Abstract
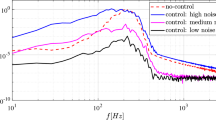
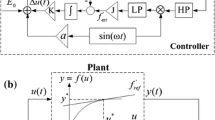
Experiments were conducted using plasma actuators to control broadband noise generated by a bluff body flow. The motivation behind the study was to explore the potential of plasma actuators to reduce landing gear noise during approach phase of an aircraft. The control effectiveness of both dielectric barrier discharge and sliding discharge plasma actuators were tested in laboratory environment, using a representative bluff body consisting of a circular cylinder and an oblique strut. Noise measurements were taken in an anechoic chamber using a phased microphone array and far-field microphones. Results showed that the upstream directed plasma forcing, located at ±90 deg on the upstream cylinder with respect to the approaching flow, could effectively attenuate the broadband noise radiated from the wake flow interaction with the downstream strut. With the same AC electrical power consumption, the sliding discharge with additional DC voltage was found to be more effective due to its elongated plasma distribution and higher induced flow momentum. Measurements using particle image velocimetry suggested that the flow speed impinging on the downstream strut was reduced by the upstream plasma forcing, contributing to the reduced noise.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D :
-
Cylinder diameter
- L :
-
Cylinder length
- Re D :
-
Reynolds number based on cylinder diameter D
- x, y, z :
-
Cartesian coordinates
- U ∞ :
-
Free stream speed
- U :
-
Streamwise (x) velocity
- V :
-
Normal (y) velocity
- DBD:
-
Dielectric barrier discharge
- SD:
-
Sliding discharge
- V p–p :
-
Peak to peak high AC voltage
- f :
-
Frequency
- PIV:
-
Particle imaging velocimetry
- SPL:
-
Sound pressure level
References
Benard N, Jolibois J, Forte M, Touchard G, Moreau E (2007) Control of an axisymmetric subsonic air jet by plasma actuator. Exp Fluids 43:603–616
Benard N, Braud P, Jolibois J, Moreau E (2008) Airflow reattachement along a NACA0015 airfoil by a surface dielectric barrier discharge actuator: time-resolved particle image velocimetry investigation. AIAA-2008-4202
Boorsma K, Zhang X, Molin N, Chow LC (2009) Bluff body noise control using perforated fairings. AIAA J 47(1):33–43
Chan S, Zhang X, Gabriel S (2007) The attenuation of cavity tones using plasma actuators. AIAA J 45(7):1525–1538
Corke TC, He C, Patel MP (2004) Plasma flaps and slats: an application of weakly-ionized plasma actuators. AIAA-2004-2127
Corke TC, Mertz B, Patel MP (2006) Plasma flow control optimized airfoil. AIAA-2006-1208
Crighton DG (1991) Aeroacoustics of flight vehicles: theory and practice. NASA RP 1258, chapter: airframe noise 1: 391–447
Dai X, Roth JR (2005) Optimization of a single plasma actuator using the one atmosphere uniform glow discharge plasma. IEEE international conference on plasma science, no. 10525
Dobrzynski W, Chow LC, Guion P, Schiells D (2002) Research into landing gear airframe noise reduction. AIAA-2002-2409
Dougherty RP (2002) Beamforming in acoustic testing. In: Mueller TJ (ed) Aeroacoustic measurements. Springer, Berlin
Gad-el HM (2000) Flow control: passive active and reactive flow management. Cambridge University Press, UK
Huang X, Zhang X (2008) Streamwise and spanwise plasma actuators for flow-induced cavity noise control. Phys Fluids 20(3):037101-1-037101-10
Huang X, Chan S, Zhang X (2008) Variable structure model for flow-induced tonal noise control with plasma actuators. AIAA J 46(1):241–250
Jolibois J, Forte M, Moreau E (2008) Application of an AC barrier discharge actuator to control airflow separation above a NACA0015 airfoil: optimization of the actuation location along the chord. J Electrostat 66:496–503
Li Y, Smith MG, Zhang X, Molin N (2007) Noise sources control of an aircraft landing gear, AIAA-2007-3465
Louste C, Artana G, Moreau E, Touchard G (2005) Sliding discharge in air at atmospheric pressure: electrical behaviour. J Electrostat 63:615–620
Macaraeg MG (1998) Fundamental investigations of airframe noise. AIAA-98-2224
Molin N, Piet JF, Chow LC, Smith M, Dobrzynski W, Seror C (2006) Prediction of low noise aircraft landing gears and comparisons with test results. AIAA-2006-2623
Moreau E (2007) Airflow control by non-thermal plasma actuators. J Phys D Appl Phys 40:605–636
Moreau E, Leger L, Touchard G (2006) Effect of a DC surface-corona discharge on a flat plate boundary layer for air flow velocity up to 25 m/s. J Electrostat 64:215–225
Moreau E, Louste C, Touchard G (2008) Electric wind induced by sliding discharge in air at atmospheric pressure. J Electrostat 66:107–114
Piet JF, Davy R, Elias G, Siller H, Chow LC, Seror C, Laporte F (2005) Flight test investigation of add-on treatments to reduce aircraft airframe noise. AIAA-2005-3007
Post ML, Corke TC (2003) Separation control on high angle of attack airfoil using plasma actuators. AIAA-2003-1024
Post ML, Corke TC (2004) Separation control using plasma actuators-dynamic stall control on an oscillating airfoil. AIAA-2004-2517
Post ML, Corke TC (2005) Overview of plasma glow control: concepts, optimization and applications. AIAA-2005-0563
Raman G, McLaughlin DK (2000) Recent aeroacoustics research in the United States. Noise Vib Worldw 31(10):15–20
Roth JR (1998) Electrohydrodynamically induced airflow in a one atmosphere uniform glow discharge surface plasma. IEEE international conference on plasma science, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, NJ
Roth JR, Sherman DM, Wilkinson SP (1998) Boundary layer flow control with a one atmosphere uniform glow discharge surface plasma. AIAA-98-0328
Roth JR, Sherman DM, Wilkinson SP (2000) Electro-hydrodynamic flow control with a glow-discharge surface plasma. AIAA J 38(7):1166–1172
Thomas FO, Kozlov A, Corke TC (2008) Plasma actuators for cylinder flow control and noise reduction. AIAA J 46(8):1921–1931
Tsikrikas GN, Serafetinides AA (1996) The effect of voltage pulse polarity on the performance of a sliding discharge pumped HF laser. J Phys D 29:2806–2810
Acknowledgments
The experiments were made possible through the support provided by Airbus Technology Programme CADWIE project monitored by Dr. L. C. Chow, which is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhang, X. & Huang, X. The use of plasma actuators for bluff body broadband noise control. Exp Fluids 49, 367–377 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-009-0806-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-009-0806-3