Abstract
Introduction
Since the construction of the first laser, many companies around the world have contributed to the development of new lasers technologies. To be user-friendly, some companies have developed a pre-setting mode in their laser devices. We aimed to review and compare all laser companies’ pre-settings (PS) already established in the market.
Materials and methods
An online search of holmium:YAG (Ho:YAG) and thulium fiber laser (TFL) devices was carried out. Manual and PS mode, pulse width and pulse modulation technology data were collected. The PS parameters were collected directly from the brochure devices or by asking the companies consulting agents.
Results
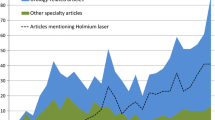
Thirty-nine laser devices were analyzed (33 Ho:YAG and 6 TFL). The power range varies from 15 to 152 W and 35 W to 60 W for Ho:YAG and TFL, respectively. PS are present in 66% of Ho:YAG lasers and the 33% of TFL. Long-pulse modes can be modified in 12 Ho:YAG and 1 TFL lasers. The median (IQR) PS for dusting stones with Ho:YAG laser is 0.4 J (0.2–1), 21.5 Hz (5–120), and 10 W (1.5–28) for energy, frequency and power, respectively; for Ho:YAG fragmentation is 0.8 J (0.3–5), 10 (3–15) Hz and 5 (1.5–50) W for energy, frequency, and power, respectively; and for popcorn is 0.8 J (0.4–1.2), 10 Hz (6–15) and 5 W (4–18) for energy, frequency, and power, respectively. Dusting and fragmentation mode of Rocamed MH01 and EMS LaserClast 35 are programmed according to the stone type. Most of these settings do not depend on the size of the fiber being used nor the location and type of stone. For TFL, the pre-sets are divided in bladder stone, dusting, fine dusting, fragmentation, and ureteral stone.
Conclusion
There is a huge variability regarding pre-sets offered by companies because there is no consensus. Pre-sets should provide a range to work efficacy and safety.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maiman TH (1960) Stimulated optical radiation in ruby. Nature 187(4736):493–494
U.S. (2010) Corporate news: news from candela corporation. Laser Med Surg News Adv 6(5):24–25. https://doi.org/10.1089/lms.1988.6.5.24
Kronenberg P, Traxer O (2015) Update on lasers in urology 2014: current assessment on holmium:yttrium–aluminum–garnet (Ho:YAG) laser lithotripter settings and laser fibers. World J Urol 33(4):463–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1395-1 (Epub 2014 Sep 4 PMID: 25185524)
Johnson DE, Cromeens DM, Price RE (1992) Use of the holmium:YAG laser in urology. Lasers Surg Med 12(4):353–363. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.1900120402 (PMID: 1386643)
Kronenberg P, Somani B (2018) Advances in lasers for the treatment of stones-a systematic review. Curr Urol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-018-0807-y
Leveillee RJ, Lobik L (2003) Intracorporeal lithotripsy: which modality is best? Curr Opin Urol 13(3):249–253
Bader MJ, Gratzke C, Hecht V et al (2011) Impact of collateral damage to endourologic tools during laser lithotripsy—in vitro comparison of three different clinical laser systems. J Endourol 25(4):667–672
Floratos DL, La de Rosette JJ (1999) Lasers in urology. BJU Int 84(2):204–211
Blackmon RL, Irby PB, Fried NM (2010) Holmium:YAG (lambda = 2,120 nm) versus thulium fiber (lambda = 1908 nm) laser lithotripsy. Lasers Surg Med 42(3):232–236
Corrales M, Traxer O (2021) Initial clinical experience with the new thulium fiber laser: first 50 cases. World J Urol 39(10):3945–3950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-021-03616-6 (Epub 2021 Feb 15 PMID: 33590280)
Traxer O, Keller EX (2020) Thulium fiber laser: the new player for kidney stone treatment? A comparison with Holmium:YAG laser. World J Urol 38(8):1883–1894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-02654-5 (Epub 2019 Feb 6. PMID: 30729311; PMCID: PMC7363731)
Schembri M, Sahu J, Aboumarzouk O, Pietropaolo A, Somani BK (2020) Thulium fiber laser: The new kid on the block. Turk J Urol. 46(Supp. 1):S1–S10. https://doi.org/10.5152/tud.2020.20093 (Epub 2020 May 27. PMID: 32479257; PMCID: PMC7731960)
Kuo RL, Aslan P, Zhong P et al (1998) Impact of holmium laser settings and fiber diameter on stone fragmentation and endoscope deflection. J Endourol 12(6):523–527
Spore SS, Teichman JM, Corbin NS et al (1999) Holmium: YAG lithotripsy: optimal power settings. J Endourol 13(8):559–566
Sea J, Jonat LM, Chew BH et al (2012) Optimal power settings for holmium:YAG lithotripsy. J Urol 187(3):914–919
Ventimiglia E, Pauchard F, Quadrini F, Sindhubodee S, Kamkoum H, Jiménez Godínez A, Doizi S, Traxer O (2021) High- and low-power laser lithotripsy achieves similar results: a systematic review and meta-analysis of available clinical series. J Endourol 35(8):1146–1152. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2020.0090 (Epub 2021 May 24 PMID: 33677987)
Kronenberg P, Traxer O (2019) The laser of the future: reality and expectations about the new thulium fiber laser-a systematic review. Transl Androl Urol 8(Suppl 4):S398–S417. https://doi.org/10.21037/tau.2019.08.01.PMID:31656746;PMCID:PMC6790412
