Abstract
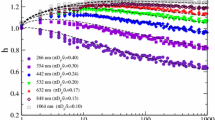
The refractive index of soot is an essential parameter for its optical diagnostics. It is necessary for quantitative interpretation of LII (Laser Induced Incandescence) signals, light scattering or extinction measurements as well as for emissivity calculations. The most cited values have been determined by intrusive methods or without taking into account the soot size distribution and its specific morphology. In the present study, soot generated by the combustion of diesel and diesel/rapeseed methyl ester (RME) mixture (70% diesel and 30% RME) are extensively characterized by taking into account the morphology, the aggregate size distribution, the mass fraction and the spectral dispersion of light. The refractive index m for wavelengths λ between 300 and 1000 nm is determined for diesel and diester fuels by both in-situ and ex-situ methods. The ex-situ method is based on the interpretation of extinction spectra by taking into account soot sizes and fractal morphology with the RDG-FA (Rayleigh–Debye–Gans for Fractal Aggregate) theory. The in-situ approach is based on the comparison of the LII signals obtained with two different excitation wavelengths. The absorption function E(m) and the scattering function F(m) are examined. This study reveals similar optical properties of soot particles generated by both studied fuels even at ambient and flame temperatures. The function E(m) is shown to reach a maximum for λ=250 nm and to tend toward a plateau-like behavior close to E(m)=0.3 for higher wavelength (600<λ (nm)<1000). The function F(m) is found to be quite constant for 400<λ (nm)<1000 and equal to 0.31.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Constant used for Single Scattering Albedo characterization
- B m−1 :
-
Constant used for Single Scattering Albedo characterization
- c ms−1 :
-
Speed of the light
- C abs m2 :
-
Absorption parameter used in RDG-FA
- C s kg m−3 :
-
Particles mass concentration (TEOM measurement)
- C sca m2 :
-
Scattering parameter used in RDG-FA
- D m:
-
Diaphragm/flame distance D in LII setup
- d f :
-
Fractal dimension
- D g m:
-
Soot particle gyration diameter
- D p m:
-
Soot primary particles (monomer) diameter (mode of the distribution)
- D m m:
-
Electrical mobility diameter of the particle (SMPS measurement)
- e C:
-
Electron charge
- E(m):
-
Absorption function, derive from optical index
- E laser J:
-
Total energy of the laser pulse radiation
- E p J:
-
Total energy absorbed by a single soot particle
- F(m):
-
Scattering function, derive from optical index
- f laser Jm−2 :
-
Laser fluence (taken at 1/e 2)
- f v :
-
Volume fraction
- g i s−1 :
-
Damping constants of bound electrons
- g c s−1 :
-
Damping constants of bound and free electrons
- h J s:
-
Planck constant
- H A W:
-
Absorbed power of a single soot particle
- k B J K−1 :
-
Boltzmann constant
- K e :
-
Dimensionless extinction coefficient
- K ext m−1 :
-
Extinction coefficient
- k f :
-
Fractal prefactor
- l m:
-
Mean free path of conduction electrons
- L m:
-
Optical path length
- L a m:
-
Aggregate maximum projected length on TEM pictures
- m=n−ik :
-
Optical index
- m ∗ kg:
-
The effective electron mass
- m v kg:
-
The electron mass in vacuum
- M abs m−3 :
-
Mean number of primary particle/momentum used for absorption calculation
- M sca m−3 :
-
Quasi-momentum used for scattering calculation
- N agg m−3 :
-
Number of particles by unit volume
- n c m−3 :
-
Free electron number density
- n i m−3 :
-
Bound electron number density
- n t m−3 :
-
Total number densities
- N p :
-
