Abstract
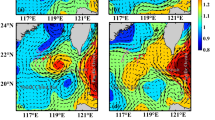
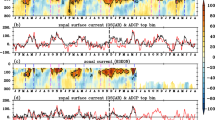
The Bohai Sea is a low-lying semi-enclosed sea area that is linked to the Yellow Sea via the Bohai straits (mixed zone). Its offshore seabed is shallow, which makes it vulnerable to serious marine meteorological disasters associated with the northward passage of Pacific tropical cyclones. Analyses on data of remote sensing and buoy of the mixed zone of the Yellow and Bohai seas indicate that all the wind speed, significant wave height, and salinity (SAL) increased, sea surface temperature decreased, and wind energy density changed considerably during the passage of tropical cyclone Matmo on July 25, 2014. It was found that the SAL inversion layer in the mixed zone of the Yellow and Bohai Seas was caused by the tropical cyclone. Furthermore, it was found that the tropical cyclone transported the northern Yellow Sea cold water mass (NYSCWM) into the mixed zone of the Yellow and Bohai Seas. The NYSCWM has direct influence on both the aquaculture and the ecological environment of the region. Therefore, further research is needed to establish the mechanism behind the formation of the SAL inversion layer in the mixed zone, and to determine the influence of tropical cyclones on the NYSCWM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao X W, Li N, Yao Z G, Wu D X. 2009. Seasonal variation characteristics of temperature and salinity of the North Yellow Sea. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 39(4): 553–562.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Bao X W, Wang C Z, Gao G P, Hung L. 2001. Thermal structural analysis and simulation of the Bohai Sea and the Huanghai Seas. Acta Oceanol ogica Sin ica, 23(6): 24–31.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Cui Y, Song Y L, Yang Q F, Yu H. 1993. The temporal and spatial variation of dissolved oxygen and the relationship between phytoplankton and environmental factors in Bohai Sea. Marine Fisheries Research,(14): 113–118.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Friedman K S, Li X F. 2000. Monitoring hurricanes over the ocean with wide swath SAR. Johns Hopkins University APL Technical Digest, 21(1): 80–85.
Guo J, He Y J, Long X, Hou C W, Liu X, Meng J M. 2015. Repair wind field in oil contaminated areas with SAR images. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 33(2): 525–533.
Guo J, Zhang H, Cui T W, He Y J, Zhang J, Guo K, Hou C W, Liu R J. 2016. Remote sensing observations of the winter Yellow Sea Warm Current invasion into the Bohai Sea, China. Adv ances in Meteorol ogy, 2016: Article ID 8170296.
Guo Q. 2005. Features in Distributions of Nutrients and Chlorophyll and Eutrophication Assessment in the Bohai Sea in Summer. Master Thesis, China Ocean University, Qingdao. p.67.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Jiang B J, Bao X W, Wu D X, Xu J P. 2007. Interannual variation of temperature and salinity of northern Huanghai Sea Cold Water Mass and its probable cause. Acta Oceanol ogica Sin ica, 29(4): 1–10.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Li X B, Sun X Y, Zhang Q F, Niu F X, Yao Z G. 2013a. Seasonal evolution of the Northern Yellow Sea cold water mass. Mar ine Sci ence Bull etin, 15(2): 15–24.
Li X F, Pichel W G, He M X, Wu S Y, Friedman K S, Clemente–Colon P, Zhao C F. 2002. Observation of hurricanegenerated ocean swell refraction at the Gulf Stream north wall with the RADARSAT–1 synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 40(10): 2 131–2 142.
Li X F, Zhang J A, Yang X F, Pichel W G, De Maria M, Long D, Li Z W. 2013b. Tropical cyclone morphology from spaceborne synthetic aperture radar. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 94(2): 215–230.
Li X F. 2015. The first Sentinel–1 SAR image of a typhoon. Acta Oceanol ogica Sin ica, 34(1): 1–2.
Liu L, Fei J F, Lin X P, Zhang L B, Ling C Q, Huang X G, Cheng X P. 2011. Effect of air–sea interaction on Typhoon Kaemi. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 35(3): 444–456.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Mai M R, Zhang B, Li X F, Hwang P A, Zhang J A. 2016. Application of AMSR–E and AMSR2 low–frequency channel brightness temperature data for hurricane wind retrievals. IEEE Trans a ctions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 54(8): 4 501–4 512.
Sheng C Y, Fan S D, Liu S J, Xia F, Rong Y M. 2016. The Matmo typhoon forecast test by Shandong WRF ensemble forecast system. Shandong Weather, 36(1): 1–7.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Su J, Li L, Bao X W, Gao G P. 2001. Numerical experiment of SST response to typhoon process in Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 31(2): 165–172.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Wen L J, Liu G Y, Liu Q R, Ruan C Q, Wang B. 2016. Statistical analysis of tropical cyclones which affected the Bohai Sea during 1960–2013. Ocean Development and Management, 33(8): 84–89.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu W L, Su J. 2007. The impact of typhoons on sea surface temperature in the western North Pacific Ocean. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 37(Sup. ): 17–22.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang B, Perrie W, Zhang J A, Uhlhorn E W, He Y J. 2014a. High resolution hurricane vector winds from C–band dual–polarization SAR observations. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 31(2): 272–286.
Zhang B, Perrie W. 2012. Cross–polarized synthetic aperture radar: a new potential measurement technique for hurricanes. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 93(4): 531–541.
Zhang B, Perrie W. 2014. Recent progress on high wind–speed retrieval from multi–polarization SAR imagery: a review. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 35(11–12): 4 031–4 045.
Zhang G S, Zhang B, Perrie W, Xu Q, He Y J. 2014b. A hurricane tangential wind profile estimation method for C–band cross–polarization SAR. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 52(11): 7 186–7 194.
Zhao Q, Tian J W, Zhao S L, Wu Z K. 2004. Winter and summer chlorophyll a and nutrient distribution and characteristics in the Bohai Sea. Marine Science, 28(4): 34–39.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhuang H B, Gao R Q, Fan W L. 2013. Characteristics of the waves in the effect of tropical cyclone. Meteorological Hydrological and Marine Instrument, 30(2): 30–34.
Acknowledgement
We acknowledge the Rain Rate from Remote Sensing Systems, www.remss.com/storm-watch. Data production is sponsored by NASA Earth Science. The SOAR-EI Project RADARSAT-2 Data and Products of MacDonald, Dettwiler, and Associates Ltd. (Year of acquisition from June 2014 to June 2016)—all rights reserved. RADARSAT is the official trademark of the Canadian Space Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) (No. XDA11020305), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41576032), and the International Cooperation in Key Projects, CAS (Detection of Oil Spill and Its Ecological Impact (No. 133337KYSB20160002)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Ji, D., Hou, C. et al. Impact of tropical cyclone Matmo on mixed zone of the Yellow and Bohai Seas. J. Ocean. Limnol. 36, 1484–1493 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-018-7085-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-018-7085-x