Abstract
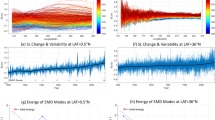
For understanding more about the water exchange between the Kuroshio and the East China Sea, We studied the variability of the Kuroshio in the East China Sea (ECS) in the period of 1991 to 2008 using a three-dimensional circulation model, and calculated Kuroshio onshore volume transport in the ECS at the minimum of 0.48 Sv (1 Sv ≡ 106 m3/s) in summer and the maximum of 1.69 Sv in winter. Based on the data of WOA05 and NCEP, The modeled result indicates that the Kuroshio transport east of Taiwan Island decreased since 2000. Lateral movements tended to be stronger at two ends of the Kuroshio in the ECS than that of the middle segment. In addition, we applied a spectral mixture model (SMM) to determine the exchange zone between the Kuroshio and the shelf water of the ECS. The result reveals a significantly negative correlation (coefficient of −0.78) between the area of exchange zone and the Kuroshio onshore transport at 200 m isobath in the ECS. This conclusion brings a new view for the water exchange between the Kuroshio and the East China Sea. Additional to annual and semi-annual signals, intra-seasonal signal of probably the Pacific origin may trigger the events of Kuroshio intrusion and exchange in the ECS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Andres M, Wimbush M, Park J H et al. 2008. Observations of Kuroshio flow variations in the East China Sea, J. Geophys. Res., 113(C05013), doi: 10.1029/2007JC004200.
Batchelor G K. 1967. An Introduction to Fluid Dynamic. Cambridge Univ. Press, London, U. K. p. 156–164.
Chai F, Liu G, Xue H et al. 2009. Seasonal and interannual variability of carbon cycle in South China Sea: A three-dimensional physical-biogeochemical modeling study. J. Oceanogr., 65: 703–720.
Chen C, Rou R, Paid S C et al. 1995. Exchange of water masses between the East-China-Sea and the Kuroshio off Northeastern Taiwan. Cont. Shelf Res., 15(1): 19–39.
Chen H, Yuan Y, Feng H. 2006. The multi-core structure of the main part of the Kuroshio at G-PN section in the East China Sea. Chinese Sci. Bull., 51(6): 738–746.
Chern C S, Wang J, Wang D P. 1990. The exchange of Kuroshio and East China Sea shelf water. J. Geophys. Res., 95(C9): 16 017–16 023.
Chuang W S, Liang W D. 1994. Seasonal variability of intrusion of the Kuroshio water across the continental shelf northeast of Taiwan. J. Oceanogr., 50(5): 531–542.
Clancy L J. 1975. Aerodynamics. Halsted Press, New York, U.S.A. p. 71–72.
Fukuoka J. 1957. A note on the westward intensification of ocean current. Records of Oceanographic Works in Japan, 1: 7–8.
Guan B. 1980. Some results from the study of the variation of the Kuroshio in the East China Sea. In: the Kuroshio I V ed. Saikon Publ., Tokyo, Japan, p. 897–911.
Guo X, Hukuda H, Miyazawa Y et al. 2003. A triply nested ocean model for simulating the Kuroshio - roles of horizontal resolution on JEBAR. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 33(1): 146–169.
Guo X, Miyazawa Y, Yamagata T. 2006. The Kuroshio onshore intrusion along the shelf break of the East China Sea: The origin of the Tsushima Warm Current. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 36(12): 2205–2231.
Hu P, Hou Y, Le K et al. 2007. Study advances on the Kuroshio in the East China Sea and currents in the region east of Ryukyu islands. Studio. Marina Sinica, 1(00): 28–34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Imasato N, Qiu B. 1987. An event in water exchange between continental-shelf and the Kuroshio off southern Japan - lagrangian tracking of a low-salinity water mass on the Kuroshio. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 17(7): 953–968.
Isobe A. 2008. Recent advances in ocean-circulation research on the Yellow Sea and East China Sea shelves. J. Oceanogr., 64: 569–584.
Isobe A, Beardsley R C. 2006. An estimate of the cross-frontal transport at the shelf break of the East China Sea with the Finite Volume Coastal Ocean Model. J. Oceanogr., 111(C0312), doi: 10.1029/2005JC003290.
James C, Wimbush M, Ichikawa H. 1999. Kuroshio meanders in the East China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 29(2): 259–272.
