Abstract
Purpose
Early clinical trials of injectable collagenase Clostridium histolyticum (CCh) for Peyronie’s disease (PD) demonstrated safety and efficacy. Since then, modified injection protocols have been proposed. Adverse events—such as bruising, swelling, hematoma, and corporal rupture—exceed 50% in many studies, but lack of standardization of hematoma severity limits conclusions about the relative safety of protocols. We propose a modification of the standard injection technique that aims to decrease the rates of adverse events. We further describe a hematoma classification rubric that may standardize safety assessment.
Methods
A modified injection procedure, termed the “fan” technique, was employed in the treatment of PD. All men receiving CCh from January 2016 through January 2019 at a single institution were included in an institutional review board (IRB) approved database. Treatment outcomes and adverse events were retrospectively assessed. A three-tiered hematoma classification rubric was devised to standardize reporting of hematoma, which was defined as concurrent bruising and swelling at the site of injection without loss of erection.
Results
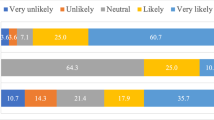
Using the fan technique, 152 patients received 1323 injections. Eight hematomas (5.3% of all patients, 0.6% of all injections) were observed. The number of grade I, grade II, and grade III hematomas were 3, 2, and 3, respectively. Bruising or swelling not meeting the definition of hematoma was seen in 54.6% and 27.0% of patients, respectively. There were zero corporal ruptures.
Conclusion
A modified injection technique results in reduced procedural morbidity. A hematoma classification system provides clarity and standardization to the assessment of safety in PD treatment. Further clinical studies with control arms are required to verify these findings.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gelbard M, Goldstein I, Hellstrom WJ, McMahon CG, Smith T, Tursi J, Jones N, Kaufman GJ, Carson CC 3rd (2013) Clinical efficacy, safety and tolerability of collagenase Clostridium histolyticum for the treatment of peyronie disease in 2 large double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled phase 3 studies. J Urol 190(1):199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2013.01.087
Levine LA, Cuzin B, Mark S, Gelbard MK, Jones NA, Liu G, Kaufman GJ, Tursi JP, Ralph DJ (2015) Clinical safety and effectiveness of collagenase Clostridium histolyticum injection in patients with Peyronie’s disease: a phase 3 open-label study. J Sex Med 12(1):248–258. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsm.12731
Lipshultz LI, Goldstein I, Seftel AD, Kaufman GJ, Smith TM, Tursi JP, Burnett AL (2015) Clinical efficacy of collagenase Clostridium histolyticum in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease by subgroup: results from two large, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III studies. BJU Int 116(4):650–656. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13096
Wymer K, Ziegelmann M, Savage J, Kohler T, Trost L (2018) Plaque calcification: an important predictor of collagenase Clostridium histolyticum treatment outcomes for men with Peyronie’s disease. Urology 119:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2018.06.003
Ziegelmann MJ, Viers BR, Montgomery BD, Avant RA, Savage JB, Trost LW (2017) Clinical experience with penile traction therapy among men undergoing collagenase Clostridium histolyticum for Peyronie disease. Urology 104:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2017.01.054
Ralph DJ, Abdel Raheem A, Liu G (2017) Treatment of Peyronie’s disease with collagenase Clostridium histolyticum and vacuum therapy: a randomized, open-label pilot study. J Sex Med 14(11):1430–1437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsxm.2017.08.015
Abdel Raheem A, Johnson M, Abdel-Raheem T, Capece M, Ralph D (2017) Collagenase Clostridium histolyticum in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease—a review of the literature and a new modified protocol. Sex Med Rev 5(4):529–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.07.005
Anaissie J, Yafi FA, DeLay KJ, Traore EJ, Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJG (2017) Impact of number of cycles of collagenase Clostridium Histolyticum on outcomes in patients with Peyronie’s disease. Urology 100:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2016.09.050
