Abstract
Purpose
To investigate transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) expression and the effects of ruthenium red (RR)—TRPV antagonist—on detrusor overactivity (DO) associated with bladder outlet obstruction (BOO).
Methods
Rats were randomly assigned to 3 groups. The control group (n = 10) included sham-operated rats. The BOO-group without RR (n = 15) and BOO-group with RR (n = 15) underwent partial BOO surgery. Three weeks postoperatively, cystometrography was performed in all rats. After confirming DO, RR was instilled intravesically in the BOO-group with RR. Urodynamic parameters were investigated, including contraction interval (CI) and contraction pressure (CP). TRPV4 expression was evaluated through immunofluorescence staining and western blotting.
Results
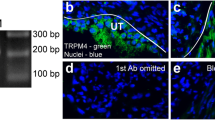
The BOO-group without RR had significantly shorter CI and significantly higher CP compared to the control. In the BOO-group with RR, CI was significantly longer compared to the BOO-group without RR. However, change in CP between BOO-group without and with RR was not significantly different. Immunofluorescence staining showed that TRPV4 was localized in the urothelium and detrusor muscles. TRPV4 immunofluorescence signals were increased in the urothelium and detrusor muscle in BOO-group without RR, compared with the control. In western blot analysis, immunoreactive bands indicating expression of TRPV4 were detected in the urothelium and detrusor muscle, and those were significantly increased in the BOO-group without RR compared with the control in the urothelium and detrusor muscle.
Conclusions
TRPV4 plays an important role in the pathophysiology of DO, and RR has a beneficial effect on DO associated with BOO.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Nunzio C, Franco G, Rocchegiani A, Iori F, Leonardo C, Laurenti C (2003) The evolution of detrusor overactivity after watchful waiting, medical therapy and surgery in patients with bladder outlet obstruction. J Urol 169:535–539
Housami F, Abrams P (2008) Persistent detrusor overactivity after transurethral resection of the prostate. Curr Urol Rep 9:284–290
Yoshimura N (2007) Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and bladder afferent activity. Neurourol Urodyn 26:908–913
Caterina MJ, Rosen TA, Tominaga M, Brake AJ, Julius D (1999) A capsaicin-receptor homologue with a high threshold for noxious heat. Nature 398:436–441
Benham CD, Davis JB, Randall AD (2002) Vanilloid and TRP channels: a family of lipid-gated cation channels. Neuropharmacology 42:873–888
Ha US, Park EY, Kim JC (2011) Effect of botulinum toxin on expression of nerve growth factor and transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 in urothelium and detrusor muscle of rats with bladder outlet obstruction-induced detrusor overactivity. Urology 78:721 e721–721 e726
Yamada T, Ugawa S, Ueda T, Ishida Y, Kajita K, Shimada S (2009) Differential localizations of the transient receptor potential channels TRPV4 and TRPV1 in the mouse urinary bladder. J Histochem Cytochem 57:277–287
Gevaert T, Vriens J, Segal A, Everaerts W, Roskams T, Talavera K, Owsianik G, Liedtke W, Daelemans D, Dewachter I, Van Leuven F, Voets T, De Ridder D, Nilius B (2007) Deletion of the transient receptor potential cation channel TRPV4 impairs murine bladder voiding. J Clin Invest 117:3453–3462
Vincent F, Duncton MA (2011) TRPV4 agonists and antagonists. Curr Top Med Chem 11:2216–2226
Everaerts W, Vriens J, Owsianik G, Appendino G, Voets T, De Ridder D, Nilius B (2010) Functional characterization of transient receptor potential channels in mouse urothelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298:F692–F701
Thorneloe KS, Sulpizio AC, Lin Z, Figueroa DJ, Clouse AK, McCafferty GP, Chendrimada TP, Lashinger ES, Gordon E, Evans L, Misajet BA, Demarini DJ, Nation JH, Casillas LN, Marquis RW, Votta BJ, Sheardown SA, Xu X, Brooks DP, Laping NJ, Westfall TD (2008) N-((1S)-1-{[4-((2S)-2-{[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)sulfonyl]amino}-3-hydroxypropanoyl)-1 -piperazinyl]carbonyl}-3-methylbutyl)-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxamide (GSK1016790A), a novel and potent transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 channel agonist induces urinary bladder contraction and hyperactivity: part I. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326:432–442
Vlaskovska M, Kasakov L, Rong W, Bodin P, Bardini M, Cockayne DA, Ford AP, Burnstock G (2001) P2X3 knock-out mice reveal a major sensory role for urothelially released ATP. J Neurosci 21:5670–5677
Mochizuki T, Sokabe T, Araki I, Fujishita K, Shibasaki K, Uchida K, Naruse K, Koizumi S, Takeda M, Tominaga M (2009) The TRPV4 cation channel mediates stretch-evoked Ca2 + influx and ATP release in primary urothelial cell cultures. J Biol Chem 284:21257–21264
Janssen DA, Hoenderop JG, Jansen KC, Kemp AW, Heesakkers JP, Schalken JA (2011) The mechanoreceptor TRPV4 is localized in adherence junctions of the human bladder urothelium: a morphological study. J Urol 186:1121–1127
Aizawa N, Wyndaele JJ, Homma Y, Igawa Y (2012) Effects of TRPV4 cation channel activation on the primary bladder afferent activities of the rat. Neurourol Urodyn 31:148–155
Everaerts W, Nilius B, Owsianik G (2010) The vanilloid transient receptor potential channel TRPV4: from structure to disease. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 103:2–17
Maggi CA, Giuliani S, Meli A (1989) Effect of ruthenium red on responses mediated by activation of capsaicin-sensitive nerves of the rat urinary bladder. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 340:541–546
Juszczak K, Ziomber A, Thor PJ (2011) Effect of partial and complete blockade of vanilloid (TRPV1-6) and ankyrin (TRPA1) transient receptor potential ion channels on urinary bladder motor activity in an experimental hyperosmolar overactive bladder rat model. J Physiol Pharmacol 62:321–326
Birder L, Kullmann FA, Lee H, Barrick S, de Groat W, Kanai A, Caterina M (2007) Activation of urothelial transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 by 4alpha-phorbol 12,13-didecanoate contributes to altered bladder reflexes in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 323:227–235
Everaerts W, Zhen X, Ghosh D, Vriens J, Gevaert T, Gilbert JP, Hayward NJ, McNamara CR, Xue F, Moran MM, Strassmaier T, Uykal E, Owsianik G, Vennekens R, De Ridder D, Nilius B, Fanger CM, Voets T (2010) Inhibition of the cation channel TRPV4 improves bladder function in mice and rats with cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:19084–19089
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Institute of Clinical Medicine Research of Bucheon St. Mary’s Hospital, Research Fund.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, K.J., Park, E.Y., Kim, H.S. et al. Expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 and effects of ruthenium red on detrusor overactivity associated with bladder outlet obstruction in rats. World J Urol 32, 677–682 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-013-1099-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-013-1099-y