Abstract
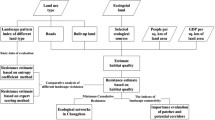
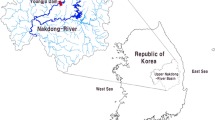
Presently, research is lacking regarding the diagnosis and evaluation of habitat degradation in enclosed bay systems. We established a diagnostic model for enclosed bay habitat degradation (EBHD model) using a multi-approach integrated diagnostic method in consideration of driving force-pressure-state-influence-response. The model optimizes the indicator standardization with annual average change rate of habitat degradation as the basic element, to reflect accurately the impact of the change and speed of degradation on the diagnostic results, to quantify reasonably the contribution of individual diagnostic indicator to habitat degradation, and to solve the issue regarding the influence of subjective factors on the evaluation results during indicator scoring. We then applied the EBHD model for the Sansha Bay in Fujian Province, China, evaluated comprehensively the situation of habitat degradation in the bay, and screened out the major controlling factors in the study area. Results show that the diagnostic results are consistent in overall with the real situation of the study area. Therefore, the EBHD model is advantageous in terms of objectivity and accuracy, making a breakthrough in diagnosis and evaluation for habitat degradation in enclosed bay systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarde R J, Ferreira S M, Kritzinger J J et al. 1996. An evaluation of habitat rehabilitation on coastal dune forests in Northern KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Restoration Ecology, 4(4): 334–345.
Ammar M S A. 2009. Coral reef restoration and artificial reef management, future and economic. Open Environ. Eng. J., 2: 37–49.
Balthis W L, Hyland J L, Scott G I et al. 2002. Sediment quality of the Neuse River estuary, North Carolina: an integrated assessment of sediment contamination, toxicity, and condition of benthic fauna. Journal of Aquatic Ecosystem Stress and Recovery, 9: 213–225.
Cantre R S, Cosner C, Fagan W F. 1998. Competitive reversals inside ecological reserves: the role of external habitat degradation. J. Math. Biol., 37: 491–533.
Carrete M, Tella J L, Blanco G et al. 2009. Effects of habitat degradation on the abundance, richness and diversity of raptors across Neotropical biomes. Biological Conservation, 142: 2 002–2 011.
Chen F, Liu W K, Chen R X et al. 1994. Chinese Bays (The seventh volume). Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Du X J, Gao X M, Ma K P. 2003. Diagnosis of the degree of degradation of an ecosystem: the basis and precondition of ecological restoration. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 27(5): 700–708. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FAO. 2010. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2010. Rome: FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department.
Feng H Y, He L P, Chang H et al. 2010. Diagnosis of the ecosyetem degradation degree of the wetlands in Binhai New Area. Environmental Science and Management, 35(9): 99–104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Filho W L ed. 2012. Climate Change and the Sustainable Use of Water Resources, Climate Change Management. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-22266-5_15, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Foluso O A, Bamidele I et al. 2012. Fuzzy logic modeling of bioaccumulation pattern of metals in coastal biota of Ondo State, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess., 184: 89–102.
Fujian Provincial Ocean and Fisheries Monitoring Center, 2012a. Survey Data of Major Bays in Fujian Province. Fujian Provincial Ocean and Fisheries Monitoring Center, China. Internal report. (in Chinese)
Fujian Provincial Ocean and Fisheries Monitoring Center. 2012b. Reports on Monitoring of Total Pollution Discharge from Rivers into the Sea and the Ecological Monitoring Area of Sansha Bay in 2012. Fujian Provincial Ocean and Fisheries Monitoring Center, China. Internal report. (in Chinese)
Han M, Sun Y N, Xu S G. 2007. Characteristics and driving factors of marsh changes in Zhalong wetland of China. Environ. Monit. Assess., 127: 363–381.
Harry W P. 2011. Fish parasites as biological indicators in a changing world: Can we monitor environmental impact and climate change? In: Mehlhorn H ed. Progress in Parasitology, Parasitology Research Monographs 2, Chapter 12, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21396-0_12, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Henrik E, Sander E L, Charles L R et al. 2010. Urban transitions: on urban resilience and human-dominated ecosystems. AMBIO, 39: 531–545.
Jiang C L, Chen Q H, Shi N et al. 2006. The Mathematical Modeling and Environmental Research of Bays in Fujian Province. Ocean Development Management of Fujian Province, China. Internal data. (in Chinese)
Jorge B, José A, Rafael S et al. 2008. Environmental indicators GIS of the Catalan coast. J. Coast. Conserv., 11(4): 185–191.
Lancelot C, Gypens N, Billen G et al. 2007. Testing an integrated river-ocean mathematical tool for linking marine eutrophication to land use: the Phaeocystisdominated Belgian coastal zone (Southern North Sea) over the past 50 years. Journal of Marine Systems, 64: 216–228.
Lei K, Meng W, Zheng B H et al. 2009. Diagnosing coastal zone habitat degradation in the Bohai Bay. Research of Environmental Sciences, 22(12): 1 361–1 365. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lin H S, Chen B Q, Xu D W et al. 2012. Assessment of coastal wetland ecosystem health based on the press-stateresponse model: a case study on Liaohe delta. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 31(3): 420–428. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ling Z Y, Yang G Z, Feng Y S. 2011. Construction of degradation diagnosis system for the ecosystems in Dongtan coastal zone of Chongming, Shanghai. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22(2): 513–518. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu Y, Liu R G, Ge Q S. 2010. Evaluating the vegetation destruction and recovery of Wenchuan earthquake using MODIS data. Nat. Hazards, 54: 851–862.