Abdel Raheem A, Capece M, Kalejaiye O, Abdel-Raheem T, Falcone M, Johnson M, Ralph OG, Garaffa G, Christopher AN, Ralph DJ (2017) Safety and effectiveness of collagenase Clostridium histolyticum in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease using a new modified shortened protocol. BJU Int 120(5):717–723. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13932
Capece M, Cocci A, Russo G, Cito G, Giubilei G, Cacciamani G, Garaffa G, Falcone M, Timpano M, Tasso G, Sessa F, Campi R, Di Maida F, Cai T, Morelli G, Giammusso B, Verze P, Palmieri A, Ralph D, Mirone V, Mondaini N (2018) Collagenase Clostridium histolyticum for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease: a prospective Italian multicentric study. Andrology 6(4):564–567. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.12497
Nguyen HMT, Anaissie J, DeLay KJ, Yafi FA, Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJG (2017) Safety and efficacy of collagenase Clostridium histolyticum in the treatment of acute-phase Peyronie’s disease. J Sex Med 14(10):1220–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsxm.2017.08.008
Carson CC 3rd, Sadeghi-Nejad H, Tursi JP, Smith TM, Kaufman GJ, Gilbert K, Honig SC (2015) Analysis of the clinical safety of intralesional injection of collagenase Clostridium histolyticum (CCH) for adults with Peyronie’s disease (PD). BJU Int 116(5):815–822. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13120
Beilan JA, Wallen JJ, Baumgarten AS, Morgan KN, Parker JL, Carrion RE (2018) Intralesional injection of collagenase Clostridium histolyticum may increase the risk of late-onset penile fracture. Sex Med Rev 6(2):272–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.07.011
Yang KK, Bennett N (2016) Peyronie’s disease and injectable collagenase Clostridium histolyticum: safety, efficacy, and improvements in subjective symptoms. Urology 94:143–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2016.04.049
Masterson TA, Galante A, Butaney M, Pastuszak A, Sadeghi-Nejad H, Ramasamy R (2019) Variation in collagenase Clostridium histolyticum practice patterns: a survey of ISSM members. Int J Impot Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-019-0126-y
Goldstein I, Knoll LD, Lipshultz LI, Smith T, Kaufman GJ, McMahon CG (2017) Changes in the effects of Peyronie’s disease after treatment with collagenase Clostridium histolyticum: male patients and their female partners. Sex Med 5(2):e124–e130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esxm.2017.02.001
Yafi FA, Anaissie J, Zurawin J, Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJ (2016) Results of SMSNA survey regarding complications following intralesional injection therapy with collagenase Clostridium histolyticum for Peyronie’s disease. J Sex Med 13(4):684–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsxm.2016.02.105
Hellstrom WJG, Tue Nguyen HM, Alzweri L, Chung A, Virasoro R, Tapscott A, Ziegelmann M, Trost L, Gelbard M (2019) Intralesional collagenase Clostridium histolyticum causes meaningful improvement in men with Peyronie’s disease: results of a multi-institutional analysis. J Urol. https://doi.org/10.1097/ju.0000000000000032
Masterson T, Patel P, Ramasamy R (2019) Re: Limited success with clostridium collagenase histolyticum following FDA approval for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-019-0127-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AA data collection and management, data analysis, manuscript writing/editing. SAM data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing/editing, illustration. SVE protocol/project development, manuscript writing/editing. KVR data collection, data analysis, manuscript editing. NM data collection, manuscript editing. JNM protocol/project development, manuscript writing/editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Jesse Mills is on the speakers’ bureau for Endo International pharmaceuticals. No other authors have any conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amighi, A., Mills, S.A., Eleswarapu, S.V. et al. A modified technique for intralesional injection of collagenase Clostridium histolyticum for Peyronie’s disease results in reduced procedural morbidity using a standardized hematoma classification rubric. World J Urol 38, 293–298 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-02812-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-02812-9