Cook® Medical. Rhapsody® H-30® Holmium Laser System: user manual. [Internet] Available from: https://www.cookmedical.eu/data/IFU_PDF/T_CD_H-30EU_REV0.PDF
Lumenis®. MosesTM Pulse 120H [Internet]. Available from: https://lumenis.com/medical/holmium-products/lumenis-moses-pulse-120h/
Olympus [Internet]. Products: Lithotripsy Systems. Olympus EMPOWER H35, H65 and H100. Available from: https://www.olympus-europa.com/medical/en/Products-and-Solutions/Products/Product/OLYMPUS-EMPOWER-H35-H65-and-H100.html
Quanta System. Products: Surgical lasers (CyberHo Family, Litho EVO and Litho) [Internet]. Available from: https://www.quantasystem.com/products/surgery/
Karl Storz. Calculase® III – The End of the Stone Age [Internet]. Available from: https://www.karlstorz.com/cps/rde/xbcr/karlstorz_assets/ASSETS/3610463.pdf
Boston Scientific. Auriga™ XL 4007 Laser System: User’s Manual [Internet]. Available from: https://base.euro-pharmat.com/PDF/14795-42894.pdf dorn
Dornier MedTech. Dornier Medilas® H Solvo® 35 [Internet] Available from: https://www.dornier.com/europe/dornier-medilas-h-solvo-35/
Richard Wolf. MegaPulse 70+. Available from: https://www.richard-wolf.com/fileadmin/user_upload/UEbergang_2021/D711en281021_MegaPulse70plus.pdf
L.I.S. Sphinx jr. Laser Holmium [Internet]. Available from: http://new.laserinsurgery.fr/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/Brochure-Sphinx-jr-10.11-Français.pdf
L.I.S. Sphinx® Holmium Laser [Internet]. Available from: http://new.laserinsurgery.fr/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/Brochures-Sphinx-07-2013.pdf
EMS Urology. Swiss Laserclast [Internet]. Available from: https://www.ems-urology.com/products/swiss-laserclast
Olympus [Internet]. SOLTIVE Premium – SuperPulsed Laser System [Internet] Available from: https://www.olympus-europa.com/medical/en/Products-and-Solutions/Products/Product/SOLTIVE-Premium.html
Matlaga BR, Chew B, Eisner B, Humphreys M, Knudsen B, Krambeck A et al (2017) Ureteroscopic laser lithotripsy: a review of dusting vs fragmentation with extraction. J Endourol. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2017.0641
Aldoukhi AH, Hall TL, Ghani KR, Maxwell AD, MacConaghy B, Roberts WW (2018) Caliceal fluid temperature during high-power holmium laser lithotripsy in an in vivo porcine model. J Endourol 32(8):724–729. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2018.0395 (Epub 2018 Jul 13. PMID: 29905092; PMCID: PMC6096348)
Okhunov Z, Jiang P, Afyouni AS, Ayad M, Arada RB, Brevik A, Akopian G, Patel RM, Landman J, Clayman RV (2021) Caveat emptor: the heat is “ON”: an in vivo evaluation of the thulium fiber laser and temperature changes in the porcine kidney during dusting and fragmentation modes. J Endourol. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2021.0206 (Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33906433)
Dragos LB, Somani B, Keller E et al (2019) 386: Super-pulse thulium fiber versus high power holmium laser: what about temperature? Eur Suppl 18:e505–e508
Chan et al (2001) A perspective on laser lithotripsy: the fragmentation processes. J Endourol 15(3):257–273. https://doi.org/10.1089/089277901750161737
Traxer O, Corrales M (2021) Managing urolithiasis with thulium fiber laser: updated real-life results-a systematic review. J Clin Med 10(15):3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153390.PMID:34362169;PMCID:PMC8347545
Keller EX, De Coninck V, Doizi S et al (2021) Thulium fiber laser: ready to dust all urinary stone composition types? World J Urol 39:1693–1698
Rocamed. Products catalogue: MH01 30W Holmium YAG laser (2020) [Internet]. Available from: https://www.rocamed.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/ 02/MKG- CT -EN- 2020.0. pdf
Sampogna G, Basic D, Geavlete P, Galán Llopis JA, Reis Santos J, Saltirov I, Sarica K, Stavridis S, Skolarikos A, Trinchieri A (2021) Endoscopic identification of urinary stone composition: A study of South Eastern Group for Urolithiasis Research (SEGUR 2). Actas Urol Esp (Engl Ed). 45(2):154–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acuro.2020.01.015
Acknowledgements
Prof. Olivier Traxer is a consultant for Coloplast, Rocamed, EMS, Boston Scientific and IPG.
Funding
This is an independent study and is not funded by any external body.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS: data collection and manuscript writing. MC: data analysis and manuscript writing. AP: data collection. MK: data management. BS: manuscript editing. OT: project development and manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent is not needed.
Human and animal rights
This research does not involve research in humans or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sierra, A., Corrales, M., Piñero, A. et al. Glossary of pre-settings given by laser companies: no consensus!. World J Urol 40, 2313–2321 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-022-04090-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-022-04090-4