Abstract
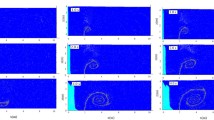
Based on a Lagrangian integral technique and Lagrangian particle-tracking technique, a numerical model was developed to simulate the underwater transport of oil from a deepwater spill. This model comprises two submodels: a plume dynamics model and an advection-diffusion model. The former is used to simulate the stages dominated by the initial jet momentum and plume buoyancy of the spilled oil, while the latter is used to simulate the stage dominated by the ambient current and turbulence. The model validity was verified through comparisons of the model predictions with experimental data from several laboratory flume experiments and a field experiment. To demonstrate the capability of the model further, it was applied to the simulation of a hypothetical oil spill occurring at the seabed of a deepwater oil/gas field in the South China Sea. The results of the simulation would be useful for contingency planning with regard to the emergency response to an underwater oil spill.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Rabeh A H, Cekirge H M, Gunay N. 1989. A stochastic simulation model of oil spill fate and transport. Appl. Math. Model., 13 (6): 322–329.
Bandara U C, Yapa P D. 2011. Bubble sizes, breakup and coalescence in deepwater gas/oil plumes. J. Hy d raul. Eng., 137 (7): 729–738.
Bemporad G A. 1994. Simulation of round buoyant jet in stratified flowing environment. J. Hy d raul. Eng., 120 (5): 529–543.
Bennett J R, Clites A H. 1987. Accuracy of trajectory calculation in a finite-difference circulation model. J. Comput. Phys., 68 (2): 272–282.
Berkowitz B, Cortis A, Dentz M, Scher H. 2006. Modeling non-Fickian transport in geological formations as a continuous time random walk. Rev. Geophys., 44 (2): RG2003, http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2005RG000178.
Bobra M A, Chung P T. 1986. A Catalogue of Oil Properties. Consultchem, Ottawa, Canada.
Boufadel M C, Abdollahi-Nasab A, Geng X L, Galt J, Torlapati J. 2014. Simulation of the Landfall of the deepwater horizon oil on the shorelines of the gulf of Mexico. Environ. Sci. Technol., 48 (16): 9 496–9 505.
Brandvik P J, Johansen Ø, Leirvik F, Farooq U, Daling P S. 2013. Droplet breakup in subsurface oil releases—Part 1: experimental study of droplet breakup and effectiveness of dispersant injection. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 73 (1): 319–326.
Chen F H, Yapa P D. 2003. A model for simulating deep water oil and gas blowouts—Part II: comparison of numerical simulations with “Deepspill” field experiments. J. Hydraul. Res., 41 (4): 353–365.
Chen F H, Yapa P D. 2004. Modeling gas separation from a bent deepwater oil and gas jet/plume. J. Marine Syst., 45 (3-4): 189–203.
Chen F H, Yapa P D. 2007. Estimating the oil droplet size distributions in deepwater oil spills. J. Hygraul. Eng., 133 (2): 197–207.
Cohen Y, Mackay D, Shiu W Y. 1980. Mass transfer rates between oil slicks and water. Can. J. Chem. Eng., 58 (5): 569–575.
Csanady G T. 1973. Turbulent Diffusion in the Environment. Springer Science, Dordrecht, Boston.
Dasanayaka L K, Yapa P D. 2009. Role of plume dynamics phase in a deepwater oil and gas release model. J. Hydro-Environ. Res., 2 (4): 243–253.
Delvigne G A L, Sweeney C E. 1989. Natural dispersion of oil. Oil Chem. Pollut., 4 (4): 281–310.
Delvigne G A L. 1994. Natural and chemical dispersion of oil. J. Adv. Mar. Tech. Conf., 11: 23–40.
Doneker R L, Jirka G H. 1990. Expert system for hydrodynamic mixing zone analysis of conventional and toxic submerged single port discharges (CORMIX1). Technical Report EPA/600/3-90/012, U.S. EPA Environmental Research Laboratory, Athens, Ga.