Number of primary particles in an aggregate
- Q abs :
-
Soot absorption efficiency
- q λ W m−2 :
-
Laser irradiance
- R g =D g /2 m:
-
Particle gyration radius
- R p =D p /2 m:
-
Soot primary particle radius
- S laser m2 :
-
Laser pulse cross-sectional area
- T K:
-
Flame temperature
- T p K:
-
Particle temperature
- x,y,z m:
-
Spatial coordinates
- Diester:
-
Diesel/RME mixture
- Dil:
-
Dilution ratio of the aerosol sampling in flame
- DLCA:
-
Diffusion Limited Cluster-Cluster Aggregation
- FPS:
-
Fine Particle Sampling system
- HAB:
-
Height Above the Burner
- LIF:
-
Laser Induced Fluorescence
- LII:
-
Laser Induced Incandescence
- PAH:
-
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon
- RDG-FA:
-
Rayleigh-Debye-Gans for Fractal Aggregate
- RME:
-
Rapeseed Methyl Ester
- SMPS:
-
Scanning Mobility Particle Sizer
- SSA:
-
Single Scattering Albedo
- TEM:
-
Transmission Electron Microscopy
- λ em m:
-
The particle emission wavelength
- Δλ em m:
-
Detection spectral-range of the measured LII signal
- Δt s:
-
Laser pulse duration
- α corr :
-
Mass concentration correction factor
- ε 0 :
-
Permittivity constant in vacuum
- λ m:
-
Detection wavelength (ex-situ method)
- λ laser, λ i , λ j m:
-
Wavelength of the laser light (in-situ method)
- ρ kg m−3 :
-
The soot material density
- σ λ m2 :
-
Absorption cross-section at a given wavelength
- σ p m:
-
Standard deviation of the Gaussian primary particle size distribution
- σ s m2 kg−1 :
-
Soot specific extinction
- ω s−1 :
-
Excitation frequency
- ω i s−1 :
-
Natural frequency of bound electrons
References
T.C. Bond, R.W. Bergstrom, Aerosol Sci. Technol. 40, 27 (2006)
C.M. Sorensen, Aerosol Sci. Technol. 35, 648 (2001)
K. Smyth, C. Shaddix, Combust. Flame 107, 314 (1996)
W.H. Dalzell, A.F. Sarofim, J. Heat Transf. 91, 100 (1969)
S. Lee, C. Tien, Symp., Int., Combust. 18, 1159 (1981)
Z.G. Habib, P. Vervisch, Combust. Sci. Technol. 59, 261 (1988)
T. Charalampopoulos, H. Chang, B. Stagg, Fuel 68, 1173 (1989)
G. Schkolnik, D. Chand, A. Hoffer, M. Andreae, C. Erlick, E. Swietlicki, Y. Rudich, Atmos. Environ. 41, 1107 (2007)
I. AyrancI, R. Vaillon, N. Selçuk, F. André, D. Escudié, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 104, 266 (2007)
J. Mullins, A. Williams, Fuel 66, 277 (1987)
R. Julien, R. Botet, Aggregation and Fractal Aggregates (World Scientific, Singapore, 1987)
C.M. Megaridis, R.A. Dobbins, Combust. Sci. Technol. 71, 95 (1990)
Ü.Ö. Köylü, G.M. Faeth, T.L. Farias, M.G. Carvalho, Combust. Flame 100, 621 (1995)
R. Dobbins, G. Mulholland, N. Bryner, Atmos. Environ. 28, 889 (1994)
S.S. Krishnan, K. Lin, G.M. Faeth, J. Heat Transf. 122, 517 (2000)
P. Van-Hulle, M. Talbaut, M. Weill, A. Coppalle, Meas. Sci. Technol. 13, 375 (2002)
F.X. Ouf, Caractérisation des aerosols émis lors d’un incendie. Thesis, IRSN-Université de Rouen, France (2006)
M. Maugendre, J. Yon, A. Coppalle, F. Ouf, in Eurotherm—5th European Thermal-Sciences Conference, Eindhoven, the Netherlands (2008)
T. Williams, C. Shaddix, K. Jensen, J. Suo-Anttila, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 1616 (2007)
M. Schnaiter, H. Horvath, O. Möhler, K. Naumann, H. Saathoff, O.W. Schöck, J. Aerosol Sci. 34, 1421 (2003)
S. Krishnan, K. Lin, G. Faeth, ASME J. Heat Transf. 123, 331 (2001)
Ü.Ö. Köylü, G.M. Faeth, J. Heat Transf. 118, 415 (1996)
H. Chang T.T. Charalampopoulos, Proc. Math. Phys. Sci. 430, 577 (1990)
E. Therssen, Y. Bouvier, C. Schoemaecker-Moreau, X. Mercier, P. Desgroux, M. Ziskind, C. Focsa, Appl. Phys. B 89, 417 (2007)
H. Michelsen, P. Schrader, F. Goulay, Carbon 48, 2175 (2010)