Jan S, Sheu D, Kuo H. 2006. Water mass and throughflow transport variability in the Taiwan Strait. J. Geophys. Res., 111(C12012), doi: 10.1029/2006JC003656.
Jia Y, Liu Q, Liu W. 2005. Primary study of the mechanism of eddy shedding from the Kuroshio bend in Luzon Strait. J. Oceanogr., 61(6): 1 017–1 027.
Jitendra M, Serge B, Thomas L et al. 2001. Contour and texture analysis for image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 43(1): 7–27.
Johns W E, Lee T, Zhang D et al. 2001. The Kuroshio east of Taiwan: Moored transport observations from the WOCE PCM-1 array. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 31(4): 1031–1053.
Km K R, Cho Y K, Kang D J et al. 2005. The origin of the Tsushima Current based on oxygen isotope measurement. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32(3): L3602.
Lai J, Huang T J, Liaw Y C 2009. A fast k-means clustering algorithm using cluster center displacement. Pattern Recogn., 42(11): 2551–2 556.
Lan Y C, Lee M A, Liao C H et al. 2009. Copepod community structure of the winter frontal zone induced by the Kuroshio branch current and the China coastal current in the Taiwan strait. Journal of Marine Science and Technology-Taiwan, 17(1): 1–6.
Large W, McWilliams J C, Doney S C et al. 1994. Oceanic vertical mixing - A review and a model with a nonlocal boundary-layer parameterization. Rev. Geophys., 32(4): 363–403.
Lee J S, Matsuno T. 2007. Intrusion of Kuroshio water onto the continental shelf of the East China Sea. J. Oceanogr., 63(2): 309–325.
Li F, Xie J, Li Y. 2004. New methods of fitting the membership function of oceanic water masses. Journal of Ocean University of China (English Edition), 3(1): 1–9.
Li G X, Han X, Yue S et al. 2006. Monthly variations of water masses in the East China Seas. Cont. Shelf Res., 26(16): 1954–1970.
Lin S, Hsieh I J, Huang K M et al. 2002. Influence of the Yangtze River and grain size on the spatial variations of heavy metals and organic carbon in the East China Sea continental shelf sediments. Chem. Geol., 182(2): 377–394.
Lin S F, Tang T Y, Jan S et al. 2005. Taiwan Strait current in winter. Cont. Shelf Res., 25(9): 1023–1042.
Liu G M, Chai F. 2009a. Seasonal and interannual variation of physical and biological processes during 1994–2001 in the Japan/East Sea: a three-dimensional physical-biogeochemical modeling study. J. Marine Syst., 66(2): 420–431.
Liu G M, Chai F. 2009b. Seasonal and interannual variability of primary and export production in South China Sea: A three-dimensional physical-biogeochemical model study. J. Marine Sci., 78(2): 265–277.
Luo B, Richard C W, Edwin R H et al. 2003. Spectral clustering of graphs. Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, Proceedings, 2756: 540–548.
Ma C, Wu D X, Lin X P. 2009. Variability of surface velocity in the Kuroshio Current and adjacent waters derived from Argos drifter buoys and satellite altimeter data. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol., 27(2): 208–217.
Matsuno T, Lee J S, Yanao S. 2009. The Kuroshio exchange with the South and East China Seas. Ocean Sci., 5(3): 303–312.
Menschaert G, Tom T, Bart L et al. 2009. Spectral clustering in peptidomics studies helps to unravel modification profile of biologically active peptides and enhances peptide identification rate. Proteomics, 9(18): 4381–4388.
Miller A R. 1950. A study of mixing processes over the edge of the continental shelf. J. Mar. Res, 9(2): 145–160.
Mizuno K, White W B. 1983. Annual and interannual variability in the Kuroshio current system. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 13(10): 1 847–1 867.
Morimoto A, Kojima S, Jan S et al. 2009. Movement of the Kuroshio axis to the northeast shelf of Taiwan during typhoon events. Estuar. Coast. Shelf S., 82(3): 547–552.
Ng A Y, Jordan M I, Weiss Y. 2002. On spectral clustering: Analysis and an algorithm. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 14(1–2): 849–856.
Nitani H. 1972. Beginning of the Kuroshio. In: Kuroshio, Physical Aspects of the Japan Current. Univ. of Wash. Press, Seattle Wash., U.S.A. p. 129–164.