Longdill P C, Healy T R, Black K P. 2008. An integrated GIS approach for sustainable aquaculture management area site selection. Ocean & Coastal Management, 51: 612–624.
Meng W. 2009. Coastal Habitat Degradation Diagnostic Techniques: the Bohai Sea Coastal Zone Typical. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Ningde Statistical Bureau. 2000. Ningde Statistical Yearbook. China Statistics Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Ningde Statistical Bureau. 2007. Ningde Statistical Yearbook. China Statistics Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Ningde Statistical Bureau. 2012. Ningde Statistical Yearbook. China Statistics Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Nouri J, Fatemi M R, Danekar A, Fahimi F G, Karimi D. 2009. Determination of environmentally sensitive zones along Persian Gulf coastlines through geographic information system. Journal of Food Agriculture & Environment, 7(2): 718–725.
Orfanidis S, Panayotidis P, Stamatis N. 2001. Ecological evaluation of transitional and coastal waters: a marine benthic macrophytes-based model. Mediterranean Mar. Sci., 2(2): 45–65.
Orfanidis S, Panayotidis P, Stamatis N. 2003. An insight to ecological evaluation index (EEI). Ecol. Indic., 3(1): 27–33.
Ou W X, Yang G S. 2003. Progress in the study on coastal environment evolvement consequence of land/cover change. Progress in Geography, 22(4): 360–368. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ray G L. 1994. A Conceptual Framework for the Evaluation of Coastal Habitats. Technical Report, Environmental Impact Research Program (U.S.), United States. Army. Corps of Engineers, US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station.
Ren P, Cheng W X, Hong B T et al. 2013. Evaluation of ecosystem degradation threat and study of spatial distribution in the upper reaches of the Changjiang River based on PSDR framework. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 33(2): 189–194. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Rodriguez I, Montoya I, SanchezM J, Carreno F. 2009. Geographic information systems applied to integrated coastal zone management. Geomorphology, 107: 100–105.
Santos R G, Martins A S, da Nobrega Farias J et al. 2011. Coastal habitat degradation and green sea turtle diets in Southeastern Brazil. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62: 1 297–1 302.
Shahbudin S, Zuhairi A, Kamaruzzaman B Y. 2012. Impact of coastal development on mangrove cover in Kilim River, Langkawi Island, Malaysia. Journal of Forestry Research, 23(2): 185–190.
Shao J X, Zhang F T, Su W C et al. 2011. Diagnosis of karst ecological landscape degradation based on set of analysis—a case study in Bijie. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 18(4): 11–15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Shields F D, Knight S S, Cooper C M. 1995. Use of the index of biotic integrity to assess physical habitat degradation in warm water streams. Hydrobiologia, 312: 191–208.
Singaraja C, Chidambaram S, Prasanna M V et al. 2012. A study on the behavior of the dissolved oxygen in the shallow coastal wells of Cuddalore District, Tamilnadu, India. Water Qual. Expo. Health, 4(1): 1–16.
Steffen M, Estes M, Al-Hamdan M. 2010. Using Remote Sensing Data to Evaluate Habitat Loss in the Mobile, Galveston, and Tampa Bay Watersheds. Coastal Education and Research Foundation, p.24. Available in http://weather.msfc.nasa.gov/applied_science/Wetland_Paper_Final.pdf. Accessed on 2013-05-20.
Tai Y D, Su D, Liu Y B et al. 2009. Degradation mechanisms of Red Beach landscape in Shuangtaizi Estuary National Reserve. Environmental Pollution and Control, 31(1): 17–20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Todd P A, Ong X Y, Chou L M. 2010. Impacts of pollution on marine life in Southeast Asia. Biodivers Conserv., 19: 1 063–1 082.
Turner S J, Thrush S F, Hewitt J E et al. 1999. Fishing impacts and the degradation or loss of habitat structure. Fisheries Management and Ecology, 6: 401–420.
US Fish and Wildlife Service. 1980. Habitat Evaluation Procedure. US Fish and Wildlife Service, Washington DC
Vogiatzakis I N, Mannion A M, Griffiths G H. 2006. Mediterranean ecosystems: problems and tools for conservation. Progress in Physical Geography, 30: 175–200.
Yang Y F, Li C H, Nie X P et al. 2004. Development of mariculture and its impacts in Chinese coastal waters. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 14(1): 1–10.
Yu G, Sun P, Liu G X et al. 2013. Diagnostic model construction and example analysis of habitat degradation in enclosed bay: II. spatiotemporal variations in habitat degradation in Sansha Bay. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00343-014-3219-y.
Zhang L B, Yang H S. 2012. Advances in principles and techniques of marine habitat restoration and biological resource conservation. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences. 24(9): 1 062–1 069. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang M. 2001. A study on the degraded gulf ecosystem of the coastal area—Taking the case of Meizhou Gulf. Fujian Geography, 16(2): 5–8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu Y L, Guo Z Y, Ye S F et al. 2011. Construction of degradation diagnosis system for the ecosystem in Dongtan coastal zone of Chongming, Shanghai. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22(2): 513–518. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Projects of Public Science and Technology Research Funds of Ocean Sector of China (No. 201205009) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41201569)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, G., Sun, P., Liu, G. et al. Diagnostic model construction and example analysis of habitat degradation in enclosed bay: I. diagnostic model construction. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 32, 626–635 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-014-3217-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-014-3217-0