Abstract
Purpose
To compare oncologic outcomes between open radical cystectomy (ORC) and robotic-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) using propensity score (PS) matching of preoperative variables.
Methods
A group of 51 consecutive patients who underwent RARC between 2009 and 2012 were matched by propensity scoring with an equal number of patients who underwent ORC. Patient demographics, clinical staging, pathologic staging, pathologic grading, histology, positive margin status, lymph node yield, duration of hospital stay, and overall survival were examined.
Results
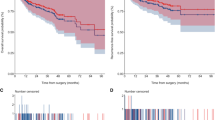
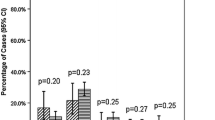
PS-matched ORC and RARC cohorts demonstrated no significant differences with respect to preoperative variables, pathologic stage, grade, histology, metastasis at preoperative staging, and postoperative positive margin status. There were statistically significant differences in nodal status (66.7 % N0 for ORC vs. 80.4 % N0 for RARC, p = 0.039) and median lymph node yield (6 for ORC vs. 18 for RARC, p < 0.0001). No positive soft tissue margins were observed in the RARC group compared to 5.9 % in the ORC group (p = 0.332). There were no significant differences in mean duration of hospital stay or mean overall survival between ORC and RARC.
Conclusion
ORC and RARC represent effective surgical approaches for the treatment of bladder cancer. Histopathologic outcomes for RARC compare favorably to ORC with respect to soft tissue margin rates and lymph node yield. These data suggest that RARC is an acceptable surgical approach for treatment of bladder cancer that can achieve outcomes that are equal or superior to those of ORC.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murta-Nascimento C, Schmitz-Dräger BJ, Zeegers MP et al (2007) Epidemiology of urinary bladder cancer: from tumor development to patient’s death. World J Urol 25(3):285–295. doi:10.1007/s00345-007-0168-5
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM et al (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107
Stenzl A, Cowan NC, De Santis M et al (2009) The updated EAU guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer. Eur Urol 55(4):815–825. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2009.01.002
Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R et al (2001) Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: long-term results in 1,054 patients. J Clin Oncol 19(3):666–675. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11157016
Novara G, De Marco V, Aragona M et al (2009) Complications and mortality after radical cystectomy for bladder transitional cell cancer. J Urol 182(3):914–921. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2009.05.032
De Nunzio C, Cindolo L, Leonardo C et al (2013) Analysis of radical cystectomy and urinary diversion complications with the Clavien classification system in an Italian real life cohort. Eur J Surg Oncol 39(7):792–798. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2013.03.008
Froehner M, Brausi MA, Herr HW, Muto G, Studer UE (2009) Complications following radical cystectomy for bladder cancer in the elderly. Eur Urol 56(3):443–454. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2009.05.008
Shabsigh A, Korets R, Vora KC et al (2009) Defining early morbidity of radical cystectomy for patients with bladder cancer using a standardized reporting methodology. Eur Urol 55(1):164–174. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2008.07.031
Wang GJ, Barocas DA, Raman JD, Scherr DS (2008) Robotic vs open radical cystectomy: prospective comparison of perioperative outcomes and pathological measures of early oncological efficacy. BJU Int 101(1):89–93. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07212.x
Ng CK, Kauffman EC, Lee M-M et al (2010) A comparison of postoperative complications in open versus robotic cystectomy. Eur Urol 57(2):274–281. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2009.06.001
Li K, Lin T, Fan X et al (2012) Systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies reporting early outcomes after robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy. Cancer Treat Rev. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2012.11.007
Nix J, Smith A, Kurpad R, Nielsen ME, Wallen EM, Pruthi RS (2010) Prospective randomized controlled trial of robotic versus open radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: perioperative and pathologic results. Eur Urol 57(2):196–201. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2009.10.024
Galich A, Sterrett S, Nazemi T, Pohlman G, Smith L, Balaji KC (2006) Comparative analysis of early perioperative outcomes following radical cystectomy by either the robotic or open method. J Soc Laparoendosc Surg Soc Laparoendosc Surg 10(2):145–150. Available at: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3016134&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract
