Abstract.
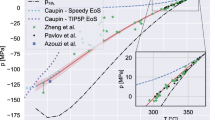
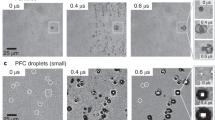
The finite element method is employed to analyze photoacoustic cavitation and heat transfer occurring when modest temperature jumps (T-jumps) are induced by a laser in D2O solution, which may contain a small concentration of a protein or peptide sample. Cavitation can be initiated through a photoacoustic mechanism at intensities well below optical breakdown thresholds. Cavitation probability is related to test medium properties, initial temperature, T-jump magnitude and test region geometry. Parameters affecting thermal conduction losses are also examined because such losses limit the useful duration of the T-jump induced in protein folding experiments. From this study, guidelines are offered for reducing the occurrence of cavitation and extending the useful duration of the T-jump.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 2 April 2001 / Revised version: 17 October 2001 / Published online: 29 November 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wray, W., Aida, T. & Dyer, R. Photoacoustic cavitation and heat transfer effects in the laser-induced temperature jump in water. Appl Phys B 74, 57–66 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400100752
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400100752