Abstract
Introduction
We sought to determine whether measured corporal length (MCL) or implanted device size (IDS) has changed.
Methods
Data were obtained from the two major penile implant companies from the years of 2005–2010 and analyzed. While we requested similar data, companies supplied information at their discretion with MCL provided by American Medical Systems and IDS provided by Coloplast. Intra-patient corporal discrepancies, disease state effects, rear tip extenders (RTEs) use and place of implantation were also provided in some part by companies.
Results
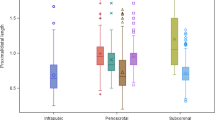
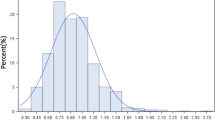
MCL and IDS increased during the study period. Despite the general trend of MCL/IDS, clinically significant (0.5 cm or greater) decreases in MCLs were noted in patients with Peyronie’s disease (PD) or a history of radical pelvic surgery (excludes prostatectomy). In only 2.7 % of cases was there an intra-patient discrepancy in cylinder size (>1 cm). IDS was longer in the USA (US, 19.4 cm) compared to outside the US (OUS, 17.7 cm, p < 0.0001). Cylinders were implanted without RTEs in 48.3 % of US cases and 73.7 % of OUS cases (p < 0.0001). In Coloplast devices there was an overall statistically significant change in the use of 16 cm (less utilized) and 20 and 22 cm (more utilized) cylinder lengths during the study period in US implants.
Conclusion
MCL and IDS increased during the study period. Men with a history of PD or radical pelvic surgery are at highest risk to have shorter MCL and to possibly receive shorter implants. Intra-patient IDS inconsistency is rare and should prompt investigation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Munding MD, Wessells HB, Dalkin BL (2001) Pilot study of changes in stretched penile length 3 months after radical retropubic prostatectomy. Urology 58:567–569
Fraiman MC, Lepor H, McCullough AR (1999) Changes in penile morphometrics in men with erectile dysfunction after nerve-sparing radical retropubic prostatectomy. Mol Urol 3:109–115
Savoie M, Kim SS, Soloway MS (2003) A prospective study measuring penile length in men treated with radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. J Urol 169:1462–1464
Tal R, Heck M, Teloken P, Siegrist T, Nelson CJ, Mulhall JP (2010) Peyronie’s disease following radical prostatectomy: incidence and predictors. J Sex Med 7:1254–1261
Welliver RC Jr, Mechlin C, Goodwin B, Alukal JP, McCullough AR (2014) A pilot study to determine penile oxygen saturation before and after vacuum therapy in patients with erectile dysfunction after radical prostatectomy. J Sex Med 11:1071–1077
Dalkin BL, Christopher BA (2007) Preservation of penile length after radical prostatectomy: early intervention with a vacuum erection device. IJIR 19:501–504
Köhler TS, Pedro R, Hendlin K, Utz W, Ugarte R, Reddy P, Makhlouf A, Ryndin I, Canales BK, Weiland D, Nakib N, Ramani A, Anderson JK, Monga M (2007) A pilot study on the early use of the vacuum erection device after radical retropubic prostatectomy. BJU Int 100:858–862
Montorsi F, Brock G, Stolzenburg JU, Mulhall J, Moncada I, Patel HR, Chevallier D, Krajka K, Henneges C, Dickson R, Buttner H (2014) Effects of tadalafil treatment on erectile function recovery following bilateral nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy: a randomised placebo-controlled study (REACTT). Eur Urol 65:587–596
Montorsi F, Brock G, Lee J, Shapiro J, Van Poppel H, Graefen M, Stief C (2008) Effect of nightly versus on-demand vardenafil on recovery of erectile function in men following bilateral nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol 54:924–931
Padma-Nathan H, McCullough AR, Levine LA, Lipshultz LI, Siegel R, Montorsi F, Giuliano F, Brock G, Study G (2008) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of postoperative nightly sildenafil citrate for the prevention of erectile dysfunction after bilateral nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy. IJIR 20:479–486
