Abstract.
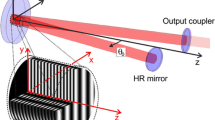
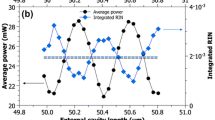
We recently demonstrated that passive mode locking of a thin-disk Yb:YAG laser is possible and that this concept leads to sources of femtosecond pulses with very high average power. Here we discuss in detail the effect of spatial hole burning on the mode-locking behavior of such lasers. We have developed an efficient numerical model and arrive at quantitative stability criteria which agree well with experimental data. The main result is that stable soliton mode locking can in general be obtained only in a certain range of pulse durations. We use our model to investigate the influence of various cavity parameters and the situation for different gain media. We also consider several methods to reduce the effect of spatial hole burning in order to expand the range of possible pulse durations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 September 2000 / Published online: 10 January 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paschotta, R., Aus der Au, J., Spühler, G. et al. Passive mode locking of thin-disk lasers: effects of spatial hole burning . Appl Phys B 72, 267–278 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400100486
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400100486