Abstract
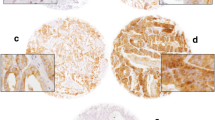
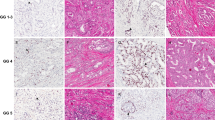
This study assesses the correlation of p53 immunoreactivity and DNA ploidy status with biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. p53 protein expression and DNA ploidy were evaluated on 84 archival paraffin-embedded radical prostatectomy specimens. Patients were divided into two groups: those with low (38/84, 45%) and those with high (46/84, 55%) p53 immunoreactivity. The results were correlated with Gleason score, stage and serum PSA. Kaplan-Meier biochemical recurrence free survival and the Cox hazard-regression model were used for analysis. Multivariate analysis revealed p53, DNA ploidy, Gleason score, PSA and stage to be independent prognostic factors in this order. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a significant difference in biochemical recurrence when p53 high expression and DNA aneuploidy were combined. The results of this study suggest that stratification for p53 expression and DNA ploidy status can provide additional prognostic information for patients with prostate carcinoma after radical prostatectomy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer JJ, Sesterhenn IA, Mostofi FK, McLeod DG, Srivastava S, Moul JW (1996) Elevated levels of apoptosis regulator proteins p53 and bcl-2 are independent prognostic biomarkers in surgically treated clinically localized prostate cancer. J Urol 156:1511–1516
Borre M, Stausbol-gron B, Overgaard J (2000) p53 accumulation associated with bcl-2, the proliferation marker MIB-1 and survival in patients with prostate cancer subjected to watchful waiting. J Urol 164:716–721
Bostwick D, Grignon D, Hammond M, Amin M, Cohen M, Crawford D, Gospadarovicz M, Kaplan R, Miller D, Montironi R, Pajak T, Pollack A, Srigley J, Yarbro J (2000) Prognostic factors in prostate cancer. College of American Pathologists Consensus Statement 1999. Arch Pathol Lab Med 124: 995–1000
Brewster SF, Oxley JD, Trivella M, Abbott C, Gillatt D (1999) Preoperative p53, bcl-2, CD44, and E-cadherin immunohistochemistry as predictors of biochemical relapse after radical prostatectomy. J Urol 161:1238–1243
Brooks J, Bova G, Ewing C, Piantadosi S, Carter B, Robinson J, Epstein J, Isaacs W (1996) An uncertain role for p53 gene alterations in human prostate cancers. Cancer Res 56:3814–3822
Carroll A, Voeller H, Sugars L, Gelmann E (1993) p53 oncogene mutations in three human prostate cancer cell lines. Prostate 23:123–134
Hawkins CA, Bergstralh EJ, Lieber MM, Zinke H (1995) Influence of DNA ploidy and adjuvant treatment on progression and survival in patients with pathologic stage T3 (PT3) prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. Urology 46: 356–364
Kallakury BV, Figge J, Ross JS, Fisher H, Figge H, Jennings T (1994) Association of p53 immunoreactivity with high Gleason tumor grade in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol 25:92–97
Krupski T, Petroni G, Frierson H, Theodoresku D (2000) Microvessel density, p53, retinoblastoma, and chromogranin A immunohistochemistry as predictors of disease-specific survival following radical prostatectomy for carcinoma of the prostate. Urology 55:743–749
Kuczyk MA, Serth J, Bokemeyer C, Machtens S, Minssen A, Bathke W, Hartmann J, Jonas U (1998) The prognostic value of p53 for long-term and recurrence-free survival following radical prostatectomy. Eur J Cancer 34:679–686
Leibovich BC, Cheng L, Weaver AL, Myers RP, Botwick D (2000) Outcome prediction with p53 immunostaining after radical prostatectomy in patients with locally advanced prostate cancer. J Urol 163:1756–1760
Lerner SE, Blute ML, Zincke H (1996) Risk factors for progression in patients with prostate cancer treated with radical prostatectomy. Semin Urol Oncol 14(4):12–20
Martinez Jaboloyas J, Ruiz Cerda J, Sanz Chinesta S, Jimenez A, Hernandez M, Jimenez Cruz J (2001) Prognostic value of DNA ploidy in prostatic cancer. Actas Urol Esp 25: 283–290
Mora LB, Moscinski LC, Diaz JI, Blair P, Cantor AB, Pow-Sang JM (1999) Stage B prostate cancer: correlation of DNA ploidy analysis with histological and clinical parameters. Cancer Control 6:587–591
Murphy GP, Mettlin C, Menck H, Winchester DP, Davidson AM (1994) National patterns of prostate cancer treatment by radical prostatectomy: results of a survey by the American College of Surgeons Commission of Cancer. J Urol 152:1817–1819
Oxley JD, Winkler MH, Parry K, Brewster SF, Abbott C, Gillatt DA (2002) p53 and bcl-2 immunohistochemistry in preoperative biopsies as predictors of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. BJU Int 89:27–32
Quinn DI, Henshall SM, Head DR, Golovsky D Wilson D, Brenner P, Turner J, Delprado W, Finlayson J, Stricker P, Grygiel J, Sutherland R (2000) Prognostic significance of p53 nuclear accumulation in localized prostate cancer treated with radical prostatetomy. Cancer Res 60:1585–1594
Stackhouse GB, Sesterhenn IA, Bauer JJ, Mostofi FK, Connelly RR, Srivastava SK, Moul JW (1999) p53 and bcl-2 immunohistochemistry in pretreatment prostate needle biopsies to predict recurrence of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. J Urol 162:2040–2045
Theodorescu D, Broder SR, Boyd JC, Mills SE, Frierson HF (1997) p53, bcl-2, and retinoblastoma proteins as long term prognostic markers in localized carcinoma of the prostate. J Urol 158:131–137
Uzoaru I, Rubenstein M, Mirochnik Y, Slobodskoy L, Shaw M, Guinan P (1998) An evaluation of the markers p53 and ki-67 for their predictive value in prostate cancer. J Surg Oncol 67:33–37
Vesalainen S, Lipponen P, Nordling S, Talja M, Syrjanen K (1995) Results of the primary treatment in T1-3M0 prostatic adenocarcinoma are dependent on tumour biology. Anticancer Res 15:569–573
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deliveliotis, C., Skolarikos, A., Karayannis, A. et al. The prognostic value of p53 and DNA ploidy following radical prostatectomy. World J Urol 21, 171–176 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-003-0345-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-003-0345-0