D.R. Snelling, F. Liu, G.J. Smallwood, Ö.L. Gülder, Combust. Flame 136, 180 (2004)
R. Lemaire, M. Maugendre, T. Schuller, E. Therssen, J. Yon, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80, 105105 (2009)
F. Ouf, J. Vendel, A. Coppalle, M. Weill, J. Yon, Combust. Sci. Technol. 180, 674 (2008)
F. Ouf, J. Yon, P. Ausset, A. Coppalle, M. Maillé, Aerosol Sci. Technol. 44, 1005 (2010)
K. Ren, F. Xu, X. Cai, J. Dorey, Chem. Eng. Commun. 197, 250 (2010)
M.F. Chandler, Y. Teng, U.O. Koylu, Proc. Combust. Inst. 31, 2971 (2007)
J. Lee, I. Altman, M. Choi, J. Aerosol Sci. 39, 418 (2008)
R.A. Dobbins, C.M. Megaridis, Langmuir 3, 254 (1987)
Ü. Köylü, G. Faeth, Combust. Flame 89, 140 (1992)
J. Cai, N. Lu, C.M. Sorensen, Langmuir 9, 2861 (1993)
K. Tian, F. Liu, K.A. Thomson, D.R. Snelling, G.J. Smallwood, D. Wang, Combust. Flame 138, 195 (2004)
R. Lemaire, A. Faccinetto, E. Therssen, M. Ziskind, C. Focsa, P. Desgroux, Proc. Combust. Inst. 32, 737 (2009)
H. Bladh, P. Bengtsson, J. Delhay, Y. Bouvier, E. Therssen, P. Desgroux, Appl. Phys. B 83, 423 (2006)
C.M. Sorensen, G.D. Feke, Aerosol Sci. Technol. 25, 328 (1996)
A.M. Brasil, T.L. Farias, M.G. Carvalho, J. Aerosol Sci. 30, 1379 (1999)
A.M. Brasil, T.L. Farias, M.G. Carvalho, Aerosol Sci. Technol. 33, 440 (2000)
C.M. Sorensen, G.C. Roberts, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 186, 447 (1997)
K. Naumann, J. Aerosol Sci. 34, 1371 (2003)
P. Wiltzius, Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 710 (1987)
G.M. Wang, C.M. Sorensen, Phys. Rev. E 60, 3036 (1999)
U. Kätzel, M. Vorbau, M. Stintz, T. Gottschalk-Gaudig, H. Barthel, Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 25, 19 (2008)
P. Gwaze, O. Schmid, H.J. Annegarn, M.O. Andreae, J. Huth, G. Helas, J. Aerosol Sci. 37, 820 (2006)
M.Y. Choi, G.W. Mulholland, A. Hamins, T. Kashiwagi, Combust. Flame 102, 161 (1995)
A. Tregrossi, R. Barbella, A. Ciajolo, M. Alfe, Combust. Sci. Technol. 179, 371 (2007)
J.F. Widmann, J.C. Yang, T.J. Smith, S.L. Manzello, G.W. Mulholland, Combust. Flame 134, 119 (2003)
G.W. Mulholland, M.Y. Choi, Symp., Int., Combust. 27, 1515 (1998)
J. Wu, S. Krishnan, G. Faeth, ASME J. Heat Transf. 119, 230 (1997)
J. Zhu, M.Y. Choi, G.W. Mulholland, S.L. Manzello, L.A. Gritzo, J. Suo-Anttila, Proc. Combust. Inst. 29, 2367 (2002)
T.L. Farias, Ü.Ö. Köylü, M.G. Carvalho, Appl. Opt. 35, 6560 (1996)
J. Yon, C. Roze, T. Girasole, A. Coppalle, L. Mees, Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 25, 54 (2008)
R.K. Chakrabarty, H. Moosmüller, W.P. Arnott, M.A. Garro, J.G. Slowik, E.S. Cross, J. Han, P. Davidovits, T.B. Onasch, D.R. Worsnop, Appl. Opt. 46, 6990 (2007)
G.J. Smallwood, D.T. Snelling, F. Liu, O.L. Gülder, J. Heat Transf. 123, 814 (2001)
R. Lemaire, E. Therssen, J.F. Pauwels, P. Desgroux, in Combustion-Generated Fine Carbonaceous Particles, ed. by H. Bockhorn, A. D’Anna, A.F. Sarofim, H. Wang (KIT Scientific Publishing, Karlsruhe, 2009), p. 619
H. Michelsen, J. Chem. Phys. 118, 7012 (2003)
C. Schulz, B.F. Kock, M. Hofmann, H. Michelsen, S. Will, B. Bougie, R. Suntz, G. Smallwood, Appl. Phys. B 83, 333 (2006)
G. Zizak, F. Cignoli, G. Montas, S. Benecchi, R. Donde, Appl. Spectrosc. 1, 17 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yon, J., Lemaire, R., Therssen, E. et al. Examination of wavelength dependent soot optical properties of diesel and diesel/rapeseed methyl ester mixture by extinction spectra analysis and LII measurements. Appl. Phys. B 104, 253–271 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-011-4416-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-011-4416-4