Abstract
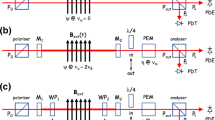
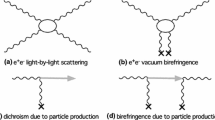
In vacuum high-intensity lasers can cause photon–photon interaction via the process of virtual vacuum polarization which may be measured by the phase velocity shift of photons across intense fields. In the optical frequency domain, the photon–photon interaction is polarization-mediated described by the Euler–Heisenberg effective action. This theory predicts the vacuum birefringence or polarization dependence of the phase velocity shift arising from nonlinear properties in quantum electrodynamics (QED). We suggest a method to measure the vacuum birefringence under intense optical laser fields based on the absolute phase velocity shift by phase-contrast Fourier imaging. The method may serve for observing effects even beyond the QED vacuum polarization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Heisenberg, H. Euler, Z. Phys. 98, 714 (1936). [arXiv:physics/0605038]
V. Weisskopf, Kong. Dans. Vid. Selsk. Math-fys. Medd. XIV, 166 (1936)
J. Schwinger, Phys. Rev. 82, 664 (1951)
J.S. Toll, The dispersion relation for light and its application to problems involving electron pairs. Dissertation, Princeton, 1952
N.B. Narozhnyi, Sov. Phys. JETP 28, 371 (1969)
V.I. Ritus, Ann. Phys. 69, 555 (1972)
W. Dittrich, H. Gies, Probing the Quantum Vacuum (Springer, Berlin, 2000)
G.M. Shore, Nucl. Phys. B 778, 219 (2007). [arXiv:hep-th/0701185]
T. Heinzl, A. Ilderton, Eur. Phys. J. D 55, 359 (2009). [arXiv:0811.1960 [hep-ph]]
G.V. Dunne, H. Gies, R. Schützhold, Phys. Rev. D 80, 111301 (2009). [arXiv:0908.0948 [hep-ph]]
V.N. Baier, V.M. Katkov, Phys. Lett. A 374, 2201 (2010). [arXiv:0912.5250 [hep-ph]]
N.B. Narozhny, Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 54, 676 (1968)
R. Schützhold, H. Gies, G. Dunne, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 130404 (2008). [arXiv:0807.0754 [hep-th]]
N.B. Norozhny, Sov. Phys. JETP 27, 360 (1968)
B. Marx, I. Uschmann, S. Höfer, R. Lötzsch, O. Werhrhan, E. Förster, M. Kaluza, T. Stöhlker, H. Gies, C. Detlefs, T. Roth, J. Härtwig, G.G. Paulus, Opt. Commun. 284, 915 (2011)
J. Rafelski, H.-T. Elze, Electromagnetic fields in the QCD vacuum, hep-ph/9806389
H.-T. Elze, B. Müller, J. Rafelski, Interfering QCD/QED vacuum polarization, hep-ph/9811372
J.M. Maldacena, Adv. Theor. Math. Phys. 2, 231 (1998) [Int. J. Theor. Phys. 38, 1113 (1999)] [arXiv:hep-th/9711200]
O. Aharony, S.S. Gubser, J.M. Maldacena, H. Ooguri, Y. Oz, Phys. Rep. 323, 183 (2000). [arXiv:hep-th/9905111]
A.V. Zayakin, Properties of the vacuum in models for QCD: holography vs. resummed field theory: a comparative study, PhD Thesis, LMU Munich, 2010
E. Zavattini, G. Zavattini, G. Ruoso, G. Raiteri, E. Polacco, E. Milotti, V. Lozza, M. Karuza, U. Gastaldi, G. Di Domenico, F. Della Valle, R. Cimino, S. Carusotto, G. Cantatore, M. Bregant, Phys. Rev. D 77, 032006 (2008). [arXiv:0706.3419 [hep-ex]]
A.N. Luiten, J.C. Petersen, Phys. Rev. A 70, 033801 (2004)
A. Di Piazza, K.Z. Hatsagortsyan, C.H. Keitel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 083603 (2006). [arXiv:hep-ph/0602039]
B. King, A. Di Piazza, C.H. Keitel, Nat. Photonics 4, 92 (2010)
A.E. Siegman, Lasers (University Science Books, California, 1986)
A. Yariv, Optical Electronics in Modern Communications (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1997)
J.W. Goodman, Introduction to Fourie Optics, Mcgraw-Hill Classic Textbook Reissue (McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 1997)
R. Karplus, M. Neuman, Phys. Rev. 83, 776 (1950)
B. De Tollis, Nuovo Cimento 32, 757 (1964)
B. De Tollis, Nuovo Cimento 35, 1182 (1965)
C. Amsler et al. (Particle Data Group), Phys. Lett. B 667, 1 (2008) and 2009 partial update for the 2010 edition
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Homma, K., Habs, D. & Tajima, T. Probing vacuum birefringence by phase-contrast Fourier imaging under fields of high-intensity lasers. Appl. Phys. B 104, 769–782 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-011-4568-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-011-4568-2