2
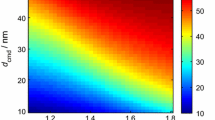
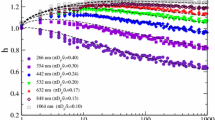
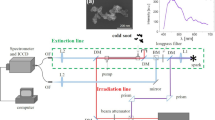
at 1064 nm, vaporization/fragmentation of soot primary particles and aggregates occurs. Optical measurements are performed using a second laser pulse to probe the effects of these changes upon the LII signal. With the exception of very low fluences, the structural changes induced in the soot lead to a decreased LII intensity produced by the second laser pulse. These two-pulse experiments also show that these changes do not alter the LII signal on timescales less than 1 μs for fluences below the vaporization threshold.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 October 1997/Revised version: 16 February 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vander Wal, R., Ticich, T. & Stephens, A. Optical and microscopy investigations of soot structure alterations by laser-induced incandescence . Appl Phys B 67, 115–123 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400050483
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400050483