Shchepetkin A F, McWilliams J C. 1998. Quasi-monotone advection schemes based on explicit locally adaptive dissipation. Mon. Weather Rev., 126(6): 1 541–1 580.
Shchepetkin A F, McWilliams J C. 2003. A method for computing horizontal pressure-gradient force in an oceanic model with a nonaligned vertical coordinate. J. Geophys. Res., 108(C3), doi: 10.1029/2001JC001047.
Shchepetkin A F, McWilliams J C. 2005. The regional oceanic modeling system (ROMS): a split-explicit, free-surface, topography-following-coordinate oceanic model. Ocean Modelling, 9(4): 347–404.
Shi J, Malik J. 2000. The 20th anniversary of the IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence. Ieee T. Pattern Anal, 22(1): 1–3.
Spall M A. 1995. Frontogenesis, subduction, and cross-front exchange at upper ocean fronts. J. Geophys. Res., 100(2): 2543–2 558.
Stommel H. 1948. The westward intensification of wind-driven ocean currents. Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union, 29(2): 202–206.
Su Y, Yu Z, Li F. 1983. Application of cluster analysis method for analyzing the water-masses in the shallow water area and the analysis of modified water masses in the Huanghai Sea and the East China Sea. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol., 14(1): 1–13.
Sverdrup H U, Johnson M W, Fleming R H. 1942. The Oceans, their Physics, Chemistry and General Biology. Pretince-Hall, New York, U.S.A. p. 16–64.
Takikawa T, Morimoto A, Onitsuka G et al. 2008. Characteristics of water mass under the surface mixed layer in Tsushima Straits and the southwestern Japan Sea in autumn. J. Oceanogr., 64(4): 585–594.
Tang T Y, Yang Y J. 1993. Low frequency current variability on the shelf break northeast of Taiwan. J. Oceanogr., 49(2): 193–210.
Teague W J, Jacobs G A, Ko D S et al. 2003. Connectivity of the Taiwan, Cheju, and Korea straits. Cont. Shelf Res., 23(1): 63–77.
Tong M R, Liu Z H, Sun C H et al. 2003. An analysis of data Quality Control Process of the ARGO Profiling Buoy. Ocean Technology, 22(4): 79–84.
Ulrike L. 2007. A tutorial on spectral clustering. Stat. Comput., 17(4): 395–416.
Wang S L, Chen C, Hong G H et al. 2000. Carbon dioxide and related parameters in the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res., 20(4–5): 525–544.
Wei L, Liu Q, Jia Y. 2004. The Kuroshio transport east of Taiwan and the sea surface height anomaly from the Interior ocean. Journal of Ocean University of China (Oceanic and Coastal Sea Research), 3(2): 135–140.
Wong G, Chao S Y, Li Y H et al. 2000. The Kuroshio edge exchange processes (KEEP) study — an introduction to hypotheses and highlights. Cont. Shelf Res., 20(4–5): 335–347.
Xiu P, Chai F, Shi L, Xue H et al. 2010. A census of eddy activities in the South China Sea during 1993–2007. J. Geophys. Res., 115(C03012), doi: 10.1029/2009JC005657.
Yanagi T., S. Takahashi. 1993. Seasonal variation of circulations in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. J. Oceanogr., 49: 503–520.
Yang J. 2007. An oceanic current against the wind: How does Taiwan island steer warm water into the East China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 37(10): 2 563–2 569.
Yuan Y, Liu Y, Su J. Variability of the Kuroshio in the East China Sea during El-Nino to La-Nina phenomenon of 1997 and 1998. Chinese J. Geophys., 44(2): 199–210.
Zhou H, Xu J, Guo P et al. 2006. A summary on studies of western boundary current system in the North Pacific Ocean. J. Marine Sci., 24(2): 49–59.
Zuo T, Wang R, Chen Y Q et al. 2006. Autumn net copepod abundance and assemblages in relation to water masses on the continental shelf of the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. J. Marine Syst., 59(1–2): 159–172.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (Nos. 2005CB422300, 2007CB411804, 2010CB428904), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 40976001, 40940025, 41006002), Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Commission Project (No. 09JCYBJC07400), the “111 Project“ (No. B07036), and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NECT-07-0781)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Xue, H., Bao, X. et al. A spectral mixture model analysis of the Kuroshio variability and the water exchange between the Kuroshio and the East China Sea. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 29, 446–459 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-011-0114-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-011-0114-7