Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate and compare postoperative changes in prostate volume and clinical outcome after bipolar plasma vaporization (BPV) and conventional transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
Patients and methods
Consecutive series of patients undergoing BPV or TURP were included in this prospective, nonrandomized study. Planimetric volumetry after transrectal three-dimensional ultrasound of the prostate was performed preoperatively and postoperatively after 6 weeks, 6 months and 12 months. Additionally, changes in clinical outcome parameters were assessed and compared between the groups. The reduction ratio and analysis of covariance were used to compare volume changes between BPV and TURP. Multiple regression analysis was performed to assess a possible interaction between preoperative prostate volume and effect of therapy.
Results
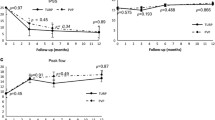
A total of 157 patients were included (BPV: n = 68, TURP: n = 89). Median preoperative prostate volume was 43.1 ml in the BPV group and 45.9 ml in the TURP group (p = 0.43). Postoperatively, the prostate volumes decreased significantly in both groups. After catheter removal, the relative residual prostate volume was significantly higher in the BPV group (66.6 vs. 60.8 %; p = 0.02). Thereafter, significant differences were not detectable anymore (12 months: 46.6 vs. 47.1 %; p = 0.82). Regression analysis revealed that tissue ablation after BPV was superior to TURP in prostates <45 ml but inferior in prostates >45 ml. All clinical outcome parameters improved significantly and were not significantly different between the groups.
Conclusions
Volume reduction and short-term clinical outcome following pure BPV was excellent and comparable to conventional TURP. However, volume reduction seems to be limited in patients with larger prostates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wroclawski ML, Carneiro A, Amarante RD et al (2016) ‘Button type’ bipolar plasma vaporisation of the prostate compared with standard transurethral resection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of short-term outcome studies. BJU Int 117:662–668
Cornu JN, Ahyai S, Bachmann A et al (2015) A systematic review and meta-analysis of functional outcomes and complications following transurethral procedures for lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from benign prostatic obstruction: an update. Eur Urol 67:1066–1096
Robert G, de la Taille A, Herrmann T (2015) Bipolar plasma vaporization of the prostate: ready to replace GreenLight? A systematic review of randomized control trials. World J Urol 33:549–554
Reich O, Schlenker B, Gratzke C et al (2010) Plasma vaporisation of the prostate: initial clinical results. Eur Urol 57:693–697
Geavlete B, Multescu R, Dragutescu M, Jecu M, Georgescu D, Geavlete P (2010) Transurethral resection (TUR) in saline plasma vaporization of the prostate vs standard TUR of the prostate: ‘the better choice’ in benign prostatic hyperplasia? BJU Int 106:1695–1699
Robert G, Descazeaud A, Delongchamps NB et al (2010) Transurethral plasma vaporization of the prostate: 3-month functional outcome and complications. BJU Int 2:1–6
Geavlete B, Georgescu D, Multescu R, Stanescu F, Jecu M, Geavlete P (2011) Bipolar plasma vaporization vs monopolar and bipolar TURP—a prospective, randomized, long-term comparison. Urology 27(78):930–935
Hermanns T, Fankhauser CD, Hefermehl LJ et al (2013) Prospective evaluation of irrigation fluid absorption during pure transurethral bipolar plasma vaporisation of the prostate using expired-breath ethanol measurements. BJU Int 112:647–654. doi:10.1111/bju.12170
Lin Y, Liu B, Xie L (2015) Bipolar button-electrode plasma vaporization of the prostate: an effective option for patients with post-brachytherapy retention. Exp Ther Med 10:1309–1310
Reich O, Gratzke C, Stief CG (2006) Techniques and long-term results of surgical procedures for BPH. Eur Urol 49:970–978 (discussion 8)
Antunes AA, Srougi M, Coelho RF, Leite KR, Freire GDC (2009) Transurethral resection of the prostate for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms related to benign prostatic hyperplasia: how much should be resected? Int Braz J Urol 35:683–689 (discussion 9–91)
Hermanns T, Gross O, Kranzbuhler B et al (2013) Ablative efficiency of 532-nm laser vaporization compared to transurethral resection of the prostate: results from a prospective three-dimensional ultrasound volumetry study. World J Urol 32(5):1267–1274. doi:10.1007/s00345-013-1203-3