Novara G, Svatek RS, Karakiewicz PI et al (2010) Soft tissue surgical margin status is a powerful predictor of outcomes after radical cystectomy: a multicenter study of more than 4,400 patients. J Urol 183(6):2165–2170. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2010.02.021
Madersbacher S (2003) Radical cystectomy for bladder cancer today—a homogeneous series without neoadjuvant therapy. J Clin Oncol 21(4):690–696. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.05.101
Bochner BH, Kattan MW, Vora KC (2006) Postoperative nomogram predicting risk of recurrence after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(24):3967–3972. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.05.3884
Karakiewicz PI, Shariat SF, Palapattu GS et al (2006) Nomogram for predicting disease recurrence after radical cystectomy for transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol 176(4 Pt 1):1354–1361. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2006.06.025 (discussion 1361–2)
Shariat SF, Karakiewicz PI, Palapattu GS et al (2006) Nomograms provide improved accuracy for predicting survival after radical cystectomy. Clin Cancer Res 12(22):6663–6676. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0372
Kassouf W, Agarwal PK, Herr HW et al (2013) Lymph node density is superior to TNM nodal status in predicting disease-specific survival after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: analysis of pooled data from MDACC and MSKCC. J Clin Oncol 26(1):121–126. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.12.9247
Parekh DJ, Messer J, Fitzgerald J, Ercole B, Svatek R (2013) Perioperative outcomes and oncologic efficacy from a pilot prospective randomized clinical trial of open versus robotic assisted radical cystectomy. J Urol 189(2):474–479. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2012.09.077
McCaffrey DF, Griffin BA, Almirall D, Slaughter ME, Ramchand R, Burgette LF (2013) A tutorial on propensity score estimation for multiple treatments using generalized boosted models. Stat Med (January 2012). doi:10.1002/sim.5753
Benson MC (2010) Editorial comment. J Urol 184(1):91. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2010.03.158
Hellenthal NJ, Hussain A, Andrews PE et al (2010) Surgical margin status after robot assisted radical cystectomy: results from the International Robotic Cystectomy Consortium. J Urol 184(1):87–91. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2010.03.037
Rink M, Shariat SF, Xylinas E et al (2012) Does increasing the nodal yield improve outcomes in patients without nodal metastasis at radical cystectomy? World J Urol 30:807–814. doi:10.1007/s00345-012-0910-5
Hellenthal NJ, Hussain A, Andrews PE et al (2011) Lymphadenectomy at the time of robot-assisted radical cystectomy: results from the International Robotic Cystectomy Consortium. BJU Int 107(4):642–646. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09473.x
Herr H, Lee C, Chang S, Lerner S (2004) Standardization of radical cystectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection for bladder cancer: a collaborative group report. J Urol 171(5):1823–1828. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000120289.78049.0e (discussion 1827–8)
Azzouni F (2012) Current status of robot-assisted radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol 9(10):573–582. doi:10.1038/nrurol.2012.144
Bochner B, Cho D, Herr H, Donat M, Kattan M, Dalbagni G (2004) Prospectively packaged lymph node dissections with radical cystectomy: evaluation of node count variability and node mapping. J Urol 172(4):1286–1290. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000137817.56888.d1
Stein JP, Penson DF, Cai J et al (2007) Radical cystectomy with extended lymphadenectomy: evaluating separate package versus en bloc submission for node positive bladder cancer. J Urol 177(3):876–881 (discussion 881–2)
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov. [online]. Available at: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01157676?term=NCT01157676&rank=1
Conflict of interest
A Charles Huggins-Grant of the German Society of Urology funded Dr. Busch. Dr. Gonzalgo has served as a consultant to Intuitive Surgical, Inc. There are no additional disclosures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahdoot, M., Almario, L., Araya, H. et al. Oncologic outcomes between open and robotic-assisted radical cystectomy: a propensity score matched analysis. World J Urol 32, 1441–1446 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1242-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1242-4