Elliott A J. 1986. Shear diffusion and the spread of oil in the surface layers of the North Sea. D eu tsch. Hydrogr. Z., 39 (3): 113–137.
Fanneløp T K, Sjøen K. 1980. Hydrodynamics of underwater blowouts. Norweg. Marit. Res., 4: 7–33.
Fischer H B, List J E, Koh R C, Imberger J, Brooks N H. 1979. Mixing in Inland and Coastal Waters. Academic Press, New York.
Frick W E. 1984. Non-empirical closure of the plume equations. Atmos. Environ., 18 (4): 653–662.
Gomez S, Ivorra B, Ramos A M. 2011. Optimization of a pumping ship trajectory to clean oil contamination in the open sea. Math. Comput. Model., 54 (1-2): 477–489.
Guo W J, Wang Y X. 2009. A numerical oil spill model based on a hybrid method. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 58 (5): 726–734.
Hirst E. 1971. Buoyant jets discharged to quiescent stratified ambient. J. Geophys. Res., 76 (30): 7 375–7 384.
Hirst E. 1972. Buoyant jets with three-dimensional trajectories. J. Hydraul. Div., 98 (11): 1 999–2 014.
Huang J C, Monastero F C. 1982. Review of the state-of-theart of oil spill simulation models. Final Report Submitted to the American Petroleum Institute, Raytheon Ocean Systems Company, East Providence, RI.
Hunter J R. 1987. The application of Lagrangian particletracking technique to modelling of dispersant in the sea. In: Noye J ed. Numerical Modelling: Application to Marine Systems. North-Holland.
Jamaluddin A K M, Kalogerakis N, Bishnoi P R. 1991. Hydrate plugging problems in undersea natural gas pipelines under shutdown conditions. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng., 5 (4): 323–335.
Johansen Ø, Brandvik P J, Farooq U. 2013. Droplet breakup in subsea oil releases—Part 2: predictions of droplet size distributions with and without injection of chemical dispersants. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 73 (1): 327–335.
Johansen Ø, Rye H, Cooper C. 2003. DeepSpill-field study of a simulated oil and gas blowout in deep water. Spill Sci. Technol. B ull., 8 (5-6): 433–443.
Johansen Ø, Rye H, Melbye A, Jensen H, Serigstad B, Knutsen T. 2001. Deep Spill JIP Experimental Discharges of Gas and Oil at Helland Hansen, Parts I, II, and III -Technical report. SINTEF Applied Chemistry, Norway.
Johansen Ø. 1984. The Halten Bank experiment-observations and model studies of drift and fate of oil in the marine environment. In: Proceedings of the 11th Arctic Marine Oil Spill Program (AMOP) Technical Seminar. Environment Canada, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. p.18–36.
Johansen Ø. 2000. DeepBlow -a Lagrangian plume model for deep water blowouts. Spill Sci. Technol. B ull., 6 (2): 103–111.
Johansen Ø. 2003. Development and verification of deepwater blowout models. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 47 (9-12): 360–368.
Lee J H W, Cheung V. 1990. Generalized Lagrangian model for buoyant jets in current. J. Environ. Eng., 116 (6): 1 085–1 106.
Li Y, Zhu J, Wang H. 2013. The impact of different vertical diffusion schemes in a three-dimensional oil spill model in the Bohai Sea. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 30 (6): 1 569–1 586.
Lonin S A. 1999. Lagrangian model for oil spill diffusion at sea. Spill Sci. Technol. B ull., 5 (5-6): 331–336.
Masutani M S, Adams E E. 2001. Experimental study of multiphase plumes with application to deep ocean oil spills. Technical report, Hawaii Natural Energy Institute, University of Hawaii, Honolulu.
Mcdougall T J. 1978. Bubble plumes in stratified environments. J. Fluid Mech., 85 (4): 655–672.
Pierson G, Neumann W J Jr. 1966. Principles of Physical Oceanography. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs N J.