Kranzbuhler B, Wettstein MS, Fankhauser CD et al (2013) Pure bipolar plasma vaporization of the prostate: the Zurich experience. J Endourol 27:1261–1266
Hakenberg OW, Helke C, Manseck A, Wirth MP (2001) Is there a relationship between the amount of tissue removed at transurethral resection of the prostate and clinical improvement in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol 39:412–417
Hermanns T, Sulser T (2011) Interventional treatment: prostate laser. In: Bachmann A, de la Rosette J (eds) OUL benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms in men, chapter 16. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Rieken M, Bachmann A, Shariat SF (2016) Long-term follow-up data more than 5 years after surgical management of benign prostate obstruction: who stands the test of time? Curr Opin Urol 26:22–27
Al-Ansari A, Younes N, Sampige VP et al (2010) GreenLight HPS 120-W laser vaporization versus transurethral resection of the prostate for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized clinical trial with midterm follow-up. Eur Urol 58:349–355
Gjengsto P, Halvorsen OJ, Akslen LA, Frugard J, Hoisaeter PA (2003) Benign growth of different prostate zones in aging men with slightly elevated PSA in whom prostate cancer has been excluded: a prospective study of 510 patients. Urology 62:447–450
Hermanns T, Strebel DD, Hefermehl LJ et al (2011) Lithium triborate laser vaporization of the prostate using the 120 W, high performance system laser: high performance all the way? J Urol 185:2241–2247
Geavlete B, Stanescu F, Moldoveanu C, Geavlete P (2014) Continuous vs conventional bipolar plasma vaporisation of the prostate and standard monopolar resection: a prospective, randomised comparison of a new technological advance. BJU Int 113(2):288–295. doi:10.1111/bju.12290
Aydogdu O, Karakose A, Atesci YZ (2014) A clinical study comparing BIVAP saline vaporization of the prostate with bipolar TURP in patients with prostate volume 30 to 80 mL: early complications, physiological changes and postoperative follow-up outcomes. Can Urol Assoc J 8:E485–E489
Falahatkar S, Mokhtari G, Moghaddam KG et al (2014) Bipolar transurethral vaporization: a superior procedure in benign prostatic hyperplasia: a prospective randomized comparison with bipolar TURP. Int Braz J Urol 40:346–355
Zhang SY, Hu H, Zhang XP et al (2012) Efficacy and safety of bipolar plasma vaporization of the prostate with “button-type” electrode compared with transurethral resection of prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Chin Med J (Engl) 125:3811–3814
Zuo W, Hiraoka Y (2003) Prostate-specific antigen levels and density in the internal and external glands of the prostate in benign prostatic hyperplasia patients with normal or gray-zone PSA levels. Urol Int 71:154–159
Mamoulakis C, Schulze M, Skolarikos A et al (2013) Midterm results from an international multicentre randomised controlled trial comparing bipolar with monopolar transurethral resection of the prostate. Eur Urol 63:667–676
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Alexandra Veloudios for the excellent patient care during this study.
Author contribution
B Kranzbühler was involved in data collection, data management, data analysis and manuscript writing/editing; O Gross, CD Fankhauser, MS Wettstein and NC Grossmann helped in data collection and data management; LJ Hefermehl was involved in protocol/project development and manuscript writing/editing; M Zimmermann collected the data; A Müller contributed to protocol/project development and data collection; T Sulser was involved in manuscript writing/editing; C Poyet helped in data collection and manuscript writing/editing; and T Hermanns was involved in protocol/project development, data collection, data management, data analysis and manuscript writing/editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1
Study profile (PDF 550 kb)
Online Resource 2
Changes in relative volume reduction (in %; y-axis) in relation to the initial prostate volume (ml; x-axis) 12 months after BPV (red line) and TURP (green line) (PDF 326 kb)
Online Resource 3
The spherical vaporization electrode before the procedure (A) and after BPV of a 50-ml prostate (B) (PDF 2050 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kranzbühler, B., Gross, O., Fankhauser, C.D. et al. Prostate volume reduction following pure transurethral bipolar plasma vaporization and conventional transurethral resection of the prostate: a prospective investigation using transrectal 3D ultrasound volumetry. World J Urol 35, 429–435 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-016-1876-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-016-1876-5