluid flows, techniques for friction control. Ellis Horwood, West Sussex, pp 263–270
Schlichting H (1979) Boundary layer theory (trans. J. Kestin), 7th edn. McGraw-Hill, pp 616 ff
Stenzel V (2009) Private communication. Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Applied Materials Research, Bremen
Stenzel V, Hage W (2009) Strömungsgünstige Beschichtung für die Senkung des Treibstoffverbrauchs. In: Nanomaterialien in der Oberflächentechnik—Chancen und Grenzen—Teil 2, Proc. 31. Ulmer Gespräch, Fachzeitschrift Galvanotechnik Heft 07/2009, Eugen G. Leuze Verlag, Bad Saulgau, Germany
Suzuki Y, Kasagi N (1994) Turbulent drag reduction mechanism above a riblet surface. AIAA J 32(9)
Walsh MJ (1982) Turbulent boundary layer drag reduction using riblets. AIAA paper 82–0169
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft within the priority program SPP 1207 “Bio-inspired fluid mechanics” and partly by the Volkswagen Foundation within the funding program “Innovative methods for the manufacturing of multifunctional surfaces” and is gratefully acknowledged. We would like to thank Professor P. S. Virk for the encouragement to consider riblet behaviour outside their useful design parameters. This conversation was of invaluable assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grüneberger, R., Hage, W. Drag characteristics of longitudinal and transverse riblets at low dimensionless spacings. Exp Fluids 50, 363–373 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-010-0936-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-010-0936-7