Abstract
Purpose
The present study introduces a modified surgical procedure, extraperitoneal laparoscopic simple prostatectomy (LSP) with urethra preservation using urethral initiation as the entry point, and evaluates its feasibility, safety, and efficacy in the treatment of benign prostatic obstruction (BPO).
Materials and methods
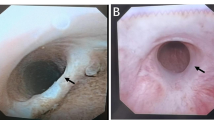
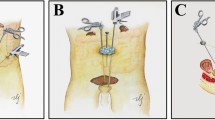
A total of 50 patients with BPO underwent modified LSP from January 2018 to December 2020. The main surgical procedures performed were as follows: transversely incision of prostate surgical capsule at the urethral initiation; creating of the subcapsular plane and the space between urethra and adenoma; removal of lobes with preservation of urethra followed by suturing of capsule. Preoperative, perioperative, follow-up parameters, and complications were recorded and analyzed.
Results
Operative time was (106.34 ± 28.00) min and intraoperative blood loss was (98.80 ± 130.58) ml. Continuous bladder irrigation (CBI) was not performed routinely, catheterization duration was (5.26 ± 2.99) days, and postoperative hospital stay was (5.42 ± 1.62) days. Significant improvements were observed in functional outcomes, whereas no retrograde ejaculation, urinary incontinence, and urethral stricture occurred. Urethral rupture was not significantly influenced by operative time, intraoperative blood loss, and prostate volume. However, it prolonged CBI duration, drainage tube retention time, catheterization duration, and postoperative hospital stay. Operative time decreased with an increase in the number of cases, and the surgeon achieved proficiency level after handling 21–25 cases.
Conclusion
Extraperitoneal LSP with urethra preservation using urethral initiation as the entry point is a feasible, repeatable, safe, and effective surgical procedure, which is suitable for treating BPO.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gravas S, Cornu JN, Gacci M et al (2021) Management of non-neurogenic male LUTS. EAU guidelines. https://uroweb.org/guideline/treatment-of-non-neurogenic-male-luts/#5
Han M, Partin AW (2016) Simple prostatectomy: open and robot-assisted laparoscopic approaches. In: AJ Wein (ed) Campbell-Walsh urology, 11th edn. Philadelphia, PA, p 2535
Dixon AR, Lord PH, Madigan MR (1990) The Madigan prostatectomy. J Urol 144:1401–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)39753-7
Kuntz RM, Lehrich K, Ahyai SA (2008) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus open prostatectomy for prostates greater than 100 grams: 5-year follow-up results of a randomised clinical trial. Eur Urol 53:160–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2007.08.036
Lin Y, Wu X, Xu A, Ren R, Zhou X, Wen Y et al (2016) Transurethral enucleation of the prostate versus transvesical open prostatectomy for large benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. World J Urol 34:1207–1219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-015-1735-9
Mariano MB, Tefilli MV, Graziottin TM, Morales CM, Goldraich IH (2006) Laparoscopic prostatectomy for benign prostatic hyperplasia–a six-year experience. Eur Urol 49:127–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2005.09.018
Rehman J, Khan SA, Sukkarieh T, Chughtai B, Waltzer WC (2005) Extraperitoneal laparoscopic prostatectomy (adenomectomy) for obstructing benign prostatic hyperplasia: transvesical and transcapsular (Millin) techniques. J Endourol 19:491–496. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2005.19.491
Morató O, Poves I, Burdío F, Sánchez-Velázquez P, Duran X, Grande L (2020) Evaluation of the learning curve for laparoscopic pancreatoduodenectomy by CUSUM analyses. Cohort study. Int J Surg 80:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.05.009
Rassweiler JJ, Fiedler-Hruza M (2019) The learning curve for robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: there is much beyond a trifecta. Eur Urol 75:257–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2018.10.022
Mariano MB, Graziottin TM, Tefilli MV (2002) Laparoscopic prostatectomy with vascular control for benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 167:2528–2529
Al-Aown A, Liatsikos E, Panagopoulos V, Kyriazis I, Kallidonis P, Georgiopoulos I et al (2015) Laparoscopic simple prostatectomy: a reasonable option for large prostatic adenomas. Urol Ann 7:297–302. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-7796.156144
Baldini A, Fassi-Fehri H, Duarte RC, Crouzet S, Ecochard R, Abid N et al (2017) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus laparoscopic transcapsular prostatectomy: perioperative results and three-month follow-up. Curr Urol 10:81–86. https://doi.org/10.1159/000447156
Desai MM, Fareed K, Berger AK, Astigueta JC, Irwin BH, Aron M et al (2010) Single-port transvesical enucleation of the prostate: a clinical report of 34 cases. BJU Int 105:1296–1300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.09106.x
Chlosta PL, Varkarakis IM, Drewa T, Dobruch J, Jaskulski J, Antoniewicz AA et al (2011) Extraperitoneal laparoscopic Millin prostatectomy using finger enucleation. J Urol 186:873–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2011.04.080
Kordan Y, Canda AE, Köseoğlu E, Balbay D, Laguna MP, de la Rosette J (2020) Robotic-assisted simple prostatectomy: a systematic review. J Clin Med 9:1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061798
Quan C, Chang W, Chen J, Li B, Niu Y (2011) Laparoscopic Madigan prostatectomy. J Endourol 25:1879–1882. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2011.0117
Xing N, Guo Y, Yang F, Tian L, Zhang J, Yan Y et al (2012) Laparoscopic simple prostatectomy with prostatic urethra preservation for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Transl Androl Urol 1:9–13. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2012.02.03
Xie JB, Tan YA, Wang FL, Xuan Q, Sun YW, Xiao J et al (2014) Extraperitoneal laparoscopic adenomectomy (Madigan) versus bipolar transurethral resection of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia greater than 80 ml: complications and functional outcomes after 3-year follow-up. J Endourol 28:353–359. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2013.0374
Matei DV, Brescia A, Mazzoleni F, Spinelli M, Musi G, Melegari S et al (2012) Robot-assisted simple prostatectomy (RASP): does it make sense? BJU Int 110:E972–E979. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11192.x
Manickam R, Nachimuthu S, Kallappan S, Pai MG (2018) Laparoscopic adenomectomy in BPH—does it have a role today? Asian J Urol 5:37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajur.2017.11.008
Rivas JG, Drewa T (2014) Laparoscopic simple prostatectomy, a lost child of laparoscopic surgery. Cent Eur J Urol 67:385–386. https://doi.org/10.5173/ceju.2014.04.art13
Yun HK, Kwon JB, Cho SR, Kim JS (2010) Early experience with laparoscopic retropubic simple prostatectomy in patients with voluminous benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Kor J Urol 51:323–329. https://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2010.51.5.323
Acknowledgements
This technique is approved and supported by “New Technology, New Project, New Treatment” in our hospital (2019-120).
Funding
This research received no specific Grant from any funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SL: project design and development, data collection and analysis, manuscript writing and editing. LZ: project development, manuscript writing. JW: data analysis. YT: manuscript writing and editing. TH: project development, manuscript writing and editing. JX: project development, manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All conflicts of interest, including specific financial interests and relationships and affiliations relevant to the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript are the following: none.
Ethics approval
This retrospective study was approved by our institution’s ethics review board.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Zhou, L., Wang, J. et al. Extraperitoneal laparoscopic simple prostatectomy with urethra preservation using urethral initiation as the entry point: a practical approach for the treatment of benign prostatic obstruction. World J Urol 40, 973–982 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-022-03932-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-022-03932-5