Raina R, Pahlajani G, Agarwal A, Zippe CD (2008) Early penile rehabilitation following radical prostatectomy: cleveland clinic experience. IJIR 20:121–126
Montorsi F, Rigatti P, Carmignani G, Corbu C, Campo B, Ordesi G, Breda G, Silvestre P, Giammusso B, Morgia G, Graziottin A (2000) AMS three-piece inflatable implants for erectile dysfunction: a long-term multi-institutional study in 200 consecutive patients. Eur Urol 37:50–55
Trost LW, Baum N, Hellstrom WJ (2013) Managing the difficult penile prosthesis patient. J Sex Med 10:893–906 quiz 7
Köhler TS, Welliver RC Jr (2014) Optimizing outcomes and patient satisfaction with penile implants. AUA Update series 2014. Lesson 5
Sellers T, Dineen M, Salem EA, Wilson SK (2013) Vacuum preparation, optimization of cylinder length and postoperative daily inflation reduces complaints of shortened penile length following implantation of inflatable penile prosthesis. Adv Sex Med 3:14–18
Henry GD, Carrion R, Jennermann C, Wang R (2015) Prospective evaluation of postoperative penile rehabilitation: penile length/girth maintenance 1 year following Coloplast Titan inflatable penile prosthesis. J Sex Med 12:1298–1304
Miranda-Sousa A, Keating M, Moreira S, Baker M, Carrion R (2007) Concomitant ventral phalloplasty during penile implant surgery: a novel procedure that optimizes patient satisfaction and their perception of phallic length after penile implant surgery. J Sex Med 4:1494–1499
Henry GD, Kansal NS, Callaway M, Grigsby T, Henderson J, Noble J, Palmer T, Cleves MA, Ludlow JK, Simmons CJ, Mook TM (2009) Centers of excellence concept and penile prostheses: an outcome analysis. J Urol 181:1264–1268
Giuliano F, Amar E, Chevallier D, Montaigne O, Joubert JM, Chartier-Kastler E (2008) How urologists manage erectile dysfunction after radical prostatectomy: a national survey (REPAIR) by the French urological association. J Sex Med. 5:448–457
Tal R, Teloken P, Mulhall JP (2011) Erectile function rehabilitation after radical prostatectomy: practice patterns among AUA members. J Sex Med. 8(8):2370–2376
Mandava SH, Serefoglu ED, Freier MT, Wilson SK, Hellstrom WJ (2012) Infection retardant coated inflatable penile prostheses decrease the incidence of infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Urol 188:1855–1860
Mulcahy JJ, Kramer A, Brant WO, Parker JL, Perito PE, Myers JB, Bryson R, Dunne M (2014) Current management of penile implant infections, device reliability, and optimizing cosmetic outcome. Curr Urol Rep 15:413
Authors’ contributions
1. Welliver involved in protocol/project development, data collection and management, data analysis, manuscript writing/editing; 2. Kottwitz involved in protocol/project development, data collection and management, manuscript writing/editing; 3. Ahmad involved in data analysis, manuscript writing/editing; 4. Wilson involved in protocol/project development, data analysis, manuscript writing/editing; and 5. Kohler involved in protocol/project development, data collection and management, data analysis, manuscript writing/editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
1. Welliver: Honoraria: American Society of Andrology; Meeting Participant: Coloplast, AMS; Investigator: Antares, NexMed, Auxilium, Sophiris, PROCEPT BioRobotics; Employee (brother): Bristol-Meyers. 2. Kottwitz: none. 3. Ahmad: none. 4. Wilson: Surgical Proctor: NeoTract, Coloplast, AMS; Consultant: Coloplast, AMS, Abreon, Sontec. 5. Kohler: Meeting Participant/Lecturer: Auxilium; Surgical proctor/Consultant/Meeting participant/Lecturer/research and grant funding: Coloplast, AMS; Grant and research funding: Abbvie; Research funding: Hollister.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welliver, C., Kottwitz, M., Ahmad, A.E. et al. Manufacturers’ data show increasing implanted cylinder sizes and measured corporal lengths in inflatable penile implants. World J Urol 34, 993–998 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-015-1705-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-015-1705-2