Rye H, Brandvik P J, Reed M. 1996. Subsurface oil release field experiment-observations and modelling of subsurface plume behavior. In: Proceedings of the 19th Arctic and Marine Oil Spill Program (AMOP) Technical Seminar, Vol. 2. Environment Canada, Ottawa. p.1 417–1 435.
Rye H, Brandvik P J. 1997. Verification of subsurface oil spill models. In: International Oil Spill Conference Proceedings: April 1997. Environment Canada, Ottawa, 1997 (1): 551–577.
Rye H. 1994. Model for calculation of underwater blow-out plume. In: Proceedings of the Seventeenth Arctic and Marine Oil Spill Program (AMOP), Technical Seminar. Environment Canada, Ottawa. p.849–865.
Schatzmann M. 1979. Calculation of submerged thermal plumes discharged into air and water flows. In: Proc. 18th IAHR Congress. Int. Assoc. for Hydr. Res., Delft, The Netherlands, 4: 379–385.
Schatzmann M. 1981. Mathematical modelling of submerged discharges into coastal waters. In: Proc. 19th IAHR Congress. Int. Assoc. for Hydr. Res., Delft, The Netherlands, 3: 239–246.
Shen H T, Yapa P D, Petroski M E. 1986. Simulation of oil slick transport in Great Lakes connecting channels. Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Clarkson University, Potsdam, NY.
Socolofsky S A, Adams E E, Sherwood C R. 2011. Formation dynamics of subsurface hydrocarbon intrusions following the deepwater Horizon blowout. Geophys. Res. Lett., 38 (9): L09602, http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2011GL047174.
Topham D R. 1975. Hydrodynamics of an oilwell blowout. In: Beaufort Sea Technical Report no.33. Department of the Environment
Victoria, B. C. Wang C H, Li X Y, Lv X Q. 2013. Numerical study on initial field of pollution in the Bohai Sea with an adjoint method. Math. Probl. Eng., 2013, Article ID 104591, 10p.
Wang S D, Shen Y M, Guo Y K, Tang J. 2008. Threedimensional numerical simulation for transport of oil spills in seas. Ocean Eng., 35 (5-6): 503–510.
Yapa P D, Wimalaratne M R, Dissanayake A L, DeGraff J A Jr. 2012. How does oil and gas behave when released in deepwater? J. Hydro-Environ. Res., 6 (4): 275–285.
Yapa P D, Zheng L, Nakata K. 1999. Modeling underwater oil/ gas jets and plumes. J. Hygraul. Eng., 125 (5): 481–491.
Yapa P D, Zheng L. 1997. Simulation of oil spills from under water accidents I: model development. J. Hydraul. Res., 35 (5): 673–688.
Zhao L, Boufadel M C, Socolofsky S A, Adams E, King T, Lee K. 2014a. Evolution of droplets in subsea oil and gas blowouts: development and validation of the numerical model VDROP-J. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 83 (1): 58–69.
Zhao L, Torlapati J, Boufadel M C, King T, Robinson B, Lee K. 2014b. VDROP: a comprehensive model for droplet formation of oils and gases in liquids -Incorporation of the interfacial tension and droplet viscosity. Chem. Eng. J., 253: 93–106.
Zheng L, Yapa P D, Chen F H. 2003. A model for simulating deepwater oil and gas blowouts -Part I: theory and model formulation. J. Hydraul. Res., 41 (4): 339–351.
Zheng L, Yapa P D. 1998. Simulation of oil spills from underwater accidents II: model verification. J. Hydraul. Res., 36 (1): 117–134.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the 12th Five-Year Project of Science and Technology of China National Offshore Oil Corporation “Development of Underwater Oil Spill Numerical Simulation in Deep Water” (No. CNOOC-KJ 125 ZDXM 00 000 00 NFCY 2011-03)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., An, W., You, Y. et al. Modeling underwater transport of oil spilled from deepwater area in the South China Sea. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 34, 245–263 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-015-4230-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-015-4230-7